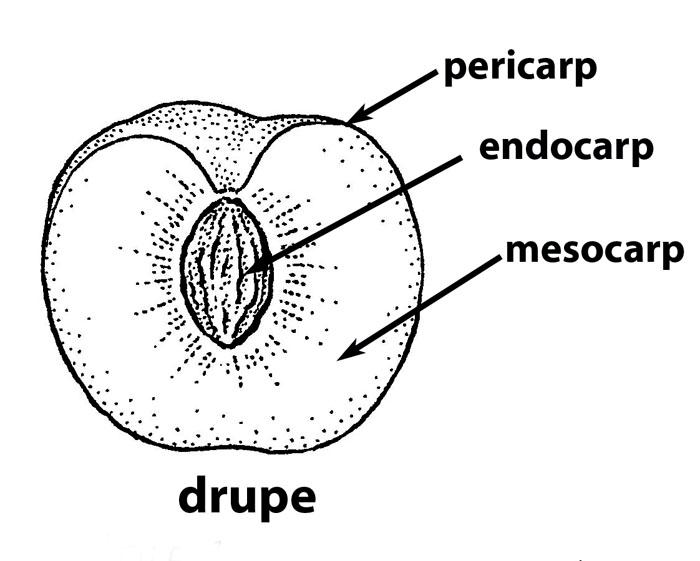
Fruits are an essential part of our daily diet and come in a wide variety of shapes, sizes, and tastes. Among the various types of fruits, one of the most interesting is the drupe. A drupe is a type of fruit that has a hard inner layer surrounding a soft, juicy pulp. In this blog post, we will explore some of the most common fruits that are drupes.
1. Mango: Mango is a tropical fruit that is widely popular for its sweet taste and juicy pulp. It is a drupe fruit that has a thin, leathery skin, a fleshy, juicy mesocarp, and a large, hard endocarp that surrounds a single seed.
2. Peach: Peach is a popular fruit that is enjoyed for its sweet, juicy flesh and delicate aroma. It is a drupe that has a soft, fuzzy skin, a juicy mesocarp, and a hard, stony endocarp that surrounds a single seed.
3. Apricot: Apricot is a small, sweet fruit that is similar in taste and texture to a peach. It is a drupe that has a smooth, velvety skin, a juicy mesocarp, and a hard, stony endocarp that surrounds a single seed.
4. Cherry: Cherry is a small, round fruit that is widely used in desserts and baked goods. It is a drupe that has a smooth, shiny skin, a juicy mesocarp, and a hard, stony endocarp that surrounds a single seed.
5. Olive: Olive is a small, oval fruit that is widely popular for its oil and flavor. It is a drupe that has a smooth, leathery skin, a fleshy mesocarp, and a hard, stony endocarp that surrounds a single seed.
6. Coconut: Coconut is a large, tropical fruit that is widely used in cooking and baking. It is a drupe that has a fibrous, hairy outer layer, a thick, fleshy mesocarp, and a hard, woody endocarp that surrounds a single seed.
Drupe fruits are a unique and interesting type of fruit that are widely enjoyed for their sweet taste and juicy pulp. They are characterized by a hard inner layer that surrounds a soft, juicy mesocarp and a single seed. Some of the most common drupe fruits include mango, peach, apricot, cherry, olive, and coconut.
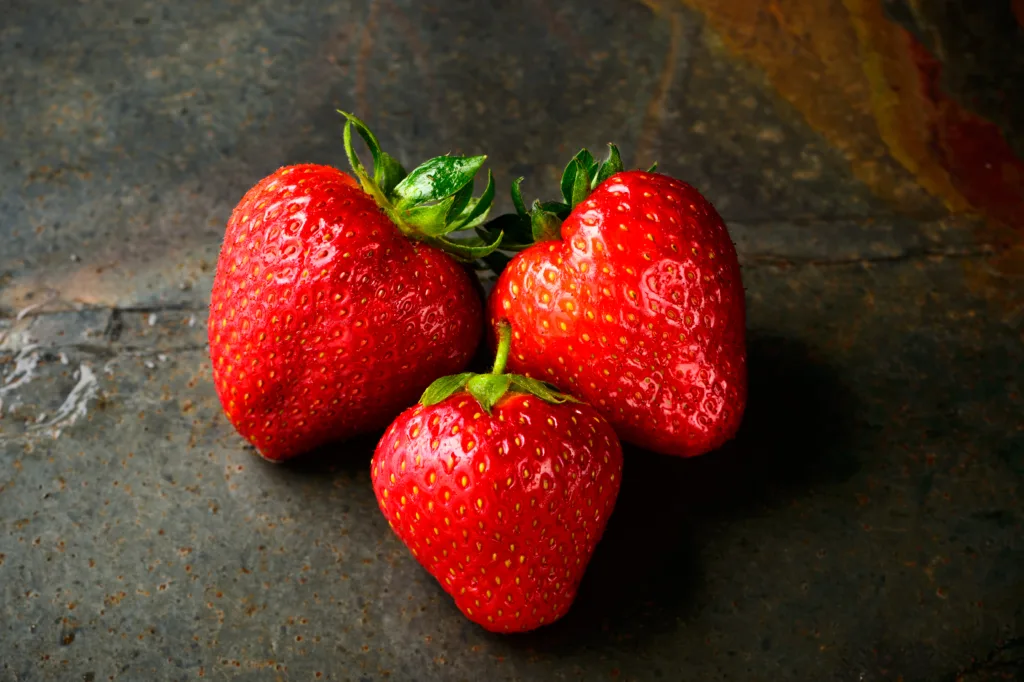
Are Strawberries Drupes?
When it comes to categorizing fruits, there are various types, and one of them is drupe. A drupe is a fruit that has a hard, outer shell, called endocarp, surrounding a single seed. Examples of drupes include peaches, plums, and cherries.
Now, when it comes to strawberries, they are not considered drupes. Instead, they are classified as aggregate fruits. An aggregate fruit is formed from multiple ovaries of a single flower. In the case of strawberries, each of the small, red, juicy structures that we typically call “strawberry” is actually an achene, a small, dry fruit that contains a single seed. These achenes are clustered on the surface of the fleshy, edible part of the strawberry, creating the characteristic appearance of the fruit.
To sum it up, strawberries are not drupes, but rther aggregate fruits composed of multiple achenes.

Is Avocado a Berry or Drupe?
Avocado, scientifically known as Persea Americana, is classified as a berry. Although it shares some characteristics with drupes, such as having a single seed, it is the fleshy endocarp that sets it apart. In botany, a berry is a type of fruit that develops from a single ovary, and the entire pericarp, including the endocarp, is fleshy.
Here are some key characteristics of avocado that make it a berry:
– The skin or exocarp is tough and leathery, while the pulp or mesocarp is soft and creamy.
– The seed or pit is large and hard, but it is not fused to the mesocarp.
– The endocarp is thin and papery, and it adheres to the seed, but it is not woody or stony like in drupes.
– The fruit is typically oblong or pear-shaped, with a pointed end and a broad base.
It is interesting to note that avocado is not the only fruit that defies classification based on its morphology. Other examples include tomatoes, cucumbers, and bananas, which are technically berries, and peaches, cherries, and plums, which are drupes. Regardless of their classification, all these fruits are nutritious and delicious, and they play an important role in our diets and cultures.
Is Mango a Drupe or Berry?
Mango is a drupe fruit that belongs to the flowering plant genus Mangifera. Drupe is a type of fruit that is characterized by a fleshy outer layer or mesocarp, a hard and stony inner layer or endocarp, and a thin skin or epicarp.
In the case of mangoes, the outer layer is typically a soft and fleshy pulp that is yellow or orange in color. This pulp surrounds a hard and woody stone or pit, which is the endocarp. The thin skin of the mango, which is the epicarp, is typically green when unripe and turns yellow or orange as the fruit ripens.
It is worth noting that a drupe fruit is different from a berry. While both types of fruits have a fleshy outer layer or mesocarp, berries do not have a hard endocarp like drupes do. Instead, the seeds of berries are embedded in the fleshy mesocarp or attached to the fruit’s inner wall. Examples of berries include grapes, blueberries, and tomatoes.
To summarize, mango is considered a drupe fruit beause it has a fleshy mesocarp, a hard endocarp, and a thin skin or epicarp.
Which Fruit Is Not a Part of the Drupe Family?
When it comes to fruits, there are vrious types of classifications based on their structure and composition. One of the most common classifications is based on whether they are a drupe or not. A drupe is a type of fruit that has a single seed enclosed in a hardened shell or pit. The pit is surrounded by a fleshy outer layer, which is also known as the exocarp. Examples of drupes include peaches, plums, cherries, and mangoes.
However, there is one type of fruit that is not a drupe, and that is Trapa. Trapa is a type of fruit that is commonly known as a water chestnut or water caltrop. Unlike drupes, Trapa is actually a nut. It has a hard outer shell that encloses a single seed. The outer layer of Trapa is not fleshy like a drupe, but rather has a spiny exterior that protects the nut inside.
To summarize, while most fruits can be classified as a drupe or non-drupe based on their structure, Trapa is an exception as it is a nut and not a drupe.
Is Coconut a Drupe or Berry?
Coconut is classified as a fibrous one-seeded drupe. A drupe is a fruit with a hard stony covering enclosing the seed, such as a peach or olive. The term “drupe” coes from the word “drupa,” meaning overripe olive, and it is a type of fruit that contains a single seed or pit surrounded by a fleshy outer layer.
The fleshy outer layer of the coconut, called the exocarp, is smooth and green when immature, turning brown and fibrous as it matures. The middle layer, known as the mesocarp, is fibrous and woody, while the innermost layer, the endocarp, is hard and encloses the coconut seed.
Coconuts are not classified as a berry, which is a type of fruit that develops from a single flower with one or more ovaries, and contains seeds embedded in the fleshy fruit wall. Unlike berries, coconuts do not have a fleshy fruit wall surrounding the seed.
Coconuts are classified as a drupe, not a berry. They have a hard, stony covering enclosing the seed, and a fibrous outer layer that is not considered a fleshy fruit wall.
Source: sweetgum.nybg.org
Is Watermelon a Drupe?
Watermelon is a drupe. A drupe is a type of fruit that has a hard outer shell or skin, and a fleshy inside with a single seed or pit in the center. Watermelon fits this definition as it has a tough rind on the outside, juicy red or yellow flesh inside, and black seeds in the center.
Watermelon belongs to the family Cucurbitaceae, which includes othr fruits such as cantaloupe, honeydew, and cucumber. While watermelon is commonly referred to as a fruit, it is technically a type of berry, according to botanists.
In addition to being a delicious summer fruit, watermelon is also packed with health benefits. It is low in calories, high in vitamins A and C, and a good source of hydration as it contains up to 90% water.
Watermelon is a tasty and nutritious drupe that is enjoyed by many people around the world.
Is Coffee Considered a Drupe Fruit?
Coffee is a drupe fruit. Drupe fruits are a type of flowering plant that produce fruit with a fleshy outer layer surrounding a hard seed inside. In the case of coffee, the outer layer is the coffee cherry, whch is red when ripe and contains two seeds, which we know as coffee beans. The coffee cherry is harvested and processed to remove the outer layer and reveal the coffee beans inside. The coffee plant is native to tropical regions of Africa, and is now grown in many countries around the world. Other examples of drupe fruits include mangoes, olives, and peaches.
Are Olives Drupes?
An olive is considered a drupe. A drupe is a type of fruit that has a single seed or pit surrounded by a fleshy outer layer. Examples of other drupes include peaches, plums, cherries, and mangoes. The outer layer of an olive is typically green or black and has a slightly bitter taste. Olives are commonly used in Mediterranean cuisine and are a good source of healthy fats. In addition to being eaten whole, olives are also pressed to produce olive oil, which is used in cooking and as a dressing for salads.
Common Types of Drupes
Drupes are a type of fruit that are characterized by a fleshy outer layer and a hard inner layer, also kown as the endocarp or stone, that surrounds the seed. Common drupes include:
1. Peach: This fruit has a fuzzy outer skin and a sweet, juicy flesh surrounding a hard, woody pit.
2. Plum: Plums are typically round or oval-shaped with a smooth, shiny skin that ranges in color from deep purple to yellow or red. The flesh is juicy and sweet, and surrounds a single, hard seed.
3. Nectarine: Nectarines are similar to peaches in flavor and appearance, but have a smooth, shiny skin instead of a fuzzy one.
4. Apricot: Apricots are small, orange-colored fruits with a velvety skin and a sweet, tangy flavor. They have a hard, oval-shaped pit in the center.
5. Cherry: Cherries are small, round fruits with a bright red or dark purple skin and a sweet, juicy flesh. They have a hard, round pit in the center.
6. Olive: Olives are small, oval-shaped fruits with a bitter taste and a hard pit in the center. They are commonly used to make olive oil and are a popular ingredient in Mediterranean cuisine.
7. Mango: Mangoes are large, tropical fruits with a sweet, juicy flesh and a hard, fibrous pit in the center. They are commonly used in smoothies, salads, and desserts.
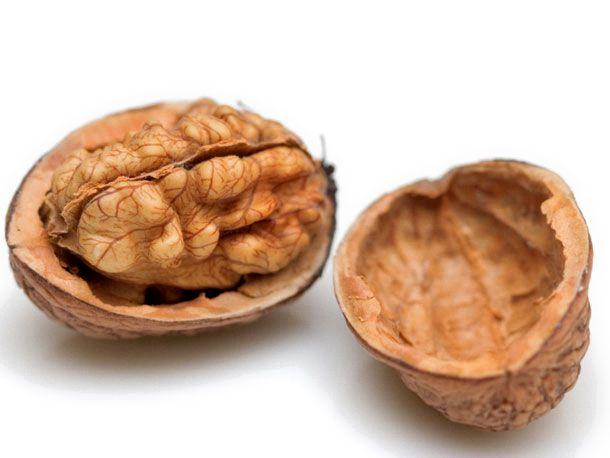
8. Almond: Almonds are small, oval-shaped nuts with a hard, woody shell that must be cracked open to access the edible kernel inside. They are commonly used in baking and as a snack.
These are the most common drupes found in the market. They are known for their unique taste and nutritional benefits.

Source: seriouseats.com
Is Almond a Drupe?
The almond is classified as a drupe. A drupe is a type of fruit that has an outer fleshy layer surrounding a hard shell that contins a seed in the center. Almonds have a hard outer shell that surrounds the edible seed we commonly eat. This means that while almonds are often referred to as nuts, they are technically not true nuts, but rather classified as drupes. Other examples of drupes include peaches, plums, and cherries. It is interesting to note that the classification of fruits can sometimes be tricky, and the terminology can vary depending on the context and the source of information.
Why Avocado Is Not Considered a Drupe
When we look at the definition of a drupe, we can see that it is a type of fruit that has a fleshy exterior and a hard pit or endocarp inside that contains a single seed. Examples of drupes include peaches, nectarines, apricots, and plums. However, unlike these fruits, an avocado cannot be classified as a drupe due to its unique anatomical features.
Firstly, the interior of an avocado is fleshy throughout. The pit inside the fruit is not hard and woody like that of a drupe, but rater soft and pliable. This means that an avocado does not have a tough endocarp like a drupe does.
Secondly, the seed inside an avocado is not a single seed like that of a drupe. Instead, it is a large, flattened seed that takes up most of the fruit’s interior. This means that an avocado does not have a pit in the traditional sense of the word, which is a defining characteristic of a drupe.
While avocados may share some similarities with drupes – such as having a fleshy exterior and a seed inside – they do not meet the full criteria to be classified as a drupe due to their unique anatomical features, such as having a fleshy interior and a large, flattened seed.
Are Apples a Drupe?
Apples are not drupes. Apples are classified as pomes, which are fruits that have a fleshy outer layer and a core that contains seeds. The core of an apple is surrounded by a papery layer that holds the seeds. This is different from drupes, which have a single seed inside a hard pit. Examples of drupes include apricots, cherries, and coconuts. While both pomes and drupes are types of fruit, they have distinct characteristics that set them apart.
Examples of Drupes
Drupes are a type of fruit that have an outer fleshy part surrounding a hard shell, also knon as a pit, which contains a seed inside. Here are three examples of drupes:
1. Peaches: Peaches are a popular drupe that are known for their juicy, sweet flesh and fuzzy skin. The pit inside a peach contains a single seed that is often used for planting new peach trees.
2. Plums: Plums are another common drupe that come in a variety of colors, including red, purple, and yellow. They have a sweet, slightly tart flavor and are often used in jams, jellies, and baked goods.
3. Cherries: Cherries are a small, sweet drupe that come in two main varieties: sweet cherries and tart cherries. Sweet cherries are often eaten fresh, while tart cherries are commonly used in pies, jams, and other baked goods.
Other examples of drupes include almonds, walnuts, and pecans, which are all drupes that we eat for their seeds instead of the fruit.

Is the Tomato a Drupe Fruit?
Tomato is a fruit that belongs to the family Solanaceae. It is often considered as a vegetable becase of its culinary uses, but botanically, it is a fruit. However, it is not a drupe fruit.
A drupe fruit is a type of fleshy fruit that has a hard, stony pit or stone at its center, which encloses a seed. Some examples of drupe fruits include plums, cherries, peaches, and olives.
On the other hand, the tomato fruit is classified as a berry. A berry is a type of fleshy fruit that develops from a single ovary of a flower and contains seeds. The tomato fruit is characterized by its fleshy pericarp, which is the edible part of the fruit that surrounds the seeds.
In summary, tomato is not a drupe fruit but a berry fruit. It is a fleshy, simple fruit that develops from a single ovary and contains seeds.
Is Eggplant a Drupe?
Eggplant is not a drupe. Drupe fruits are characterized by having a single seed enclosed in a hard shell or pit, surrounded by fleshy fruit. Examples of drupe fruits include plums, peaches, and olives.
Eggplants, on the other hand, belong to the berry family. Berries are characterized by having several small seeds surrounded by fleshy fruit. Other examples of berries include tomatoes and grapes.
Therefore, eggplants are not classified as drupe fruits but as berries.
Conclusion
After exploring the topic of drupes, it is clear that this type of fruit is characterized by hving a single seed encased in a hard, stony endocarp that is surrounded by a fleshy mesocarp and thin epicarp. Examples of drupes include popular fruits such as peaches, plums, and cherries, as well as lesser-known fruits such as coconuts and almonds.
It is important to note that not all fruits with hard shells or pits are drupes. For example, nuts such as walnuts and hazelnuts are a completely different type of fruit. Similarly, fruits like strawberries may have a similar appearance to drupes, but they are actually aggregate fruits made up of multiple achenes.
Understanding the characteristics of drupes is important for both consumers and horticulturists. Being able to identify and classify different types of fruits can help with everything from selecting the right fruit for a recipe to identifying potential pests or diseases that may affect a particular crop.
