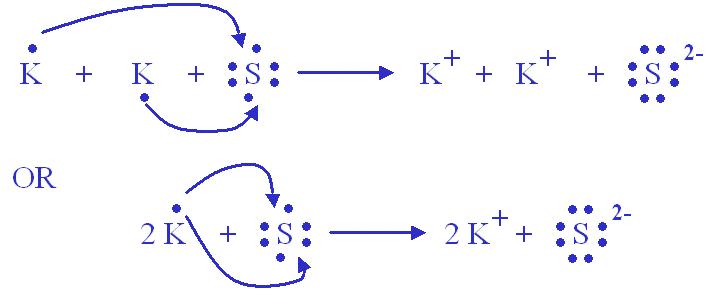
Sulfide ion, also knwn as S2-, is a negatively charged ion formed by the addition of two electrons to a neutral sulfur atom. The resulting ion has a charge of -2, which is represented as S2-.
The formula for sulfide ion is relatively simple, as it consists of only one sulfur atom and two electrons. The chemical equation for the formation of sulfide ion is:
S + 2e- → S2-
This equation shows that a neutral sulfur atom (S) gains two electrons (2e-) to form sulfide ion (S2-).
Sulfide ions are commonly found in nature, often in the form of sulfide minerals such as pyrite, galena, and sphalerite. These minerals can be found in rocks, soils, and even in some bodies of water.
Sulfide ions are also important in many industrial processes, including the production of chemicals such as sulfuric acid and sodium sulfide. They are also used in wastewater treatment to remove heavy metals and other pollutants from water.
It is important to note that sulfide ions are different from sulfite ions, which are oxidized sulfur-containing compounds. Sulfite ions have a charge of -2 as well, but they are formed by the addition of one electron to a neutral sulfur atom, rather than two.
The formula for sulfide ion is S2-, which is formed by the addition of two electrons to a neutral sulfur atom. This ion plays an important role in both natural and industrial processes, and is distinct from sulfite ions, which are oxidized sulfur compounds.
The Benefits of Sulfide
Sulfide (S2-) is a negatively charged ion, meaning it has gained electrons. In the case of sulfide, it has gained two electrons. This is because a neutral sulfur atom has six valence electrons in its outermost energy level, meaning it needs to gain two more electrons to complete its octet and becoe stable. When sulfur gains two electrons, it forms the sulfide ion, which has a 2- charge.
It is important to note that the charge of an ion is determined by the number of electrons gained or lost. In the case of sulfide, it has gained two electrons, resulting in a charge of 2-. This is why sulfide is referred to as S2-.
Sulfide is 2- because it has gained two electrons to complete its octet and become stable, resulting in a negative charge of 2.

Charge of Sulfide Ion
Sulfide ion is a chemical compound composed of sulfur and two electrons. The charge on a sulfide ion is 2-, which means the ion has two more electrons than protons. This charge is due to the addition of two electrons to the sulfur atom, which is located in the 16th group of the periodic table and has six valence electrons. The sulfide ion is a anion, which means it is negatively charged due to its excess of electrons.
The sulfide ion is commonly found in nature, especially in minerals such as pyrite, galena, and sphalerite. It also plays an important role in biological processes such as metabolism and the synthesis of amino acids. In addition, sulfide ions are used in varios industrial applications, such as in the production of sulfuric acid, paper, and dyes.
To summarize, the sulfide ion has a charge of 2-, which is due to the addition of two electrons to the sulfur atom. This ion is negatively charged and has various applications in nature and industry.
Are Sulfide and Sulfide Compounds the Same?
Sulfite and sulfide are not the same. They are two different types of sulfur-containing compounds that exist in wine. Sulfites are oxidized sulfur compounds that are often used as preservatives in winemaking to prevent spoilage and oxidation. Sulfides, on the other hand, are reduced sulfur compounds that can cause a fault in wine known as reduction.
Reduction occurs when sulfides react with other compounds in the wine, such as aldehydes and ketones, to produce unpleasant aromas and flavors such as rotten eggs, sewage, or burnt rubber. This can happen during winemaking, aging, or even after the bottle is opened.
It’s important to note that not all sulfides are bad. In fact, some sulfides can contribute positively to the aroma and flavor of wine, such as the fruity and floral aromas found in certain white wines. It’s only when sulfides are present in excess or in the wrong combination with other compounds that they beome a fault.
To prevent reduction, winemakers use various techniques such as adding oxygen during winemaking, using different yeasts, or aging the wine in barrels. Additionally, when sulfide reduction does occur, winemakers can try to remove the sulfides through processes such as copper fining or aeration.
Sulfite and sulfide are two different types of sulfur-containing compounds that have distinct roles in winemaking. While sulfites are often used as a preservative, sulfides can cause a wine fault known as reduction. Understanding the difference between these compounds can help wine enthusiasts and professionals alike better understand the complexities of wine chemistry.
The Chemical Form of Sulfur
Sulfur is represented by the chemical symbol S and has an atomic number of 16. It is a non-metal element that can be found in many forms, including as a yellow powder, crystals, or in volcanic gases.
It is important to note that sulfur does not exist as S2. This is becuse the chemical formula for sulfur is simply S, meaning it is made up of individual sulfur atoms.
Sulfur is commonly used in a variety of industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers, sulfuric acid, and rubber. It is also used in the manufacturing of some medications and skincare products.
In terms of its properties, sulfur is a brittle solid at room temperature and has a melting point of 115.21°C. It is also a non-metal and can be classified as a non-metallic element.
Sulfur is represented by the chemical symbol S and does not exist as S2. It is a non-metal element with a variety of industrial and practical applications.
Number of Electrons in S2
Sulfur is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is a non-metal and has six valence electrons in its outermost shell. When sulfur gains two electrons, it forms a negatively charged ion called sulfide, with a charge of -2. Thus, S2- has 18 electrons, two more than the neutral sulfur atom.
To understand why S2- has 18 electrons, we need to look at the electronic configuration of sulfur. The electronic configuration of sulfur is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4. In this configuration, the outermost shell of sulfur has six electrons in the 3s and 3p orbitals. When sulfur gains two electrons to form S2-, the two electrons occupy the 3p orbital, making it a filled shell. The electronic configuration of S2- is therefore 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6, whih is the same as the noble gas argon.
It is interesting to note that S2- has the same number of electrons as the calcium ion Ca2+. Calcium is a metal and loses two electrons to form a positively charged ion with a charge of +2. The electronic configuration of Ca2+ is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6, which is also the same as the noble gas argon.
The number of electrons in S2- is 18, which is the result of sulfur gaining two electrons to form a negatively charged ion with a filled 3p orbital.

Formation of a S2− Ion
The sulfide anion, S2−, is formed through the addition of two electrons to a neutral sulfur atom. The neutral sulfur atom has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4. When two electrons are added to this configuration, they occupy the 3p-orbitals, which can hold a maximum of six electrons betwen them. This results in the formation of a stable S2− ion.
It is important to note that the addition of electrons to an atom can significantly affect its chemical properties. The addition of two electrons to a sulfur atom in this case results in the formation of a negatively charged ion, which can participate in a variety of chemical reactions.
S2− ions are commonly found in compounds such as metal sulfides and are important in various industrial and biological processes. Understanding the formation and properties of S2− ions is therefore crucial in many fields of study.
The sulfide anion, S2−, is formed by adding two electrons to a neutral sulfur atom, which occupy the 3p-orbitals. This results in the formation of a negatively charged ion with important applications in various industries and fields of study.
Ion With a 2+ Charge
When an element commonly forms more than one ion, Roman numeral notation is used to indicate the charge of the ion. For example, iron is one such element that forms more than one ion, and its ions have varying charges. Iron(II) ion, also known as ferrous ion, has a 2+ charge. This means that it has lost two electrons, leaving it with a net positive charge of 2. The iron(II) ion is commonly found in compounds such as iron(II) sulfate (FeSO4) and iron(II) chloride (FeCl2).
The Effects of H2S and SO2
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) are two important gases that are produced naturally within the human body. H2S is a colorless gas with a distinctive odor of rotten eggs, while SO2 is a colorless gas with a pungent, suffocating odor. Both gases are produced as a byproduct of the metabolism of sulfur-containing amino acids in the body.
H2S is known to play a number of important roles in the body, including regulating blood pressure, reducing inflammation, and protecting against oxidative stress. Additionally, H2S has been shown to have a protective effect on the cardiovascular system, helping to reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
SO2, on the other hand, is a gas that is primarily produced through the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil. This gas is a major contributor to air pollution and is known to have a number of negative health effects, including respiratory irritation, bronchoconstriction, and increased risk of asthma and other respiratory diseases.
Despite their differences, both H2S and SO2 are important gases that play a significant role in human health and disease. Understanding the mechanisms by which thse gases are produced and regulated within the body is an important area of research with potential implications for the treatment and prevention of a wide range of diseases.
Is Hydrogen Sulfide an Ion?
H2S is not an ion, but a covalent compound. An ion is an atom or molecule that has an electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons. In contrast, a covalent compound is formed when two or more atoms share electrons to form a stable molecule.
In the case of H2S, it is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one sulfur atom. These atoms share electrons to form covalent bonds, whih hold the molecule together. Each hydrogen atom shares one electron with the sulfur atom, and the sulfur atom shares two electrons with each hydrogen atom, resulting in a stable molecule with no net electrical charge.
It is important to note that the difference between ionic and covalent compounds lies in the way the atoms are bonded together, and this affects their properties such as melting point, boiling point, and solubility. Ionic compounds dissolve in polar solvents, while covalent compounds dissolve in non-polar solvents.
H2S is a covalent compound and not an ion.
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Is Sulfur an Ion?
Sulfur can exist as an ion. Specifically, sulfur can form a sulfide ion (S2-) or a sulfite ion (SO32-), depending on its chemical bonding with other elements. The sulfide ion is formed when sulfur gains two electrons, while the sulfite ion is formed when sulfur gains two electrons and bonds with three oxygen atoms. Both of these ions are negatively charged and have important roles in vrious chemical processes. Additionally, sulfur can also form other ions such as thiosulfate (S2O32-) and sulfate (SO42-), depending on the specific chemical reactions it undergoes. sulfur has the ability to exist as an ion and participate in a variety of chemical reactions and processes.
Is Sodium Sulfide an Ion?
Sodium sulfide is a chemical compound that is composed of sodium cations (Na+) and sulfide anions (S2-). As an ionic compound, it is held together by electrostatic forces between these oppositely charged ions.
In more scientific terms, sodium sulfide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2S. It is classified as a salt, which is a type of ionic compound that is formed when an acid and a base react with each other. In the case of sodium sulfide, it is formed when sodium hydroxide (NaOH) reacts with elemental sulfur (S) in a process called synthesis.
When sodium sulfide is dissolved in water, it dissociates into its component ions. This means that the sodium cations and sulfide anions separate from each oher and become surrounded by water molecules. This process is known as ionization, and it is what allows ionic compounds like sodium sulfide to conduct electricity in solution.
It can be concluded that sodium sulfide is indeed an ion, as it is an ionic compound made up of positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged sulfide ions.
Is Hydrogen Sulfide a Sulfide?
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is a sulfide compound. It is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one sulfur atom, giving it the chemical formula H2S. As a sulfide, it is similar to other compounds such as sodium sulfide (Na2S) and iron sulfide (FeS).
Sulfides are a type of chemical compound that contain sulfur atoms bonded to one or more other elements. They can be found naturally in minerals, rocks, and other materials, and are also used in a variety of industrial processes. Some common examples of sulfides include pyrite (FeS2), which is also known as “fool’s gold,” and hydrogen sulfide (H2S), which is known for its distinct odor and toxicity.
Sulfides can be formed through a variety of processes, including reactions between sulfur and other elements, biological processes, and geological activity. They can also be synthesized in the laboratory for use in varous applications.
Hydrogen sulfide is a sulfide compound, composed of two hydrogen atoms and one sulfur atom, and belongs to the larger group of sulfide compounds.
Is Sulfide a Sulfur or Sulfate?
Sulfide is a sulfur compound that contains one or more sulfur atoms with a negative charge. On the other hand, sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid, which contains sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms. These two compounds have distinct chemical structures and properties.
In the context of wine, sulfides are often used as preservatives to prevent oxidation and microbial spoilage. They are commonly added to wine during the winemaking process to maintain freshness and stability. Sulfides can also occur naturally during fermentation, but excessive amounts can lead to off-flavors and odors.
Sulfates, on the other hand, are not commonly used in winemaking. They are present in small amounts in some vineyards and can affect the soil and grape composition. However, they do not have a direct impact on the taste or aroma of the wine.
To summarize, sulfide is a sulfur compound commonly used in winemaking as a preservative, while sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid that has minimal impact on wine. It is important to note the distinction btween these two compounds to understand their role in wine production and their potential effects on the final product.
Source: socratic.org
Conclusion
Sulfide ion, also known as S2-, is a negatively charged ion that is formed when a neutral sulfur atom gains two electrons. This ion is represented by the chemical formula S2-, and it is an important component of many chemical reactions and compounds.
One of the primary differences between sulfides and other sulfur-containing compounds is that sulfides are reduced sulfur compounds. This means that they have gained electrons, resulting in a negative charge. Sulfides are an important group of volatile sulfur compounds that can cause wine faults, specifically the fault known as reduction.
It is important to note that the charge on a sulfide ion is 2-. This means that the ion has gained two electrons, resulting in an overall negative charge of 2-. This charge is represented by the superscript 2- in the chemical formula S2-.
Sulfide ions are negatively charged ions that are formed when neutral sulfur atoms gain two electrons. These ions are important components of many chemical reactions and compounds, and their charge is represented by the chemical formula S2-. By understanding the formula for sulfide ion, we can better understand its properties and role in varous chemical processes.
