Theoretical research is a crucial part of scientific inquiry. It involves developing and exploring concepts, models, and theories to understand how a system works and its potential implications. In this blog post, we will explore some examples of theoretical research.
One of the most well-known examples of theoretical research is in the field of physics. Theoretical physicists develop models and theories to explain how the universe works at a fundamental level. For example, the Standard Model of particle physics is a theoretical framework that describes the fundamental particles and forces that make up the universe. Theoretical research in physics has led to many important discoveries, such as the existence of the Higgs boson, which was predicted by the Standard Model and later confirmed by experiments at the Large Hadron Collider.
Another example of theoretical research is in the field of economics. Economists develop models and theories to understand how markets and economies work, and how they can be improved. For example, the concept of supply and demand is a theoretical framework that explains how prices are determined in a market economy. Theoretical research in economics has led to many important policy decisions, such as the implementation of minimum wage laws and the development of trade agreements.
In the field of psychology, theoretical research is used to develop models and theories to explain human behavior. For example, the social learning theory developed by Albert Bandura explains how people learn new behaviors by observing others. Theoretical research in psychology has led to many important discoveries, such as the role of cognitive processes in decision making and the development of effective treatments for mental health disorders.
Theoretical research is also used in the social sciences to understand complex social phenomena. For example, sociologists develop theories to explain how social structures and institutions affect human behavior. Theoretical research in sociology has led to many important insights into issues such as poverty, inequality, and social mobility.
Theoretical research is a fundamental part of scientific inquiry. It allos us to develop models and theories to understand complex systems and their potential implications. Examples of theoretical research can be found in many different fields, from physics and economics to psychology and sociology. By continuing to develop and explore theoretical frameworks, we can gain a deeper understanding of the world around us and make important discoveries that can improve our lives.
The Benefits of Theoretical Research: An Example
Theoretical research is a type of research methodology that involves exploring and analyzing a concept, idea, or system of beliefs. It aims to develop a theoretical framework that explains the underlying principles and relationships that govern the phenomenon of interest. Theoretical research is uually conducted using deductive reasoning, starting with a set of assumptions or hypotheses and then testing them through logical reasoning and analysis.
An example of theoretical research is the study of the relationship between economic growth and income inequality. The theoretical framework used in this research would involve defining key concepts such as economic growth, income inequality, and the factors that influence them. The researcher would then explore the potential causal relationships between these factors, such as how economic growth might lead to increased income inequality or how income inequality might hinder economic growth.
Through this process of theoretical exploration, the researcher would develop a set of hypotheses or theories about the relationship between economic growth and income inequality. These theories could then be tested using empirical research methods such as statistical analysis or case studies. theoretical research plays a crucial role in advancing our understanding of complex phenomena and informing the development of practical solutions to real-world problems.
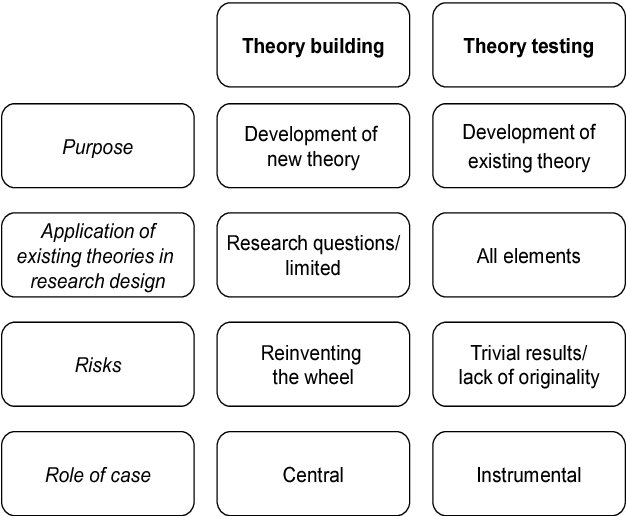
The Meaning of Theoretical
In scientific language, the term “theoretical” is generally used to describe ideas, concepts, or entities that cannot be directly observed or measured. In other words, a term is theoretical if it refers to nonobservational entities. These may include hypothetical entities, such as dark matter or strings in string theory, as well as well-established entities that cannot be directly observed, such as atoms, molecules, or subatomic particles like electrons and neutrinos.
Theoretical entities also include concepts that are not directly observable, but are essential for understanding and explaining observable phenomena. Examples of such concepts include gravitational forces, magnetic fields, and evolutionary processes. In general, any scientific theory that attempts to explain or predict the behavior of the natural world relies on a combination of theoretical and observational concepts.
It is important to note that theoretical concepts are not just abstract ideas, but are based on empirical evidence and supported by mathematical models and other forms of scientific reasoning. Theories that are supported by strong empirical evidence and have successfully predicted new observations are considered robust and reliable, even if they rely on nonobservational entities.
Exploring Theoretical Situations
A theoretical situation is a situation that is based on theory or hypothesis rather than being a real-life situation. It is a situation that is supposed to exist in a certain way or be true based on a particular theory, but it may not necessarily exist that way in reality. A theoretical situation is often used to test a theory or hypothesis and to explore dfferent scenarios or possibilities. It is important to note that a theoretical situation is not the same as a hypothetical situation, which is a situation that is imagined or supposed but may not have any basis in reality or theory.
Theoretical Problem: An Example
Sure, I’d be happy to help! A theoretical problem, in research terms, is a question or issue that has yet to be fully explored or understood. An example of a theoretical problem could be the relationship between technology use and mental health in adolescents, or the impact of language barriers on international business negotiations. These problems are often complex and require careful consideration and analysis in order to develop a solid theoretical framework. Theoretical problems can be challenging to tackle, but they are also an important part of the research process, as they help to advance our knowledge and understanding of the world aroud us.
Examples of Theoretical Models
A theoretical model is a simplified representation of a complex phenomenon or system that aims to explain how different factors interact with each other to produce certain outcomes. An example of a theoretical model could be a study investigating the factors that contribute to a student’s success on an important standardized test. The model wuld likely draw on previous research and theories about different factors that could affect test performance, such as prior academic achievement, test-taking strategies, motivation, and self-efficacy. The model would outline how these different factors interact with each other to influence a student’s likelihood of passing the test successfully. By using a theoretical model, researchers can better understand the complex relationships between different variables and develop hypotheses to test in their empirical research.
The Meaning of Theoretically
Sure, I’d be happy to provide a detailed answer to your question. The term “theoretically” is an adverb that describes something in a way that is based on theory or assumptions rather than practical or real-world experience. For example, if we say that something is theoretically possible, we mean that it could happen in theory, but we’re not sure if it will actually happen in practice. Another example could be that a scientific concept might be theoretically sound, but until it is tested and proven through experiments, it remains only a theory. In short, when we use the word “theoretically,” we are describing something that is based on theoretical or hypothetical assumptions rather than actual experience or evidence.
Types of Theoretical Models
According to sociologists, there are at least four types of theory that are relevant to the field of sociology. These types of theory include: theory as classical literature in sociology, theory as sociological criticism, taxonomic theory, and scientific theory. While these types of theory may have rough parallels in social education, they can also be useful for guiding research in sociology. It is important to note, however, that there may be other types of theory that are relevant to other fields of study.
Theoretical Considerations
There are three theoretical considerations that are commonly used to classify developmental theories. The first dimension is environmental versus maturational. This dimension examines the extent to which development is influenced by genetic factors versus environmental factors. Maturational theories suggest that development is primarily driven by genetic factors, while environmental theories emphasize the impact of external factors such as parenting, education, and social interactions.
The second dimension is performance versus competence. This dimension focuses on the distinction between what a person can do versus what they are capable of doing. Performance theories focus on observable behaviors and actions, while competence theories look at the underlying abilities and knowledge that support those behaviors.
The third dimension is general versus specific. This dimension considers whether developmental theories apply to all aspects of development or are specific to certain domains, such as cognitive or social development. General theories propose that development follows a universal pattern acros all domains, while specific theories focus on particular aspects of development.
By considering these three dimensions, researchers can better understand the underlying assumptions and implications of different developmental theories. This can help inform research and practice in areas such as education, child development, and psychology.
The Benefits of Asking Theoretical Questions
Theoretical questions are those that are posed to explore a particular concept or idea without necessarily expecting a concrete answer. They are often used in academic or intellectual contexts to encourage critical thinking and discussion. The purpose of a theoretical question is not to solve a problem or arrive at a definitive conclusion, but rather to generate new insights and perspectives by exploring different possibilities and hypothetical scenarios. Theoretical questions can be thought-provoking and can help to expand our understanding of complex topics by encouraging us to cosider alternative viewpoints and examine ideas from multiple angles. theoretical questions play an important role in intellectual inquiry and can help us to deepen our understanding of the world around us.
Conclusion
Theoretical research is a type of logical exploration that involves theorizing or defining a system of beliefs and assumptions. This type of research is characterized by the exploration of non-observational entities such as electrons, neutrinos, and genes. Examples of theoretical research problems include the relationship between gender, race, and income inequality in the gig economy, and the role of the British Empire in the development of Scotland’s national identity. While thee examples are hypothetical in nature, they highlight the importance of theoretical research in providing a deeper understanding of complex phenomena. By exploring these theoretical concepts, researchers can gain valuable insights that can inform future empirical studies and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields.
