Continuity is an important concept in electrical engineering, as it refers to the uninterrupted flow of current from one point to another. The continuity symbol is used to represent this concept and can be found on many electrical diagrams.
The continuity symbol is a circle with a straight line running through its center. It is typically used to indicate that two points are connected electrically, meaning there is no interruption in the flow of current between them. This symbol can be used in both AC and DC circuits, alhough it is more commonly seen in DC diagrams.
The continuity symbol can also be used to represent switches or other components that are part of a circuit. In such cases, the straight line through the center will be broken when the switch or component is open and unbroken when it’s closed and active. This helps clarify complex circuits by separating active components from inactive ones at a glance.
Continuity symbols provide an easy way for electricians and engineers to quickly understand how a circuit functions without having to dive into the details of each individual component. Knowing where current flows, where it doesn’t, and which components are connected together makes troubleshooting simpler and faster.
Although a simple concept, continuity symbols are an essential element of any electrical diagram and should not be overlooked when designing or troubleshooting circuits!
Measuring Continuity with a Multimeter
Continuity on a multimeter is a feature that allows you to check if there is an uninterrupted path for electricity to flow through. A multimeter with a continuity test mode measures the resistance between two points in a circuit by sending a small current through the circuit. If the resistance is low enough, usually less than 50 ohms, it will produce an audible beep or other signal indicating that there is a complete path for current flow. This test can be used to check switches, fuses, electrical connections, conductors and other components in an electrical system.
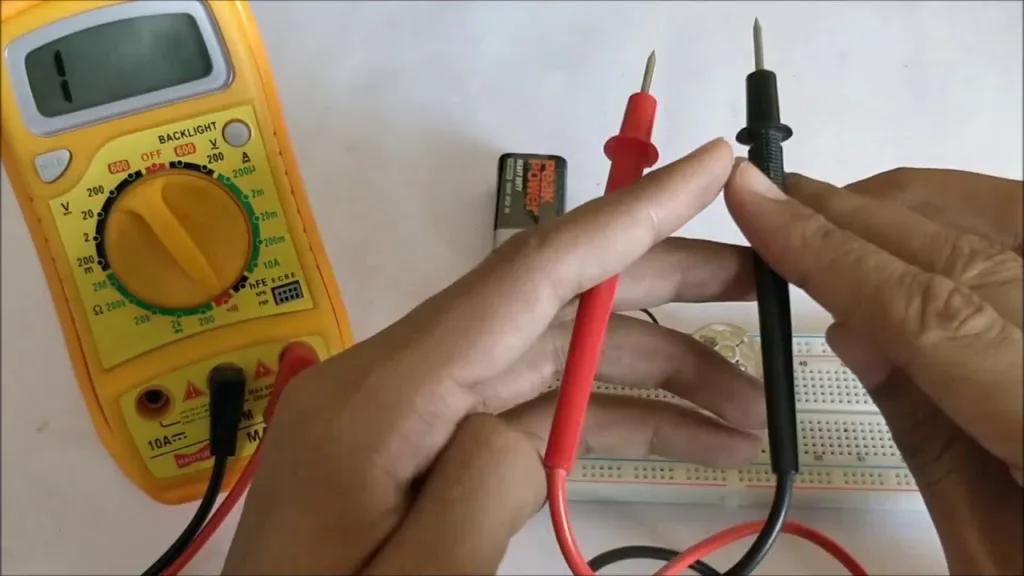
The Difference Between Continuity and Ohms
No, continuity and ohms are not the same. Ohms measure the resistance to electrical flow between two points, while continuity is a yes or no statement that indicates whether there is a complete circuit or not. An ohmmeter is a device used to measure ohms, while continuity can be tested in several different ways, such as with an ohmmeter or a continuity tester.
Unit of Measurement for Continuity
The unit for continuity is ohms (Ω). This is the standard unit of measurement for electrical resistance. A closed circuit will typically have a resistance between 0-50 ohms, and when this occurs, most continuity meters will emit a brief sound from their built-in beeper.
The Benefits of Good Continuity Reading
A good continuity reading is a measurement of electrical conductivity, which indicates how well two points are connected. It is usually measured in ohms (Ω), and a good reading is one that is below 1.0 Ω. A reading of 0.2 Ω, for example, indicates excellent conductivity between the two points being tested.
Understanding the Symbols on a Multimeter
On most multimeters, you’ll find three symbols – V (for voltage), A (for current), and Ω (for resistance). Voltage is measured in Volts, current is measured in Amps, and resistance is measured in Ohms. These are the three main measurements that a multimeter can take. Additionally, you may also see other symbols such as Hz (for frequency) or mV (for millivolts). Knowing what each of these symbols mean will help you get the most out of your multimeter.

Does Continuity Exist in the Number 0?
Yes, 0 (or near zero) means continuity. This means that there is a continuous path for electric current to flow from one probe to the other. If the screen displays 1 or OL (open loop), there’s no continuity—that is, there’s no path for electric current to flow from one probe to the other.
What Does a Reading of 0.0 Ohms Mean?
0.0 ohms is a measurement of resistance in a circuit. It indicates that there is no resistance in the circuit, meaning that electricity can flow freely through it. This means that an electric current can pass through the circuit without any interruption or impedance, making it an ideal and efficient conductor of electricity.
Understanding Continuity
Continuity is a state or situation of uninterrupted duration or continuation, especially without essential change. It is often used in reference to management of a company, meaning that the leadership remains essentially the same over time. In other cases, it may refer to a consistent pattern of behavior or ideas that are not disrupted by changes in external circumstances. Continuity is an important aspect of many aspects of life, from business operations to family relationships.
Conditions of Continuity
The three conditions of continuity are as follows:
1. The limit must exist at the point in question. This means that the function must have a defined value at the point, and that the value of the function approaches a fixed value as x approaches the point from both sides.
2. The function must be defined at that point. This means that the function has a single, well-defined value for x at this particular point, rather than an undefined or non-existent one. Without this condition being met, it is impossible to determine whethr or not a function is continuous.
3. The limit and the function must have equal values at that point. This means that when x approaches a certain point from both sides, the values of the limit and of the function itself must be identical in order for continuity to be present. If they are not equal, then there is a discontinuity present at this particular point.
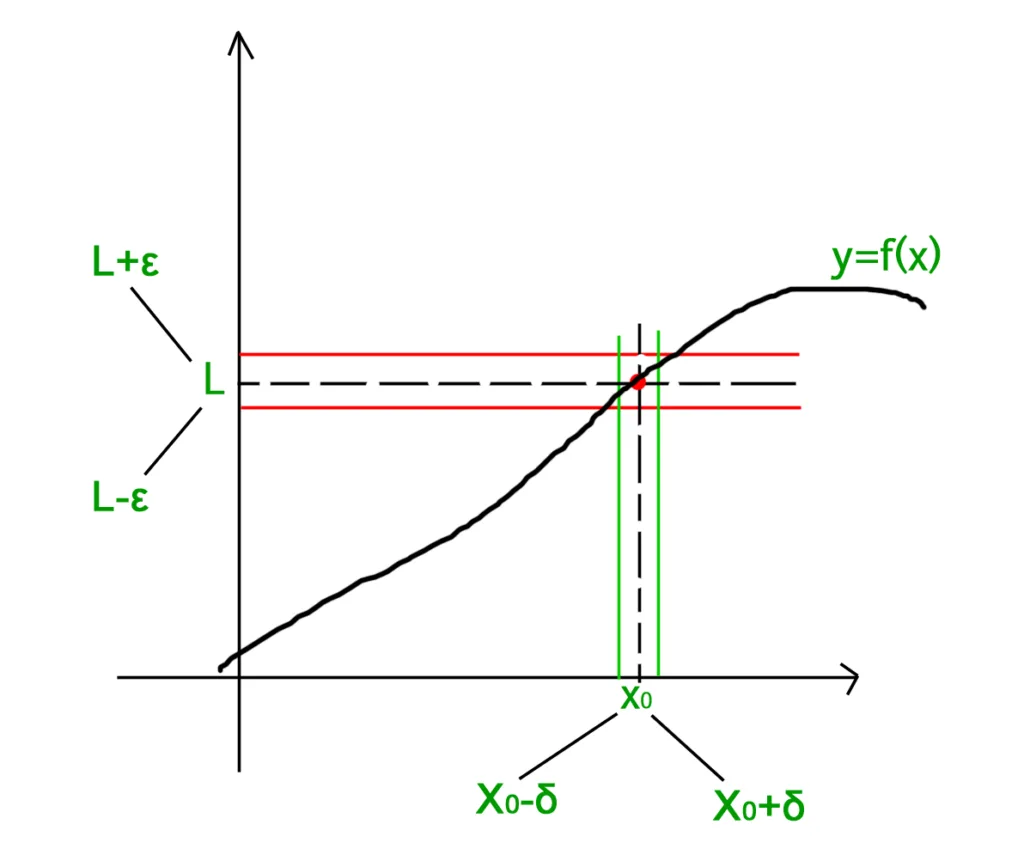
Defining Continuity
Continuity is a concept in mathematics that describes a function or relation in which the output of the function or relation does not change abruptly, but instead gradually changes with any small change in its input. Essentially, it means that a function or relation is continuous if it has no abrupt jumps or breaks in its graph. To be more precise, a function is said to be continuous at a certain point if it is defined at that point, its limit exists at the point, and the value of the function at that point equals the value of the limit at that point. A relation is said to be continuous if for every x-value within its domain tere exists a unique y-value corresponding to it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the continuity symbol is a universal symbol used to represent a complete path or circuit that allows electricity to flow. It is used as a visual indicator in circuit diagrams and other electrical drawings, as well as on switches and other electrical components. It is also an important part of testing for continuity, which can be done with a digital multimeter in Continuity Test mode or with an Ohmmeter. By understanding the significance of the continuity symbol, electricians can quickly identify any issues with circuits and troubleshoot them accordingly.
