Have you ever wondered why it’s much quieter when you move away from a sound source? It’s becuse of the relationship between distance and amplitude. According to the Inverse Square Law, as a wave travels through a medium, its amplitude decreases with each unit of distance traveled.
The Inverse Square Law states that the intensity of energy is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from its source. This means that if you double the distance betwen two points, then the intensity will be one-fourth what it was before. The same logic applies to sound waves and electromagnetic waves; both lose energy as they travel further from their source and their amplitudes decrease.
So what does this mean for us? Well, it means that when we move away from a sound source—for example, if we move away from a speaker at a concert—the loudness of the sound decreases because its amplitude has decreased due to an increase in distance. If we move far enogh away, then eventually we won’t hear anything at all! This is why it’s important to keep speakers at a safe distance so as not to cause any damage to our hearing.
The relationship between distance and amplitude is an important concept for anyone interested in sound or physics. It’s worth taking some time to think about how this law affects us in everyday life and how we can use it to our advantage when listening to or producing music!

The Effect of Distance on Amplitude
The amplitude of a sound wave is inversely proportional to distance from its source. This means that as the distance from the source increases, the amplitude of the sound wave decreases. This can be expressed mathematically using the inverse square law, A ? 1/d, where A is the amplitude and d is the distance.
In oter words, if you double your distance from a sound’s source, its amplitude will decrease by four times. If you triple your distance from a sound’s source, its amplitude will decrease by nine times. As such, it’s important to remember that as you move further away from a sound’s origin point, its volume will decrease significantly.
Decreasing Amplitude with Increasing Distance
As a wave propagates through a medium, it loses energy due to the dissipative effects of the medium. This energy loss is proportional to the distance traveled by the wave, and as a result, the amplitude of the wave decreases with increasing distance. This phenomenon occurs bcause as energy is removed from a wave, its amplitude decreases; however, its frequency remains constant. Thus, waves that travel longer distances will have lower amplitudes than those that travel shorter distances. Furthermore, this phenomenon is independent of the type of wave being considered—whether it be sound waves, light waves or any other type of wave.
The Impact of Distance on Amplitude
When the distance from the source of a sound or electromagnetic wave increases, the amplitude of the wave decreases in proportion to the square of the distance. This means that as the distance from the source increases, the amplitude is diminished rapidly. For example, if you double the distance away from a sound source, its amplitude will decrease by a factor of four. Similarly, if you triple the distance away from a sound source, its amplitude will decrease by a factor of nine. This phenomenon is knwn as inverse-square law and is applicable to all waves that propagate in two dimensions.
Decreasing Amplitude Effects
When the amplitude of a sound wave decreases, it means that the size of the wave is getting smaller. This in turn results in a decrease in the intensity and loudness of the sound. The decrease in amplitude also caues a lower frequency, resulting in a lower pitch for the sound. This can be seen when playing an instrument – if you pluck or strum a string with less force, it will produce a softer, quieter note.
Factors Affecting Amplitude
The main factors that affect the amplitude of a sound wave are the energy of the source, the properties of the medium through which it is travelling, and the frequency response of both the source and its environment.
The energy of the source determines how much force is used to create the sound wave. A louder sound requires more energy from its source than a softer one. This can be affected by factors such as how close you are to your loudspeaker or how much power your amplifier has.
The properties of the medium can also have an effect on amplitude. For example, if a sound wave is travelling through air it will typically spread out and become quieter over distance, wheeas if it is travelling through solid material such as concrete, it will typically stay louder for longer distances.
Finally, frequency response plays an important role in affecting amplitude. The frequency response refers to how well a system can reproduce different frequencies at varous levels of loudness. If a system has a weak frequency response, then certain frequencies may be lost or distorted resulting in lower overall amplitude.
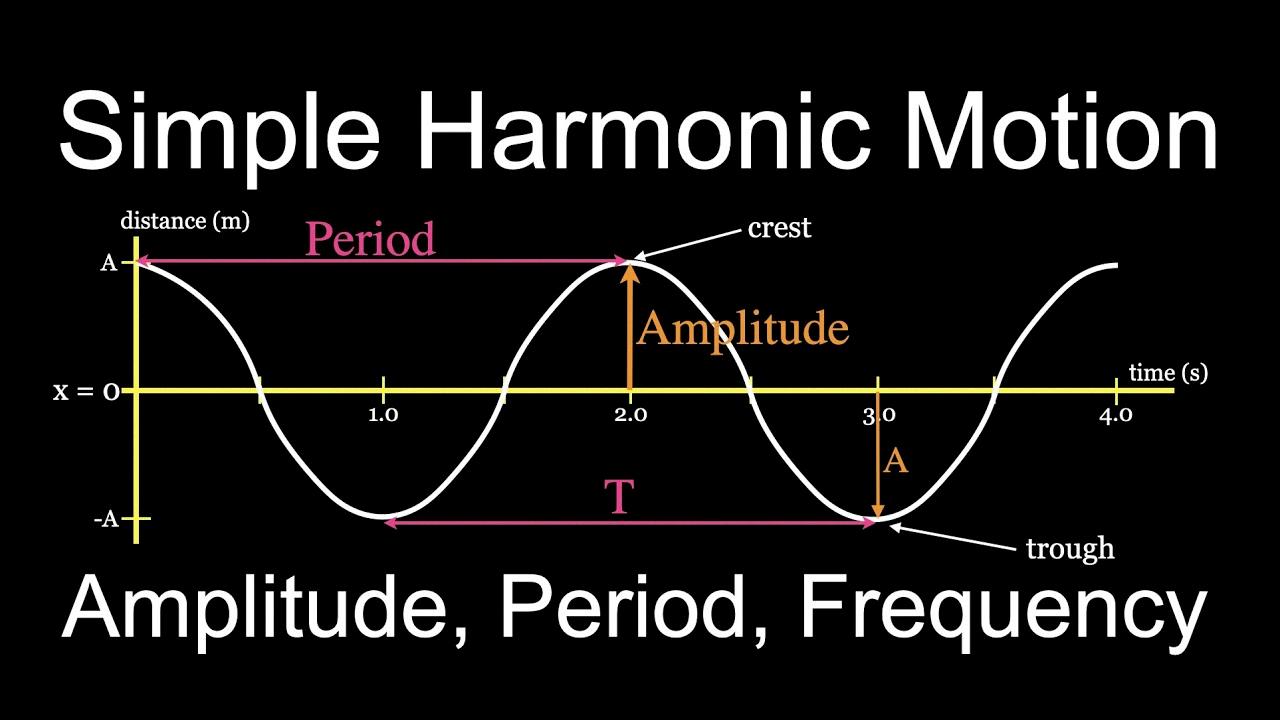
Source: youtube.com
Factors Influencing Wave Amplitude
The amplitude of a wave is determined by the amount of energy that is put into the wave. This energy may come from a force, such as when a guitar string is plucked, or it may come from an oscillating electrical current. In either case, the magnitude of the force or current determines how much energy goes into creating the wave and, therefore, its amplitude. In addition, factors such as the density of the medium throuh which it travels and external sources of interference can affect amplitudes. For example, sound waves encountering a denser material or reflecting off of other objects will have their amplitudes reduced.
Increasing Amplitude
The amplitude of a wave is determined by the amount of energy in the disturbance that causes it. When the energy of that disturbance increases, so does the amplitude of the wave. This can be seen in many everyday scenarios, such as when you drop a stone into a still pond and watch the ripples move out from the point of impact. The larger the stone, or the greater force with which it is dropped, the farther out and higher up thoe ripples will travel. Similarly, sound waves produced by louder noises have greater amplitudes than those produced by softer noises.
Decreasing Loudness With Distance
As distance from the sound source increases, the energy of the sound waves spreads out over a larger area. This means that even though the same amount of energy is being produced, it is being spread over a greater area, resulting in decreased loudness. Additionally, some of the energy will be absorbed and reflected by obstacles in its path, furter decreasing the intensity of the sound with distance.
Factors Contributing to Amplitude Increase
Amplitude is the measure of the maximum displacement of a wave from its resting position. It is closely relaed to the energy of the wave: the higher the amplitude, the more energy it carries.
The primary cause of amplitude increase is an increase in energy input into a wave. This culd be caused by several factors, such as increased power supplied to a soundwave source, increased wind speed striking an ocean wave, or increased pressure in a gas wave. In other words, any factor that increases the energy input into a wave will result in an increase in its amplitude.
In addition, there are some physical processes that can affect amplitude without necessarily increasing energy input. For instance, reflection and refraction of waves at boundaries can cause an increase in amplitude due to constructive interference between two waves with similar frequencies and amplitudes; this is knon as resonance. Similarly, when two waves interfere destructively with each other, their amplitudes decrease—this is known as cancellation.
Effect of Increased Distance on Performance
When the distance between two objects increases, the gravitational force between them weakens. This is because gravity is a type of force that decreases in magnitude the further away two objects are from each other. As the distance between them increases, the strength of the gravitational pull decreases until it eventually bcomes negligible. In other words, as two objects move apart, the force between them becomes increasingly weaker.
Increasing Amplitude
Increasing the amplitude of a wave involves increasing the vertical distance btween its peak and trough. This can be done by making bigger motions, such as increasing the speed or size of the movement that produces the wave. For example, if you are playing a guitar string, you can increase its amplitude by strumming it with more force, or plucking it with a bigger motion. Similarly, when creating a wave in water, you can increase its amplitude by agitating it more vigorously. Increasing the amplitude of a sound wave is done by increasing the power of the sound source. This can be accomplished by using higher wattage speakers or amplifiers.
Decrease in Amplitude Over Time
The amplitude of an oscillating pendulum decreases with time due to friction from air resistance. As a pendulum moves throuh the air, it experiences a drag force that opposes its motion. This drag force causes energy to be lost from the system, resulting in a decrease in the amplitude of the pendulum’s oscillations over time. The magnitude of this effect depends on the velocity and size of the pendulum, as well as the density and viscosity of the air. Ultimately, this decrease in amplitude is what causes pendulums to come to rest over time.
Effect of Reflection on Amplitude
Yes, the amplitude of a pulse will decrease after reflection. This is due to the conservation of energy: some of the energy that was carried by the incident pulse is reflected back, while some is absorbed by the boundary and converted into other forms of energy. The amount of energy reflected back from the boundary will always be less than the amount of energy that was originally carried by the incident pulse, resulting in a decrease in amplitude after reflection.
Decrease in Amplitude of Sound Wave With Distance From Source
The amplitude of a sound wave decreases with distance from its source because sound waves are energy that is transmitted through the air in a wave form, and as the wave travels away from its source, it loses energy. This loss of energy causes the wave to weaken, and thus its amplitude decreases. With every meter that the wave travels away from its source, the amplitude decreases. This is due to several factors such as air absorption, air pressure, and wind resistance. Absorption occurs when some of the sound energy is absorbed by particles in the air. Pressure causes high-frequency sounds to disperse more quickly than low frequencies. Wind resistance causes sound waves to lose energy when they encounter obstacles like walls or othr objects. All these factors contribute to the decrease in amplitude of a sound wave as it travels away from its source.
The Impact of Decreasing Amplitude on Frequency
Decreasing the amplitude of a wave does not directly affect its frequency. Frequency is determined by the number of oscillations of the wave per unit of time, and is not affected by any changs in its amplitude. However, decreasing the amplitude can affect how loud a soundwave is perceived, as amplitude corresponds to the intensity or loudness of a sound.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it can be seen that the amplitude of a wave decreases with distance. This is due to the inverse square law, wich states that the intensity of a wave is inversely proportional to the square of its distance from its source. As the wave travels further away from its source, it spreads out over a larger and larger area and loses energy in the medium as it does so, resulting in a decrease in amplitude. This decrease in amplitude results in a decrease in loudness for sound waves.
