The xiphoid process, also known as the xiphisternum, is a small, cartilaginous extension at the lower end of the sternum or breastbone. It plays a crucial role in connecting the sternum to the ribs and the thoracic cage. In normal circumstances, the xiphoid process lies flat against the chest wall and does not cause any discomfort. However, in some cases, it can stick out, leading to a condition known as xiphoid process sticks out or xiphoid prominence.
Xiphoid prominence can be a cause of concern for individuals experiencing this condition. It may appear as a small, bony protrusion at the bottom of the sternum, just above the abdomen. This protrusion can vary in size and shape, ranging from a minor bump to a more prominent and noticeable projection. It can sometimes be mistaken for a lump or tumor, causing anxiety and worry for those affected.
There can be several factors contributing to the development of xiphoid process sticks out. One of the primary causes is significant weight gain. Excessive fat accumulation in the abdominal area can push the xiphoid process outward, making it more prominent. Additionally, repeated trauma to the chest region can also lead to xiphoid prominence. This can occur due to accidents, falls, or any other physical injury that affects the sternum and surrounding area. Unaccustomed heavy lifting or strenuous exercise can also strain the xiphoid process, causing it to stick out.
Another possible cause of xiphoid prominence is perichondritis, which is the inflammation of the cartilage surrounding the xiphoid process. This inflammation can result from infections, such as bacterial or fungal, or even from autoimmune disorders. Perichondritis can lead to swelling and tenderness around the xiphoid process, causing it to become more noticeable.
When individuals experience xiphoid process sticks out, they may also experience associated symptoms. These can include pain or discomfort in the chest area, especially when pressure is applied to the protrusion. The pain may worsen with certain movements, such as bending or twisting. In some cases, the pain may radiate to the abdomen or even the back.
If you are experiencing symptoms of xiphoid process sticks out, it is essential to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Your doctor will conduct a physical examination and may order additional tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, to evaluate the condition further.
Treatment for xiphoid process sticks out will depend on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. If the condition is a result of recent trauma, your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication to relieve pain and recommend hot and cold therapy to reduce swelling. It is also important to avoid activities that may aggravate the condition and allow time for the injury to heal.
In cases where the xiphoid process sticks out due to excessive weight gain, weight management strategies may be recommended. This can include a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
In more severe cases or if other underlying conditions are present, such as perichondritis or autoimmune disorders, additional treatment options may be necessary. This can include antibiotics or antifungal medications to treat infections, or immunosuppressive drugs to manage autoimmune conditions.
Xiphoid process sticks out is a condition where the xiphoid process protrudes or sticks out from the sternum. It can be caused by factors such as significant weight gain, repeated trauma, heavy lifting, exercise, or perichondritis. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and may include pain management, lifestyle changes, or medication. If you are experiencing symptoms of xiphoid process sticks out, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
Why Would Your Xiphoid Process Stick Out?
The xiphoid process, located at the lower end of the sternum or breastbone, may stick out or have an anterior displacement due to various reasons. Here are some possible causes:
1. Weight gain: Significant weight gain can lead to the xiphoid process protruding outward. This occurs when excess fat accumulates in the abdominal area, putting pressure on the xiphoid process and causing it to stick out.
2. Repeated trauma: If the xiphoid process is subjected to repeated trauma, such as from a direct blow or injury, it can become displaced. This could happen during accidents, falls, or contact sports where the chest area is at risk of impact.
3. Unaccustomed heavy lifting: Engaging in unaccustomed or excessive heavy lifting can strain the muscles and ligaments around the xiphoid process. This strain can cause the xiphoid process to move forward, resulting in an anterior displacement.
4. Exercise: Certain exercises that involve repetitive movements or strain on the abdominal muscles may contribute to xiphodynia, a condition characterized by xiphoid process pain and displacement. This is more commonly seen in activities like weightlifting, sit-ups, or intense core exercises.
5. Perichondritis: Perichondritis is the inflammation of the connective tissue surrounding the xiphoid process. This condition can cause pain, swelling, and tenderness in the area, leading to an anterior displacement of the xiphoid process.
It is important to note that these are just some of the potential causes of xiphoid process protrusion or displacement. If you are experiencing this condition or have concerns about your xiphoid process, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
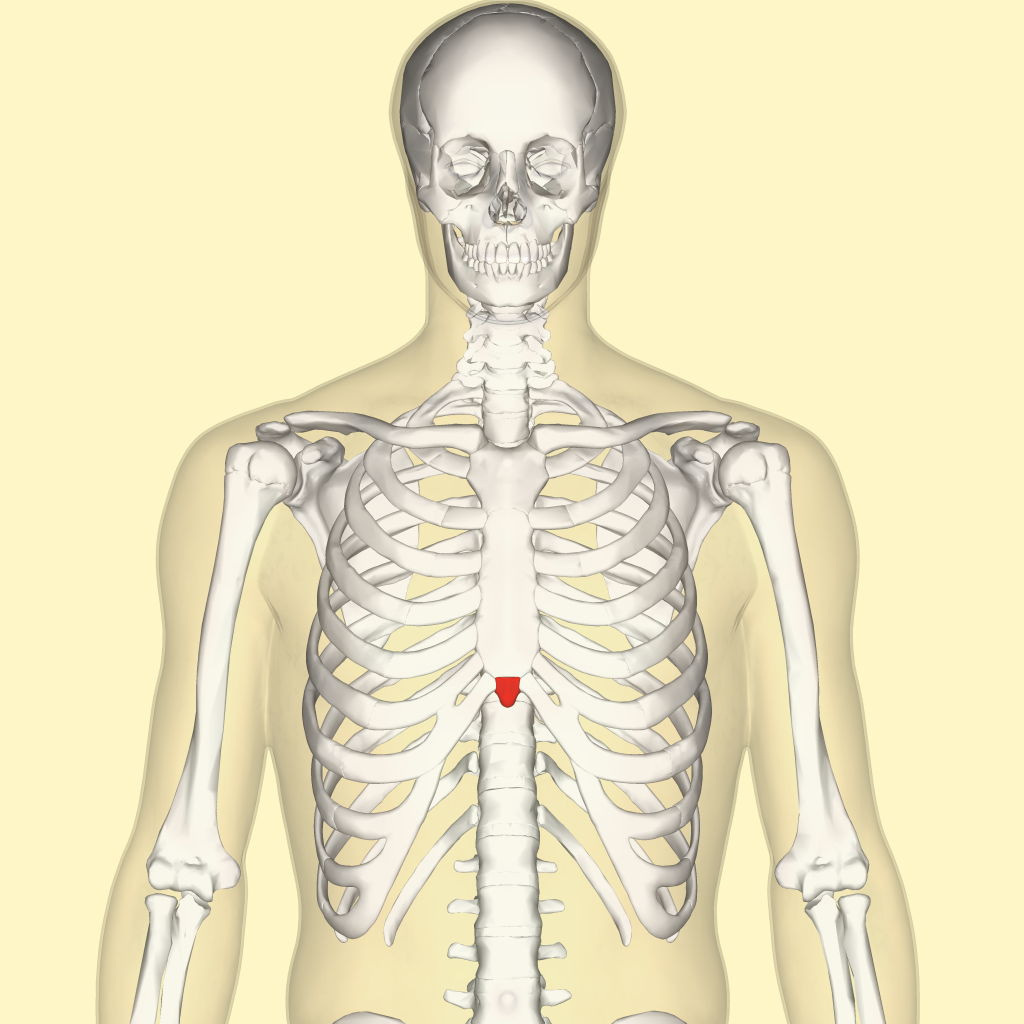
What Is It Called When Xiphoid Process Sticks Out?
When the xiphoid process sticks out, it is known as xiphoid process prominence or xiphoid syndrome. The xiphoid process is a small, cartilaginous extension at the lower end of the sternum. It is usually not visible or palpable, but in some cases, it can protrude or become more prominent due to various reasons. This condition can be caused by trauma, inflammation, or abnormal growth of the xiphoid process itself. In some cases, it may be associated with certain medical conditions such as costochondritis, fibromyalgia, or osteoarthritis. Xiphoid process prominence can cause discomfort or pain in the affected area, especially during physical activity or when pressure is applied. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of this condition.
How Do You Treat An Enlarged Xiphoid Process?
Treatment for an enlarged xiphoid process depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options:
1. Medications: Your doctor may prescribe pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate any discomfort or inflammation associated with an enlarged xiphoid process.
2. Rest and activity modification: Avoiding activities or movements that aggravate the symptoms can help reduce pain and promote healing. Your doctor may recommend limiting certain activities or modifying your movements until the enlargement subsides.
3. Ice or heat therapy: Applying ice packs or heat pads to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation. Alternating between cold and heat therapy throughout the day can provide relief.
4. Physical therapy: In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve flexibility. This can help alleviate pain and prevent further complications.
5. Surgical intervention: If conservative treatments are not effective or if the enlargement is due to a more serious underlying condition, surgery may be necessary. The surgical procedure may involve removing a portion of the xiphoid process or addressing the underlying cause.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate treatment plan for an enlarged xiphoid process. They will consider the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual factors to develop a personalized treatment approach.
What Causes Xiphoid Process Lump In Adults?
The xiphoid process lump in adults, also known as xiphodynia or xiphoid syndrome, can be caused by various factors. Here are the most common causes:
1. Chest trauma: A direct blow or injury to the chest can result in inflammation of the xiphoid process. This can cause swelling and the formation of a lump on the abdomen.
2. Repetitive strain: Certain occupations or activities that involve repetitive movements of the upper body, such as heavy lifting or strenuous exercise, can lead to xiphoid process inflammation and the development of a lump.
3. Poor posture: Prolonged slouching or hunching over can put pressure on the xiphoid process, leading to irritation and swelling. This can eventually result in the formation of a lump.
4. Infection: In rare cases, an infection in the xiphoid process or surrounding tissues can cause inflammation and the appearance of a lump. This may be accompanied by symptoms such as pain, redness, and fever.
5. Costochondritis: This condition involves inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum, including the xiphoid process. Costochondritis can cause tenderness, swelling, and the formation of a lump in the affected area.
6. Tumors: Although uncommon, tumors or growths in the xiphoid process or nearby structures can lead to the development of a lump. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and medical evaluation is necessary to determine the cause.
If you notice a lump on your abdomen or experience persistent pain or discomfort in the xiphoid process area, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
The xiphoid process sticking out, also known as pectus carinatum, is a condition where the sternum protrudes more than usual. This is the opposite of pectus excavatum, where the breastbone is depressed inward. Xiphodynia, or xiphoid syndrome, can occur when the xiphoid process is damaged and becomes inflamed, resulting in swelling and the formation of a lump on the abdomen.
Causes of xiphodynia can include significant weight gain, repeated trauma to the area, unaccustomed heavy lifting, exercise, and perichondritis. If symptoms occur after a recent trauma, treatment may involve prescription anti-inflammatory medication to relieve pain, as well as alternating between hot and cold therapy. Limiting certain activities until the injury heals may also be recommended.
It is important to seek medical attention if experiencing xiphoid process pain or if the protrusion becomes more pronounced. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan based on the individual’s specific circumstances.
