Chlorous acid, also known as hydrogen chlorite, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula HClO2. It is a weak acid that is formed when chlorine dioxide (ClO2) reacts with water. The molecular formula HClO2 indicates that the compound consists of one hydrogen atom (H), one chlorine atom (Cl), and two oxygen atoms (O).
Chlorous acid is a relatively unstable compound and is not commonly found in its pure form. It is more commonly encountered as a solution or in its salt form, known as chlorites. In solution, chlorous acid can undergo a process called disproportionation, where it decomposes into hypochlorous acid (HClO) and chloric acid (HClO3).
The structure of chlorous acid can be visualized as a central chlorine atom bonded to two oxygen atoms and one hydrogen atom. The chlorine atom has an oxidation state of +3, meaning that it has lost three electrons. The oxygen atoms are each bonded to the chlorine atom through a single bond, and the hydrogen atom is bonded to one of the oxygen atoms.
Chlorous acid is a relatively weak acid compared to other chlorine-containing acids such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) or perchloric acid (HClO4). It is a bleaching agent and has antimicrobial properties, which make it useful in certain industrial and disinfection applications. However, due to its instability and potential for decomposition, it must be handled with caution.
The chemical formula for chlorous acid is HClO2. It is an inorganic compound that consists of one hydrogen atom, one chlorine atom, and two oxygen atoms. Chlorous acid is relatively unstable and can decompose into hypochlorous acid and chloric acid. It is used as a bleaching agent and has antimicrobial properties.
How Do You Write Chlorous Acid?
Chlorous acid is written as HClO2. This chemical or molecular formula represents the composition of chlorous acid. The formula indicates that chlorous acid is composed of one hydrogen atom, one chlorine atom, and two oxygen atoms. The hydrogen atom is bonded to one of the oxygen atoms, while the chlorine atom is bonded to the other oxygen atom. The formula HClO2 provides a concise and standardized way to represent the structure and composition of chlorous acid.
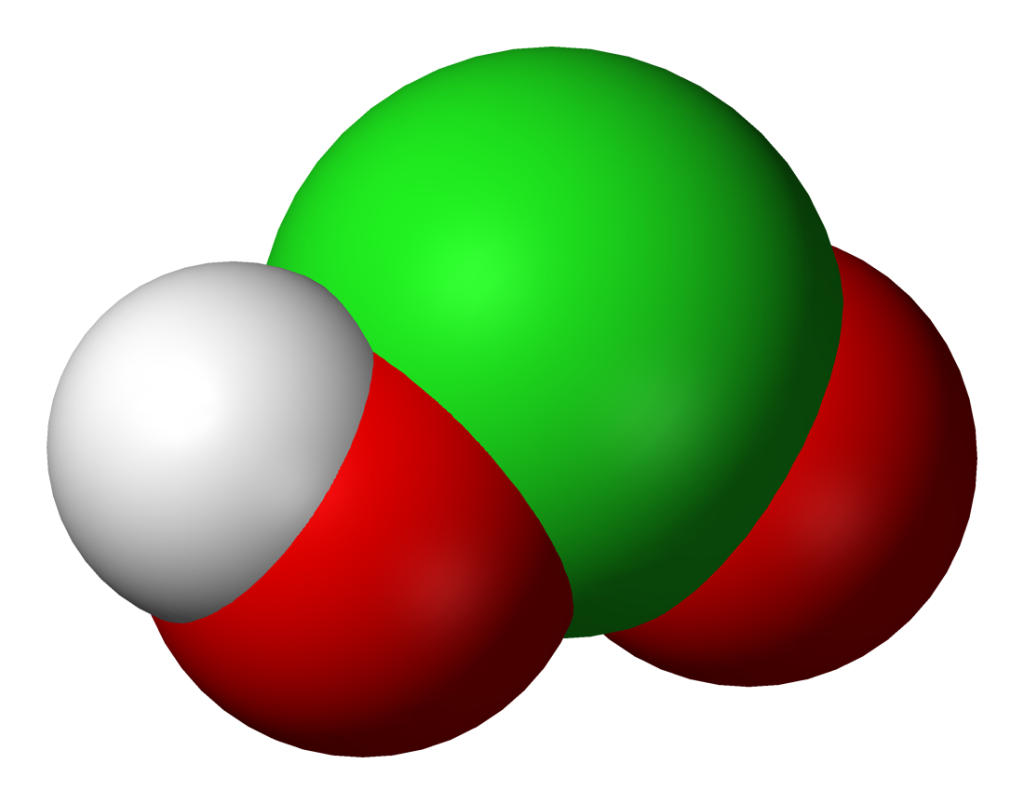
What Is Chlorous Acid In Chemistry?
Chlorous acid is a chemical compound that falls under the category of inorganic acids. Its chemical formula is HClO2, indicating that it is composed of hydrogen, chlorine, and oxygen atoms. In terms of its chemical structure, chlorous acid consists of a single chlorine atom bonded to two oxygen atoms, with a hydrogen atom attached to one of the oxygen atoms.
It is important to note that chlorous acid is considered an unstable substance in its pure form. This means that it tends to undergo chemical reactions easily, leading to its decomposition into other compounds. Specifically, chlorous acid disproportionates into two different compounds: hypochlorous acid (HClO) and chloric acid (HClO3). This means that when chlorous acid reacts, it forms both hypochlorous acid and chloric acid as products.
Chlorous acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula HClO2. It is an unstable substance that decomposes into hypochlorous acid and chloric acid.
What Is The Name Of The Acid Chlorous Acid?
The acid with the name chlorous acid is also known as hydrogen chlorite or chlorous acid. It is a weak acid with the chemical formula HClO2. This acid is formed by the combination of chlorine dioxide and water. Chlorous acid is an unstable compound and exists primarily in solution form. It is commonly used as a bleaching agent, disinfectant, and in the production of other chemicals. The acid is characterized by its oxidizing properties and is typically handled with caution due to its potential reactivity.
Conclusion
The chemical formula for chlorous acid is HClO2. Chlorous acid is an inorganic compound that contains hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and oxygen (O). It is important to note that chlorine in this acid has an oxidation state of +3. The pure form of chlorous acid is highly unstable and readily undergoes a process called disproportionation, where it breaks down into hypochlorous acid (HClO) and chloric acid (HClO3).
It is crucial to understand the distinction between chlorous acid and chloric acid, as they have different chemical formulas and properties. Chloric acid is represented by the formula HClO3 and contains hydrogen, chlorine, and oxygen. Both chlorous acid and chloric acid are classified as acids and can exhibit different chemical reactivity and behavior.
The chemical formula HClO2 represents chlorous acid, an inorganic compound with chlorine in an oxidation state of +3. It is important to differentiate chlorous acid from chloric acid, which has the chemical formula HClO3. Understanding the chemical formulas and properties of these acids is essential for studying their reactivity and applications in various chemical processes.
