Eyes are one of the most sensitive and intricate organs in our body, allowing us to see and perceive the world around us. Regular eye examinations are crucial for maintaining good eye health and detecting any potential issues early on. One common test performed during these examinations is the “air puff test,” also known as non-contact tonometry (NCT). In this article, we will explore why this test is conducted and its significance in assessing eye health.
The primary purpose of the air puff test is to measure intraocular pressure (IOP), which refers to the pressure inside the eye. Monitoring IOP is essential as elevated pressure can indicate the presence of certain eye conditions, particularly glaucoma. Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases characterized by damage to the optic nerve, often caused by increased IOP. If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to permanent vision loss.
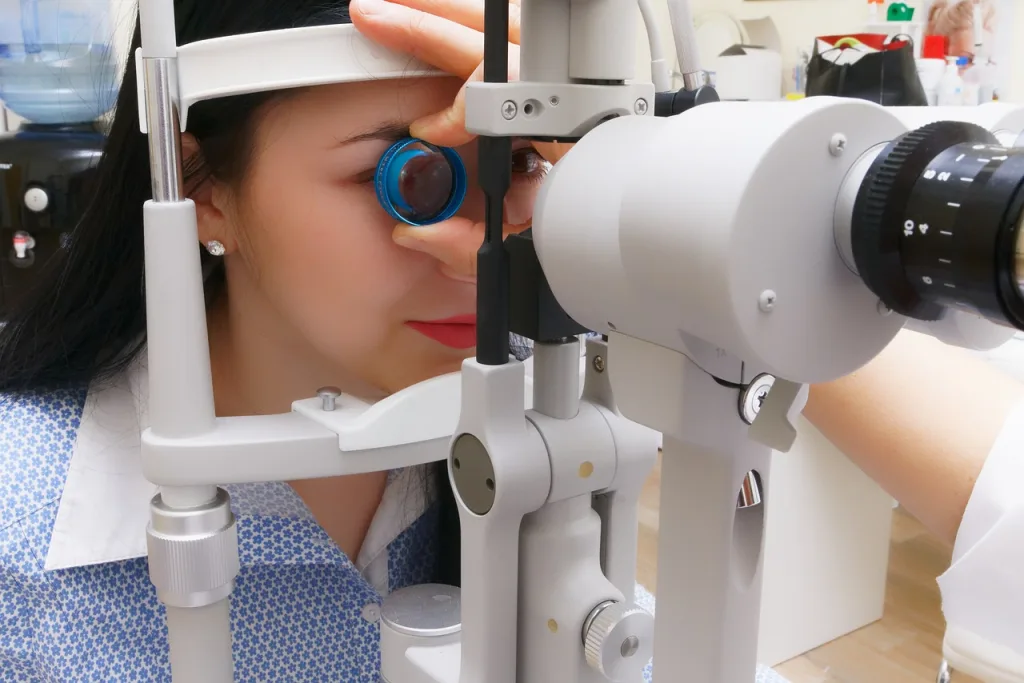
The air puff test, or NCT, is a quick and non-invasive way to measure IOP. It involves using a specialized instrument called a tonometer, which works by directing a small burst of air onto the surface of the eye. The tonometer then measures the force exerted by the air on the eye and calculates the corresponding IOP reading.
One might wonder why air is used instead of directly touching the eye. The use of air eliminates the need for physical contact with the eye, making the test more comfortable and hygienic for the patient. Additionally, the air puff test is suitable for individuals of all ages, including children, who may find it challenging to undergo other types of eye examinations.
During the air puff test, you will be asked to position your chin on a support and look at a target. The eye care professional will then aim the tonometer at your eye and release a gentle puff of air. The machine will capture the pressure readings obtained from the air bouncing back off your eye. The entire process is quick and painless, although some people may experience a tickling sensation or a reflexive blinking response due to the sudden burst of air.
The IOP reading obtained from the air puff test provides valuable information about the condition of your eyes. A normal IOP range typically falls between 10 and 21 mmHg (millimeters of mercury). If the measurement exceeds this range, it may indicate increased pressure within the eye, which could be a sign of glaucoma or other ocular conditions.
However, it is important to note that a single elevated IOP reading does not necessarily mean you have glaucoma. Further diagnostic tests and examinations may be required to confirm the presence of the disease. Eye care professionals will consider various factors, including family history, optic nerve health, and visual field tests, to make an accurate diagnosis.
The air puff test, or non-contact tonometry, is a valuable tool used during eye examinations to assess intraocular pressure. By measuring the pressure inside the eye, this test helps detect potential issues such as glaucoma. The use of air instead of direct contact makes the procedure more comfortable and suitable for individuals of all ages. If you are due for an eye examination, do not hesitate to discuss the air puff test with your eye care professional, as it plays a crucial role in maintaining your eye health.
Why Do Eye Doctors Shoot Air Into Your Eye?
Eye doctors shoot air into your eye as part of a test called the puff test or the non-contact tonometry test. This test is specifically conducted to measure the intraocular pressure (IOP) in your eyes. The air that you feel during the puff is used by the machine to bounce back and provide a reading of your eye pressure.
The reason why eye doctors measure IOP is because it can be an indicator of potential eye problems, particularly glaucoma. Glaucoma is a condition where the pressure inside the eye builds up and can cause damage to the optic nerve, leading to vision loss if left untreated.
By measuring the IOP, eye doctors can assess whether the pressure inside your eyes is within the normal range or if it is too high. If the pressure is higher than normal, it may signal the presence of glaucoma or other eye conditions that need further investigation.
The puff test is a quick and painless procedure that is typically performed during a routine eye exam. It can help detect elevated eye pressure early on, allowing for appropriate treatment and management of any underlying eye conditions.
Eye doctors shoot air into your eye to measure the intraocular pressure, which can indicate potential eye problems such as glaucoma. The puff test helps in early detection and proper management of these conditions.
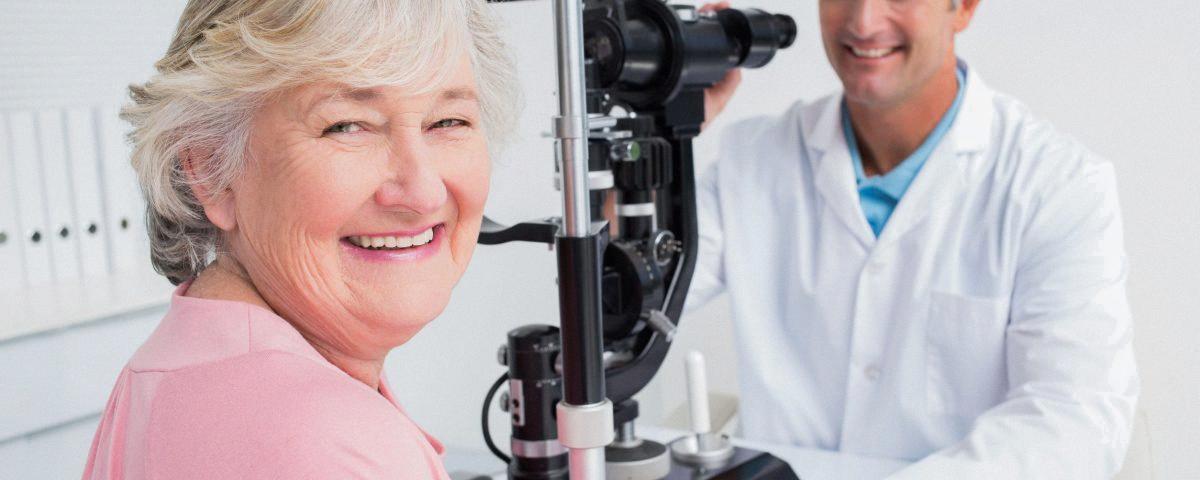

What Is The Air Puff Test On Eyes Called?
The air puff test, also known as non-contact tonometry (NCT), is a diagnostic procedure used during an eye examination to assess the pressure inside the eye. It is a non-invasive technique that aids in the detection and monitoring of glaucoma, a condition characterized by increased intraocular pressure (IOP). By delivering a controlled puff of air onto the surface of the eye, the test measures the amount of resistance the cornea offers to the air. This measurement is then used to estimate the IOP, which is an important factor in evaluating the health of the eyes and diagnosing glaucoma.
Does Eye Pressure Test Hurt?
The eye pressure test, also known as the glaucoma test, is a non-invasive procedure that measures the pressure inside your eyes. It is typically done using a method called non-contact tonometry, where a puff of air is blown onto your eye.
Now, you may be wondering if this test hurts. Well, the good news is that the eye pressure test does not typically cause any pain. However, it can sometimes make you feel a tickling sensation or even cause you to jump due to the unexpectedness of the puff of air.
To summarize, the eye pressure test is not a painful procedure. While it may tickle or startle you, it is generally a quick and painless way to measure the pressure inside your eyes and screen for potential glaucoma.
How Does The Air Puff Test Work?
The air puff test, also known as non-contact tonometry, is a diagnostic procedure that measures the intraocular pressure (IOP) of the eye. It is a quick and painless test commonly performed during routine eye exams.
Here is a detailed explanation of how the air puff test works:
1. Preparation: Before the test, you will be asked to sit in a comfortable position and place your chin on a chin rest. Your forehead will also be supported to keep your head steady.
2. Alignment: The technician or optometrist will align the tonometer, a small device attached to the machine, with your eye. They may use a light beam or a target to help position your eye correctly.
3. Air Puff: Once your eye is properly aligned, the machine will release a small burst of air towards your eye. The air puff is directed onto the cornea, the transparent front surface of the eye.
4. Air Rebound: When the air puff hits the cornea, it causes a slight indentation on the surface. The cornea then quickly rebounds or returns to its normal shape. The machine measures the amount of force required for the cornea to return to its original state.
5. Pressure Calculation: Based on the corneal rebound, the machine calculates the intraocular pressure. The rebound time provides an indirect measurement of the pressure inside the eye. An algorithm in the machine converts the rebound time into a numerical value, which represents the IOP.
6. Result: The test result is displayed on the machine, indicating the estimated intraocular pressure of your eye. This measurement is important as abnormal IOP levels can be an indicator of certain eye conditions, such as glaucoma.
It is worth noting that while the air puff test provides a quick and convenient way to estimate IOP, it is not the most accurate method. For a more precise measurement, your eye doctor may perform other tests such as Goldmann applanation tonometry or use a handheld tonometer.
The air puff test uses a small burst of air to measure the intraocular pressure. The cornea’s rebound time after the air puff is used to calculate the pressure inside the eye. This test is a valuable tool in evaluating eye health and detecting potential issues like glaucoma.
Conclusion
Our eyes are incredibly complex and vital organs that allow us to see and experience the world around us. They consist of various structures, each with its own important role in the process of vision. From the cornea and lens that focus light onto the retina, to the optic nerve that transmits visual information to the brain, every component plays a crucial part.
Regular eye exams are essential for maintaining optimal eye health and detecting any potential problems early on. Tests such as the puff test, or non-contact tonometry, help measure intraocular pressure, which can indicate issues like glaucoma. By identifying and addressing these issues promptly, we can prevent or minimize vision loss and maintain the overall health of our eyes.
It’s important to take care of our eyes by practicing good eye hygiene, such as avoiding excessive strain from digital screens, wearing protective eyewear in hazardous environments, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Eating a balanced diet rich in eye-nourishing nutrients, like vitamins A, C, and E, can also support eye health.
Remember, our eyes are precious and irreplaceable, so it’s crucial to prioritize their care. Regular eye exams, proper eye hygiene, and a healthy lifestyle are key to ensuring clear vision and maintaining the overall well-being of our eyes. So, let’s appreciate and take care of our eyes for a lifetime of sight and enjoyment.
