When it comes to creating art or manufacturing objects, there are various techniques available. One of the most common methods is the subtractive method, which involves removing material to shape and form the desired object. In this article, we will delve deeper into the subtractive method, exploring its applications, benefits, and the processes involved.
The subtractive method is a technique used in sculpture, woodworking, stone carving, and even ceramics. It is a process where material is systematically eliminated from the outside in, resulting in the creation of a finished work. This method stands in contrast to the additive process, where material is added layer by layer.
Carving is one of the primary processes used in the subtractive method. It involves cutting or chipping away at a mass of stone, wood, or other hard materials to achieve the desired shape. Carving requires precision and skill, as the artist or craftsman must carefully remove material to bring their vision to life.
In the field of ceramics, the subtractive method is most commonly used for sculptural works. However, functional potters can also experiment with this technique to create unique and artistic pieces. By removing material from a clay body, intricate designs and shapes can be achieved, resulting in visually stunning and functional pottery.
One of the significant advantages of the subtractive method is the ability to work with a wide range of materials. Whether it is wood, stone, clay, or other materials, this technique allows artists and manufacturers to shape their creations according to their specifications. Additionally, subtractive manufacturing provides the opportunity to work with end-use materials, making it suitable for both prototyping and large-scale production runs.
Another advantage of the subtractive method is the versatility it offers in terms of finishes and mechanical properties. By removing material, artists can create smooth surfaces, intricate details, and unique textures that add depth and character to their work. This flexibility allows for endless possibilities in terms of design and aesthetics.
In contrast to the additive manufacturing processes, subtractive manufacturing offers a different approach to creating objects. While additive manufacturing builds objects by adding material layer by layer, subtractive manufacturing removes material to shape and form parts. This method is particularly suitable for those looking for specific finishes or mechanical properties in their final product.
The subtractive method is a valuable technique used in various artistic and manufacturing processes. Whether it is carving stone or wood, shaping clay, or creating intricate designs, this method offers artists and craftsmen the ability to bring their visions to life. With its versatility, wide range of materials, and the ability to work with end-use materials, the subtractive method is an excellent choice for both small and large-scale production runs. So, next time you admire a beautifully carved sculpture or hold a meticulously crafted pottery piece, remember the subtractive method behind its creation.
What Is The Subtractive Method In Art?
The subtractive method in art refers to a technique where material is removed or carved out from a solid mass to create a desired shape or form. This method is most commonly used in sculpting and involves cutting or chipping away material from a block of stone, wood, or other hard substances.
Here are some key points to understand about the subtractive method in art:
1. Material removal: In the subtractive method, the artist starts with a solid mass of material and systematically eliminates unwanted portions to reveal the desired shape. This can be done using various tools such as chisels, gouges, or saws depending on the material being worked with.
2. Precision and planning: The subtractive method requires careful planning and precision, as the artist needs to have a clear vision of the final form and strategically remove material to achieve it. It involves a step-by-step process of removing layers or sections of the material until the desired shape is achieved.
3. Gradual refinement: The subtractive method often involves working from the outside in, gradually refining the shape by removing more material as the sculpture progresses. This allows for greater control over the final result and allows the artist to make adjustments or corrections along the way.
4. Versatility: The subtractive method can be used with various materials, including stone, wood, metal, and even ice or wax. Each material has its own unique properties and challenges, requiring different tools and techniques to achieve the desired outcome.
5. Historical significance: The subtractive method has been used by artists throughout history, with notable examples found in ancient sculptures, religious artifacts, and classical art. It continues to be a popular technique in contemporary art as well, with artists pushing the boundaries and exploring new possibilities within this method.
The subtractive method in art involves the removal or carving out of material from a solid mass to create a desired shape or form. It requires precision, planning, and a gradual refinement process to achieve the desired outcome. This technique has a long history and is used with various materials, making it a versatile approach in the world of art.
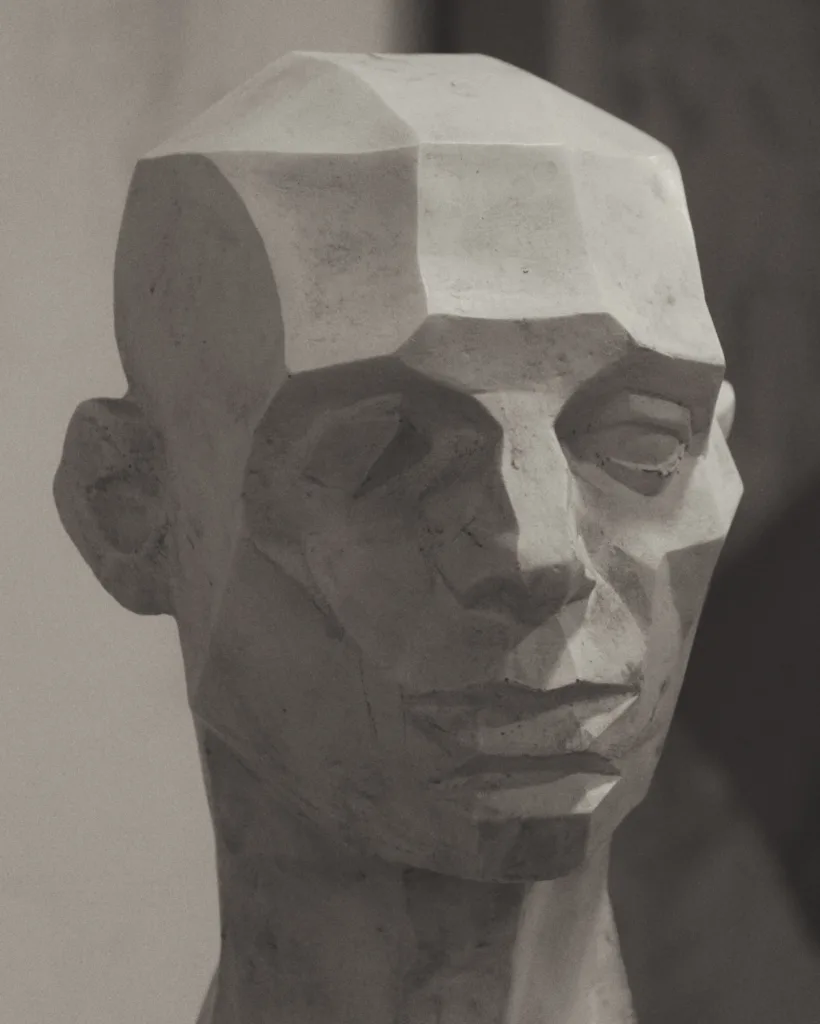

What Is Subtractive Method In Sculpture?
The subtractive method in sculpture refers to a technique where the artist removes material from a solid block or mass to create a finished artwork. This approach is the opposite of the additive process, where material is added to build up the sculpture.
In the subtractive method, the artist typically starts with a solid block of stone, wood, or other materials that can be carved or shaped. Using various tools such as chisels, knives, or saws, the artist carefully removes unwanted material. This gradual removal process allows the artist to refine the form and create intricate details.
Subtractive sculpture is commonly used in ceramics to create sculptural pieces. However, functional potters can also utilize this technique to add artistic elements to their creations.
Advantages of the subtractive method include:
1. Control: By removing material gradually, the artist has precise control over the shape, texture, and overall design of the sculpture.
2. Flexibility: The subtractive method allows for experimentation and exploration of different forms and ideas. Artists can refine their work as they progress, making adjustments along the way.
3. Detailing: Since material is removed, the artist can achieve intricate and delicate details that may not be easily achievable through the additive process.
4. Preservation of material: The subtractive method can be economical as it maximizes the use of the initial material. Artists can create multiple sculptures from a single block, reducing waste.
5. Traditional and historical significance: Subtractive sculpture has a long history and has been used by numerous cultures throughout time. By utilizing this method, artists can connect to the traditions and techniques of the past.
The subtractive method in sculpture offers artists a unique way to bring their vision to life by removing material and shaping it into a desired form. It provides a level of control, precision, and artistic expression that can result in stunning and visually captivating sculptures.
What Is Additive Or Subtractive Method?
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a process that builds objects by adding material layer by layer. It starts with a digital model, which is sliced into thin cross-sections. These cross-sections are then sequentially printed one on top of the other, creating a three-dimensional object.
The additive method involves the use of various materials, such as plastics, metals, ceramics, or even biological materials, which are deposited or fused together in a controlled manner. This allows for the creation of highly complex and customized shapes that are often difficult or impossible to produce through traditional manufacturing methods.
On the other hand, subtractive manufacturing is a process that removes material to create parts. In this method, a solid block of material, such as metal or plastic, is shaped and formed by cutting, milling, drilling, or grinding away the excess material. This subtractive process is often used for mass production of parts that require high precision and accuracy.
Here are some key points about additive and subtractive manufacturing:
Additive Manufacturing:
– Builds objects by adding material layer by layer.
– Starts with a digital model that is sliced into cross-sections.
– Materials are deposited or fused together to create the final object.
– Allows for the creation of complex and customized shapes.
– Can use a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and biological materials.
Subtractive Manufacturing:
– Removes material to create parts.
– Involves cutting, milling, drilling, or grinding away excess material.
– Used for mass production of parts that require high precision and accuracy.
– Commonly used for shaping and forming solid blocks of material.
– Can be used with various materials, including metals and plastics.
Additive manufacturing builds objects by adding material layer by layer, while subtractive manufacturing removes material to create parts. Both methods have their advantages and are used in different applications depending on the desired outcome.
What Is Subtractive Method For Prototype Development?
The subtractive method for prototype development is a manufacturing technique that involves removing material from a solid block or sheet to create a desired shape or form. It is also known as machining or milling.
Here is a detailed explanation of the subtractive method for prototype development:
1. Design: The process begins with the design of the prototype using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The designer creates a virtual model of the desired part or product.
2. Material Selection: Once the design is finalized, the next step is to select the appropriate material for the prototype. Subtractive manufacturing can be done with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
3. Machining: With the design and material in place, the subtractive manufacturing process begins. A computer numerical control (CNC) machine is used to precisely cut and remove material from the solid block or sheet based on the CAD design.
4. Tooling: The CNC machine uses various cutting tools such as drills, end mills, and lathes to shape the material. The specific tooling required depends on the complexity of the design and the material being used.
5. Finishing: After the initial machining process, the prototype may require additional finishing to achieve the desired surface quality and precision. This may involve sanding, polishing, or other techniques to smooth out any rough edges or imperfections.
6. Testing and Iteration: Once the prototype is complete, it can be tested for functionality, fit, and performance. If any modifications or improvements are necessary, the design can be refined and another prototype can be created using the subtractive method.
Advantages of the subtractive method for prototype development:
– Wide range of materials: Subtractive manufacturing allows for the use of various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, providing flexibility in material selection.
– High precision: CNC machines offer a high level of accuracy and repeatability, allowing for the creation of complex and precise prototypes.
– Strength and durability: Prototypes created using the subtractive method often exhibit excellent mechanical properties due to the use of end-use materials.
– Surface finishes: Subtractive manufacturing can achieve specific surface finishes, such as smooth or textured, depending on the requirements of the prototype.
– Suitable for small and large volume production: The subtractive method can be used for both small-scale and large-scale production runs, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
The subtractive method for prototype development involves removing material from a solid block or sheet using CNC machines to create functional and precise prototypes. It offers the flexibility to work with various materials, achieve specific surface finishes, and is suitable for small and large volume production runs.
Conclusion
The subtractive method is a highly versatile and precise technique used in various industries, such as sculpture and ceramics. This process involves removing material from a mass to create a desired shape or form. By systematically eliminating material from the outside in, craftsmen and manufacturers can create intricate and detailed designs.
The subtractive method offers several advantages. It allows for the use of a wide range of materials, including stone, wood, and other hard substances. This flexibility enables artists and manufacturers to choose the most appropriate material for their specific needs, whether it be for functional or artistic purposes. Additionally, subtractive manufacturing provides the opportunity to work with end-use materials, ensuring the final product possesses the desired mechanical properties and finishes.
This method also allows for greater control and precision in the creation process. Craftsmen can carefully chip away at the material, ensuring every detail is meticulously crafted. It provides the ability to create complex and intricate designs that may not be possible through other manufacturing methods. Moreover, subtractive manufacturing is suitable for both small and large volume production runs, making it a viable option for various production needs.
The subtractive method is a valuable tool for artists, craftsmen, and manufacturers alike. Its ability to remove material and create unique shapes and forms offers endless possibilities for creativity and functionality. Whether it be in the realm of sculpture, ceramics, or other industries, the subtractive method provides a reliable and precise approach to manufacturing and design.
