Bacterial contamination is a serious concern when it comes to food safety and laboratory procedures. The presence of harmful bacteria can lead to food poisoning or compromised lab results. Fortunately, there are steps that can be taken to prevent bacterial contamination and ensure the safety of both food and lab samples.
When it comes to preventing food poisoning, cleanliness is key. It is crucial to wash your hands and work surfaces before, during, and after preparing food. This helps to remove any bacteria that may be present on your hands or surfaces. Additionally, it is important to separate raw meat, poultry, seafood, and eggs from ready-to-eat foods. This prevents cross-contamination and the spread of harmful bacteria.
Cooking food to the right internal temperature is also essential in killing harmful bacteria. Using a food thermometer to ensure that food reaches the appropriate temperature can help prevent foodborne illnesses. It is recommended to keep your refrigerator at 40°F or below to inhibit the growth of bacteria.
In the context of laboratory procedures, avoiding contamination is vital to obtaining accurate and reliable results. To prevent lab contamination, it is recommended to automate processes whenever possible. This reduces the chances of human error and minimizes the risk of contamination. Wearing proper protective equipment, such as gloves and lab coats, is also important in preventing the transfer of bacteria.
Sterilizing equipment before and after use is another effective way to avoid lab contamination. This can be done through various methods, such as autoclaving or using disinfectants. Regularly cleaning surfaces, including countertops and equipment, helps to maintain a sterile environment and prevent the growth of bacteria.
Reducing the number of touches and using separate utensils, plates, and chopping boards for raw and cooked food can also help prevent bacterial contamination. Ensuring that raw meat is not washed, and washing hands thoroughly after handling raw food and before handling ready-to-eat food are important practices to follow.
In laboratory settings, it is crucial to check the water source for any potential contaminants. Using filtered or distilled water can help minimize the risk of bacterial contamination. Additionally, using air filters and laminar flow hoods can help create a clean environment and prevent the entry of bacteria.
Preventing bacterial contamination requires a combination of cleanliness, proper handling techniques, and attention to detail. By following these steps, both in the kitchen and the laboratory, you can significantly reduce the risk of bacterial contamination and ensure the safety of food and lab samples.
What Is The Best Way To Avoid Bacterial Contamination In Food?
To avoid bacterial contamination in food, follow these steps:
1. Clean:
– Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after preparing food.
– Clean all work surfaces, utensils, and cutting boards before and after use.
– Use hot, soapy water to wash dishes, cutting boards, and utensils, and sanitize them regularly.
2. Separate:
– Keep raw meat, poultry, seafood, and eggs separate from ready-to-eat foods.
– Use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods to prevent cross-contamination.
– Store raw meats, poultry, and seafood in sealed containers or plastic bags to prevent their juices from coming into contact with other foods.
3. Cook:
– Cook food to the right internal temperature to kill harmful bacteria. Use a food thermometer to ensure proper cooking.
– Cook poultry and ground meats to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C).
– Cook steaks, roasts, fish, and eggs to an internal temperature of 145°F (63°C).
– Reheat leftovers to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C).
4. Chill:
– Keep your refrigerator at a temperature of 40°F (4°C) or below to slow down bacterial growth.
– Refrigerate perishable foods within two hours of cooking or purchasing.
– Thaw frozen foods in the refrigerator, not at room temperature, to prevent bacterial growth.
– Avoid leaving perishable foods, such as meat or dairy products, at room temperature for an extended period.
Following these steps will help minimize the risk of bacterial contamination in your food and ensure safer consumption.
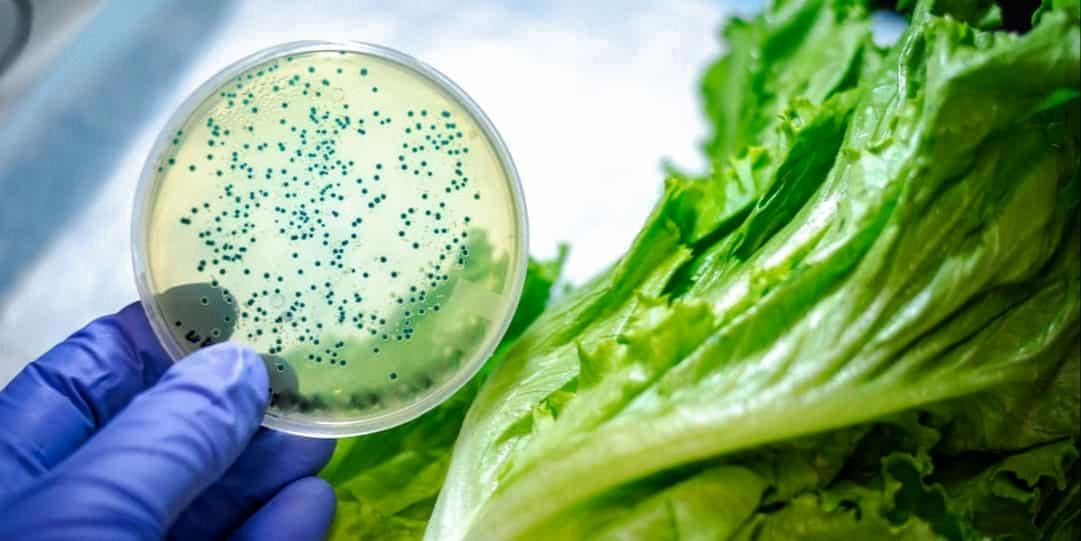
What Is The Best Way To Avoid Bacterial Contamination 360 Training?
To ensure the best way to avoid bacterial contamination during food service, it is essential to follow proper hygiene practices and maintain a clean environment. Here are some detailed steps to prevent bacterial contamination:
1. Personal Hygiene:
– Wash hands thoroughly with soap and warm water before handling any food or utensils.
– Use disposable gloves when handling ready-to-eat foods to minimize direct contact.
– Avoid touching your face, hair, or any other part of your body while handling food.
2. Clean and Sanitize Surfaces:
– Clean and sanitize all food contact surfaces, such as cutting boards, countertops, and utensils, before and after use.
– Use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods to prevent cross-contamination.
– Regularly clean and sanitize sinks, dishwashers, and any other equipment used for food preparation.
3. Proper Food Storage:
– Store raw and cooked foods separately to prevent cross-contamination.
– Keep raw meats and seafood on lower shelves in the refrigerator to prevent their juices from dripping onto other foods.
– Ensure that food storage areas are clean and properly organized to avoid any potential contamination.
4. Safe Food Handling:
– Use separate utensils and equipment for different types of food, especially between raw and cooked items.
– Cook foods thoroughly to kill any bacteria present. Use a food thermometer to ensure proper cooking temperatures.
– Avoid leaving perishable foods at room temperature for an extended period; refrigerate them promptly.
5. Employee Training:
– Provide comprehensive training to all employees on proper food handling and hygiene practices.
– Regularly update staff on food safety regulations and guidelines.
– Monitor and reinforce good hygiene practices among employees.
6. Regular Inspections:
– Conduct regular inspections of the food service area to identify any potential sources of contamination.
– Address any issues promptly to ensure a safe and clean environment.
Remember, following these steps consistently will help minimize the risk of bacterial contamination and ensure the safety of your food and customers.
What Are 4 Methods For Preventing Cross Contamination?
Cross contamination occurs when bacteria or other harmful microorganisms are transferred from one food item to another, leading to potential foodborne illnesses. To prevent cross contamination, there are several methods that can be implemented:
1. Use separate utensils, plates, and chopping boards: It is crucial to designate specific utensils, plates, and chopping boards for raw food and separate ones for cooked or ready-to-eat food. This minimizes the risk of bacteria from raw food coming into contact with cooked food, reducing the chances of cross contamination.
2. Thoroughly clean utensils, plates, and chopping boards: After each use, especially when switching between raw and cooked food, it is essential to wash utensils, plates, and chopping boards thoroughly. Use hot, soapy water and scrub them well to remove any bacteria or residue. Rinse them thoroughly before using them for the next task.
3. Avoid washing raw meat: Washing raw meat, such as chicken or beef, under running water can spread bacteria onto other surfaces, including kitchen sinks, countertops, and utensils. It is best to cook raw meat thoroughly to kill any bacteria present, rather than relying on washing to remove them.
4. Practice proper hand hygiene: Always remember to wash your hands after handling raw food and before touching ready-to-eat food. Use warm water and soap, and scrub your hands for at least 20 seconds, ensuring you clean all areas, including between your fingers and under your nails. Dry your hands with a clean towel or disposable paper towel.
By following these methods, you can significantly reduce the risk of cross contamination and promote food safety in your kitchen.
How Can Bacterial Contamination Be Prevented In A Lab?
To prevent bacterial contamination in a lab, it is crucial to follow strict protocols and maintain a clean environment. Here are some steps to take:
1. Automate the process with lab automation: Utilize automated systems, such as robotic workstations, to minimize human contact and reduce the risk of contamination.
2. Wear proper protective equipment: Always wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, lab coats, and masks, to prevent the transfer of bacteria from your body to the lab environment.
3. Sterilize equipment: Thoroughly clean and sterilize all lab equipment before and after each use. Autoclaving, using chemicals like bleach or alcohol, or other appropriate sterilization methods can be employed.
4. Check your water source: Ensure that the water used in the lab is free from contaminants. Regularly test and monitor the quality of water, and use water purification systems if needed.
5. Clean surfaces regularly: Regularly clean and disinfect benchtops, equipment, and other surfaces in the lab. Use appropriate disinfectants and follow recommended protocols for effective cleaning.
6. Reduce the number of touches: Minimize unnecessary contact with lab equipment and samples. Avoid touching surfaces or items that are not essential for the experiment or analysis.
7. Use an air filter and laminar flow hood: Install air filters in the lab to reduce airborne contaminants. Additionally, use laminar flow hoods in areas where sterile work is performed to create a controlled, clean environment.
8. Stay organized: Maintain a well-organized workspace to minimize the risk of cross-contamination. Keep samples, reagents, and equipment separate and properly labeled.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of bacterial contamination in the lab, ensuring accurate and reliable results in your experiments and analyses.
Conclusion
Bacterial contamination poses a significant risk to food safety and laboratory procedures. To prevent food poisoning, it is crucial to maintain cleanliness and hygiene in the kitchen. This includes regularly washing hands and work surfaces, separating raw and ready-to-eat foods, cooking food to the appropriate internal temperature, and keeping the refrigerator at the correct temperature. Cross-contamination should be avoided when serving food by not touching food contact surfaces, using racks or trays instead of stacking dishes, and not using bare hands or glassware to handle ready-to-eat foods or ice.
In laboratory settings, it is essential to take precautions to avoid contamination. This can be achieved by automating processes, wearing proper protective equipment, sterilizing equipment, checking the water source, regularly cleaning surfaces, reducing the number of touches, using air filters and laminar flow hoods, and maintaining organization.
By following these steps and implementing proper hygiene practices, the risk of bacterial contamination can be significantly reduced, ensuring the safety of food and laboratory experiments.
