A stye, also known as a hordeolum, is a common eye condition that can cause discomfort and irritation. It is a small, red, painful lump that forms on the edge of the eyelid. Styes are usually caused by a bacterial infection that affects the oil glands in the eyelids.
When a stye pops, it means that the pus inside the lump is released. This can happen when the surface over the stye breaks, or it may occur naturally as the body’s immune system fights off the infection. When the pus drains out, the swelling and pain associated with the stye typically subside quite quickly.
However, in some cases, the stye may not burst on its own. In these instances, the swelling may take longer to go down. The body’s immune system will continue to work to control the infection, and eventually, the stye may resolve without bursting.
If the stye does drain, you may notice some discharge or drainage from the affected area. This is normal and is a sign that the infection is being cleared from the body. It is important to keep the area clean and avoid touching or rubbing the eye to prevent further irritation or spread of the infection.
During the healing process, it is advisable to refrain from using eye makeup, including mascara, as it can introduce bacteria into the area and prolong the healing time. If possible, it is also recommended to avoid wearing contact lenses until the stye has completely healed.
It is worth noting that a stye may come and go within a few days, but it can take up to seven to ten days for the eye to fully heal. The redness and tenderness associated with the stye may gradually resolve, leaving behind a painless eyelid bump.
When a stye pops, the pus is released, leading to a reduction in swelling and discomfort. The healing process can vary, but with proper care and hygiene, the stye should resolve within a week or so. It is important to avoid using eye makeup and contact lenses during this time to aid in the healing process.
What Happens When A Stye Pops On Its Own?
When a stye pops on its own, it typically means that the surface of the stye breaks, allowing the pus to drain out. This can happen naturally as part of the body’s immune response to the infection. Here is a step-by-step explanation of what happens when a stye pops on its own:
1. The stye, which is a red, painful lump usually found on the eyelid, becomes filled with pus due to a bacterial infection.
2. Over time, the pressure from the pus buildup may cause the surface of the stye to rupture.
3. Once the stye pops, the pus is released, relieving the pressure within the lump.
4. The drainage may be accompanied by some discomfort or relief from pain.
5. The body’s immune system will then work to control the infection and promote healing.
6. After the pus is drained, the swelling and redness of the stye will start to subside.
7. The healing process may take some time, but without the presence of pus, the stye should gradually improve.
8. It is important to keep the area clean and avoid touching or rubbing the affected eye to prevent further infection or irritation.
When a stye pops on its own, the pressure is relieved as the pus drains out. This allows the body’s immune system to take over, leading to the resolution of the infection and the gradual reduction of swelling and discomfort.
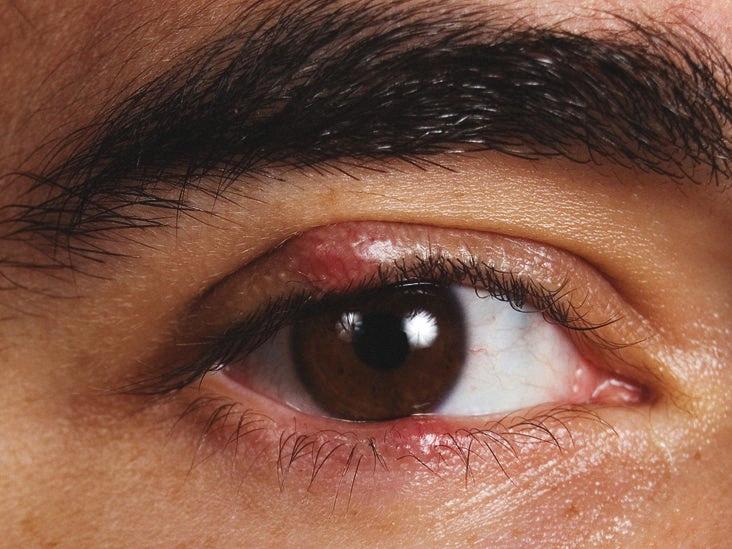
How Do You Know If A Stye Is Draining?
There are several signs that can indicate if a stye is draining. These include:
1. Swelling reduction: When a stye starts to drain, you may notice a decrease in the size of the swollen area on the eyelid. This is because the accumulated pus or fluid is being released.
2. Discharge: As the stye drains, you may observe a discharge or drainage coming from the affected area. This can be in the form of a yellowish or whitish substance.
3. Relief of symptoms: As the stye drains, you may experience relief from the pain and tenderness that was previously present. This can be a positive indication that the stye is resolving.
4. Redness reduction: The redness around the stye can also diminish as it starts to drain. This is because the inflammation is gradually subsiding.
5. Eyelid bump: After the stye has drained, you may be left with a painless bump on the eyelid. This is a common occurrence and should not cause any discomfort.
It is important to note that if you suspect a stye is draining, it is recommended to avoid squeezing or manipulating the area, as this can lead to further complications or spread of infection. If you have concerns or the symptoms worsen, it is advisable to consult an eye care professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
How Long After A Stye Pops Will It Heal?
After a stye pops, it typically takes about seven to 10 days for your eye to fully heal. During this healing period, it is important to take certain precautions to aid in the recovery process. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Avoid Eye Makeup: It is recommended to refrain from using any eye makeup, including mascara, as it can introduce bacteria into the healing area and potentially prolong the recovery time.
2. Minimize Contact Lens Use: If possible, try to avoid wearing contact lenses while your eye is healing. Contact lenses can further irritate the affected area and impede the healing process. Instead, opt for wearing glasses during this time.
3. Maintain Good Hygiene: To promote healing and prevent reinfection, it is crucial to maintain good hygiene practices. Wash your hands thoroughly before touching your eye area, and avoid rubbing or touching the stye directly.
4. Apply Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected eye can help alleviate discomfort and promote faster healing. Gently place a clean, warm compress on the stye for about 10-15 minutes several times a day.
5. Avoid Squeezing or Popping: While it may be tempting to pop or squeeze a stye, it is important to resist this urge. Popping a stye can lead to further infection and potential complications. Instead, allow the stye to rupture naturally, and follow the aforementioned hygiene practices for optimal healing.
Remember, each individual’s healing time may vary slightly, so it is crucial to monitor your symptoms and consult a healthcare professional if your condition worsens or does not improve after the expected healing period.
Conclusion
A stye is a common and often harmless infection that occurs on the eyelid. It is characterized by a red, tender lump that can cause discomfort and irritation. While most styes will go away on their own within a few days to a week, some may require medical intervention or take longer to heal.
The healing process of a stye involves the body’s immune system controlling the infection. If the stye bursts, releasing the pus, the lump will quickly disappear. However, if the swelling does not burst, it may take longer for the stye to go down. During this time, it is important to avoid using eye makeup and contact lenses to prevent further irritation and potential reinfection.
It is not uncommon for a stye to cause mild irritation of the eye on the affected side. This may result in drainage or discharge from the stye. However, with time, the redness and tenderness can typically resolve, leaving behind a painless eyelid bump.
While a stye can be bothersome, it is generally a temporary condition that will heal with time. It is important to practice good hygiene, avoid touching or rubbing the affected area, and seek medical attention if the stye persists or worsens. By following these guidelines, you can ensure a faster and smoother recovery from a stye.
