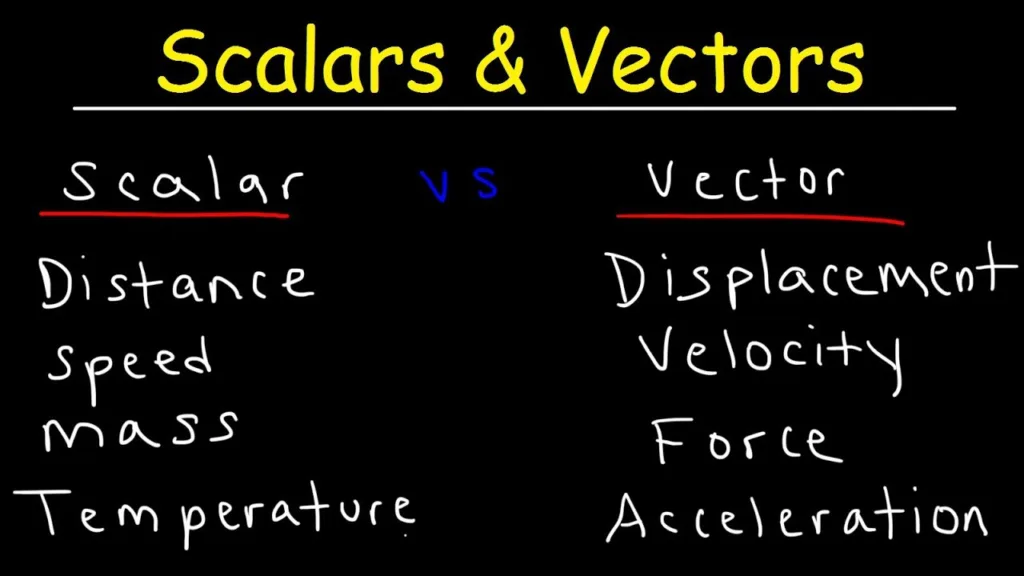
In the world of physics and mathematics, there are two types of quantities that are used to describe the properties of an object or a phenomenon. These are scalar and vector quantities. Scalar quantities refer to quantities that have only magnitude or size, while vector quantities refer to quantities that have both magnitude and direction.
To understand the difference between scalar and vector quantities, let’s take an example of distance and displacement. Distance is a scalar quantity that refers to the total amount of space that an object has covered during its motion. It does not take into account the direction of motion or the final position of the object. On the other hand, displacement is a vector quantity that refers to the change in position of an object from its initial position to its final position. It takes into account both the magnitude and direction of motion.
Another example of scalar and vector quantities is speed and velocity. Speed is a scalar quantity that refers to how fast an object is moving, while velocity is a vector quantity that refers to the speed and direction of motion.
Distance is a scalar quantity because it only has magnitude or size and does not have direction. When we measure the distance between two points, we only conider the total amount of space that needs to be covered to reach from one point to the other. We do not consider the direction of motion or the final position of the object.
However, it is important to note that distance can be used to calculate other vector quantities such as displacement and velocity. For example, if we know the distance and time taken to cover that distance, we can calculate the speed or velocity of the object. Similarly, if we know the distance and the direction of motion, we can calculate the displacement of the object.
Scalar and vector quantities are important concepts in physics and mathematics. Scalar quantities have only magnitude or size, while vector quantities have both magnitude and direction. Distance is a scalar quantity that refers to the total amount of space that an object has covered during its motion. It does not have direction. However, distance can be used to calculate other vector quantities such as displacement and velocity. Understanding the difference between scalar and vector quantities is essential for solving problems related to motion, force, and energy.
Is Distance a Vector Quantity?
When we talk about physical quantities in physics, we classify them into two categories, namely, scalars and vectors. Scalars are quantities that have only magnitude, while vectors have both magnitude and direction.
Distance is a scalar quantity, which means that it has only magnitude and no direction. It is a measure of the space between two points, and it can be calculated using varios methods such as using a ruler, tape measure, odometer, or GPS device.
On the other hand, displacement is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. It is the shortest distance between two points, and it can be calculated by subtracting the initial position from the final position of an object.
To differentiate between the two, we can say that distance is the total length covered by an object, while displacement is the change in position of an object in a given time.
Distance is not a vector quantity, but it is a scalar quantity that represents only magnitude and not direction.
The Difference Between Distance and Displacement
Distance and displacement are two important concepts in physics that are used to describe the motion of objects. While they may seem similar at first glance, there are some key differences between the two.
Distance is a scalar quantity, which means that it only has magnitude and not direction. This means that distance is simply a measure of how far an object has moved from one point to another, regardess of the path taken. For example, if you walk 10 meters to the right and then 10 meters back to the left, your total distance traveled would be 20 meters, even though your final position is the same as your starting position.
Displacement, on the other hand, is a vector quantity, which means that it has both magnitude and direction. Displacement is a measure of the overall change in position of an object, taking into account its starting and ending points. For example, if you walk 10 meters to the right and then 10 meters back to the left, your displacement would be zero, since your final position is the same as your starting position.
To understand why distance is scalar and displacement is vector, it helps to think about how each quantity is calculated. Distance is simply the total length of the path taken by an object, while displacement takes into account the starting and ending points of an object’s motion. Because displacement involves both magnitude and direction, it is a vector quantity. Distance, on the other hand, only involves magnitude and not direction, so it is a scalar quantity.
Distance and displacement are two important concepts in physics that are used to describe the motion of objects. While distance is a scalar quantity that only has magnitude, displacement is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction. Understanding the differences between these two concepts is essential for accurately describing an object’s motion.
Is Distance a Measurement of Scalar Velocity?
Distance is a scalar quantity that refers to the length of the path traveled by an object. It has only magnitude and no direction. For example, if a car travels a distance of 100 kilometers, it means that it has covered a length of 100 kilometers irrespective of the direction it moved.
On the other hand, velocity is a vector quantity that refers to the rate of change of position of an object with respect to time. It has both magnitude and direction. For example, if a car travels at a velocity of 60 kilometers per hour towads the north, it means that it is moving with a speed of 60 kilometers per hour in the northward direction.
It is important to note that while distance and displacement are scalar quantities, velocity and acceleration are vector quantities.
To summarize, distance is a scalar quantity that measures the length of the path traveled by an object, while velocity is a vector quantity that measures the rate of change of position of an object with respect to time and has both magnitude and direction.
Conclusion
It is important to understand the fundamental difference between vector and scalar quantities. Vectors have both magnitude and direction, while scalars only have magnitude. This distinction is crucial in physics and other fields that deal with measurements and quantities.
When dealing with motion, displacement is a vector quantity that takes into account both the distance traveled and the direction of the movement. On the other hand, distance is a scalar quantity that only considers the magnitude of the motion.
It is also important to note that velocity is a vector quantity, as it includes both speed and direction. Acceleration, however, is a scalar quantity that only considers the rate of change of velocity.
Understanding the difference between vector and scalar quantities is essential for accurate measurements and calculations in various fields of study. By beig able to distinguish between the two, we can more effectively analyze and predict the behavior of physical phenomena.
