Hematomas are a type of swelling that occurs when blood accumulates uner the skin or within tissues due to a ruptured blood vessel. They can be caused by blunt force trauma, surgery or medical conditions such as blood disorders. Hematomas can be large or small, depending on the severity of the injury, and can be painful or uncomfortable. In this article, we will explore how long it takes for a hematoma to reabsorb.
The reabsorption of a hematoma depends on various factors, including the size and location of the swelling, the severity of the injury, and the individual’s overall health. Generally, it takes around four to six weeks for a hematoma to disappear, but in some cases, it may take several months.
During the first 48 hours after the injury, it is important to apply ice or a cold compress to the affected area to reduce swelling and pain. After this initial period, warm compresses can be applied 2 or 3 times a day to help reabsorb the blood. The warmth helps to increase blood flow to the area, which can help speed up the healing process.
If the hematoma is painful, over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be taken to ease discomfort. However, it is important to follow the recommended dosage and not exceed the maximum dose.
If the hematoma is large or causing significant discomfort, medical attention may be necessary. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to drain the excess blood and relieve pressure on the surrounding tissues.
The reabsorption of a hematoma is a complex process that depends on various factors. While it typically takes around four to six weeks for a hematoma to disappear, each case is unique and may take longer. Applying ice or a cold compress during the first 48 hours, and warm compresses thereafter, can help speed up the healing process. If the hematoma is causing significant discomfort or is large, medical attention may be necessary.
Speeding Up Hematoma Resorption
A hematoma is a collection of blood outside of a blood vessel, usually caused by trauma or injury. The body will naturally reabsorb the blood over time, but there are some things you can do to speed up the process.
1. Apply ice: In the firt 48 hours after the injury, applying ice to the area can help reduce swelling and pain. Wrap the ice in a cloth and apply it to the area for 20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
2. Elevate the affected area: Elevating the area above the heart can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow to the area, which can speed up the reabsorption process.
3. Take over-the-counter pain relievers: If you are experiencing pain, taking over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help. Follow the recommended dosage on the label.
4. Use heated compresses: After the first 48 hours, you can use heated compresses to help reabsorb the blood. This can be a heating pad or a warm washcloth. Apply the compress to the area for 20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
5. Massage the area: Gently massaging the area can help improve blood flow and speed up the reabsorption process. Use a circular motion and be careful not to apply too much pressure.
It is important to note that if the hematoma is large or causing severe pain, you should seek medical attention. In some cases, the hematoma may need to be drained by a medical professional to ensure proper healing.
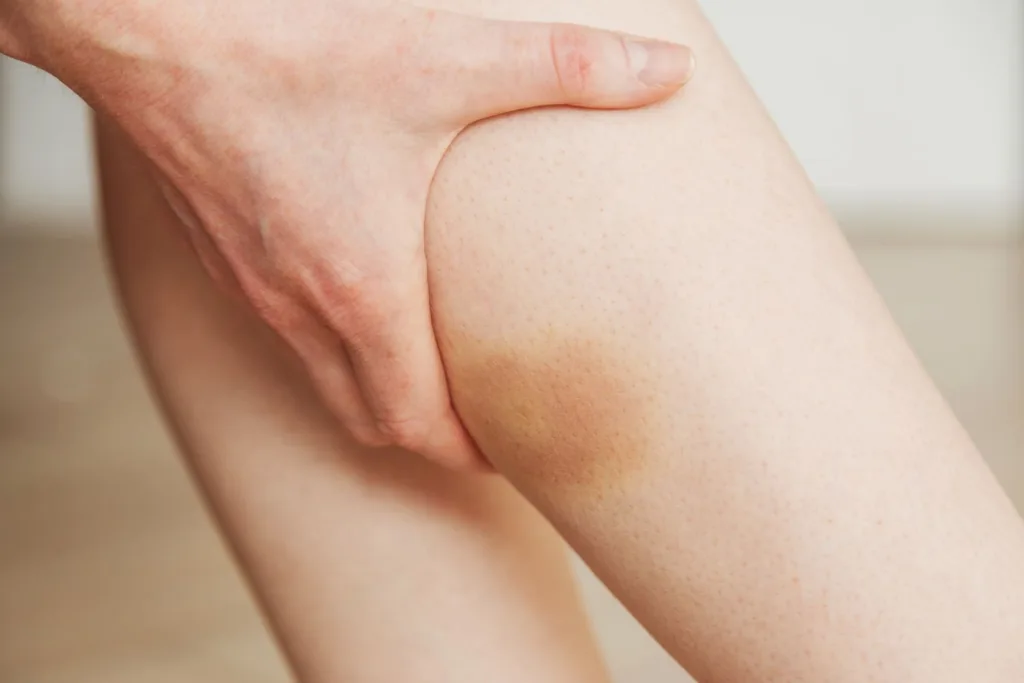
What Are the Consequences of an Undissolved Hematoma?
A hematoma is a collection of blood that forms outside of a blood vessel due to trauma or injury. Generally, hematomas disappear on teir own over time as the body reabsorbs the blood. However, if a hematoma doesn’t dissolve, it can lead to serious complications.
If a hematoma is not treated, it can cause pressure and compression on surrounding tissues and organs. The pressure can lead to tissue death, also known as necrosis, in the affected area. The necrosis can cause the skin to become discolored, and the tissue may become dry and flaky. In severe cases, the affected area may develop an infection, which can spread to other parts of the body.
If a hematoma is left untreated, the pressure within the hematoma can exceed the blood pressure in the surrounding capillaries, leading to a large area of necrosis of the overlying skin. This condition is known as skin necrosis, and it can be a life-threatening complication. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a hematoma that is not resolving on its own.
To avoid complications associated with an untreated hematoma, a medical professional may need to drain the blood from the affected area. This procedure involves making a small incision to allow the blood to drain out, relieving the pressure on the surrounding tissues. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove the hematoma completely.
If a hematoma doesn’t dissolve, it can lead to serious complications such as tissue necrosis, infection, and even a life-threatening condition. Seeking medical attention early, and following the recommended treatment plan, is essential to avoid these potential complications.
How Long Does It Take for a Hematoma Lump to Resolve?
A hematoma is a collection of blood outside of a blood vessel that forms a lump or swelling. Hematomas can occur due to trauma, injury, surgery, or an underlying medical condition. The size and severity of the hematoma can vary depending on the cause.
The healing time for a hematoma lump can vary depending on the size, location, and severity of the hematoma. In general, it takes around four to six weeks for a hematoma to heal and for the lump to go away. However, in some cases, it may take longer, up to several months, for the hematoma to fully disappear.
During the healing process, the body reabsorbs the blood from the hematoma and breaks down the clot. As the blood is reabsorbed, the swelling and pain associated with the hematoma will gradually decrease. In some cases, the body may also form scar tissue around the hematoma, whih can take longer to heal.
To help speed up the healing process, it is important to rest the affected area and avoid any activities that may cause further injury. Applying ice or a cold compress to the area can help reduce swelling and pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also be used to help manage any discomfort.
In some cases, medical treatment may be necessary to help the hematoma heal. This may include draining the hematoma using a needle or surgery to remove the blood clot. It is important to follow any instructions provided by a healthcare provider to ensure proper healing and prevent any complications.
Treating a Hematoma to Make it Go Away
A hematoma is a type of injury that occurs when blood vessels are damaged, causing blood to pool under the skin. Hematomas can be painful and unsightly, and they can take some time to heal. Fortunately, there are several things you can do to help a hematoma go away more quickly.
The first step in treating a hematoma is to rest the affected area. This means avoiding any activities that could further damage the injured blood vessels. In addition to rest, you can also use the following methods to help reduce swelling and promote healing:
– Ice: Applying a cold pack to the hematoma can help reduce swelling and pain. Wrap a bag of ice or a cold gel pack in a towel and apply it to the hematoma for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
– Compression: Wrapping the hematoma in a compression bandage can help reduce swelling and prevent further bleeding. Be sure to wrap the bandage snugly, but not too tight.
– Elevation: Elevating the affected area can help reduce swelling and promote blood flow. For example, if you have a hematoma on your leg, you can prop your leg up on a pillow or other soft surface.
Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can also help manage pain and swelling associated with a hematoma. However, be sure to follow the recommended dosages on the label and check with your doctor befre taking any new medications.
In some cases, your doctor may recommend draining the hematoma to help it heal more quickly. This involves using a needle or other instrument to remove the accumulated blood. This procedure should only be performed by a trained medical professional.
The key to helping a hematoma go away is to be patient and take care of yourself. Rest, ice, compression, and elevation can all help reduce swelling and promote healing, while pain relievers can help manage any associated discomfort. If you have concerns about a hematoma or if it does not seem to be improving over time, be sure to consult with your doctor.
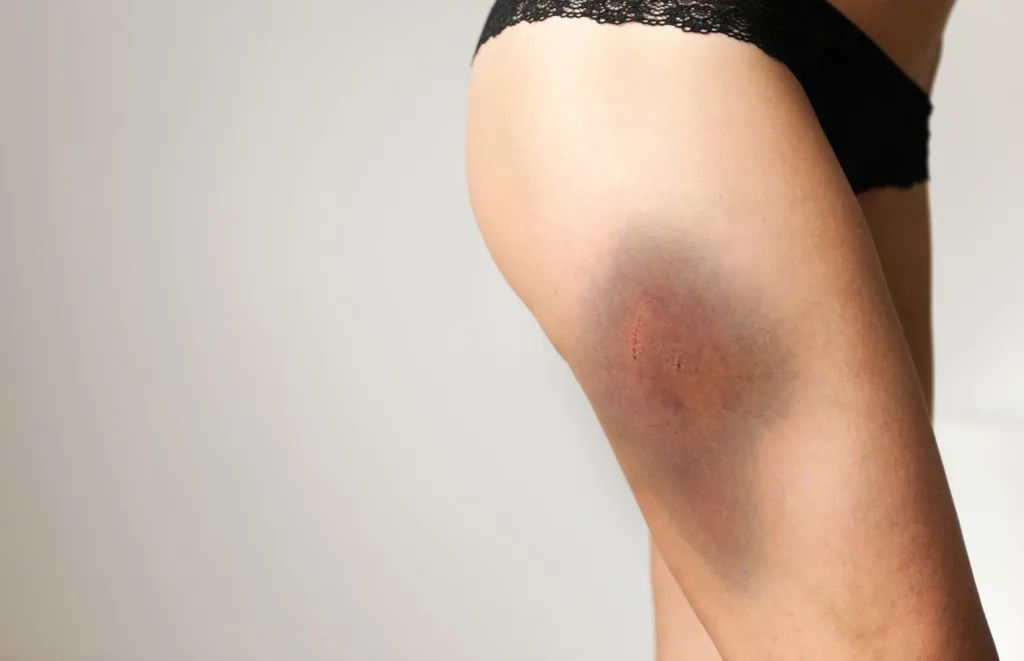
Conclusion
A hematoma is a common injury that occurs when there is bleeding uner the skin or in an organ. It can be caused by trauma, surgery, or other medical conditions. While most hematomas will heal on their own with rest and time, it is important to monitor the size and location of the injury to ensure that it does not cause further complications. Treatment options may include pain management with over-the-counter medications, the use of heated compresses, and in severe cases, surgical intervention. If you suspect that you have a hematoma or are experiencing any symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional. With proper care and treatment, most individuals will recover from a hematoma without any long-term effects.
