Static electricity is a natural phenomenon that we encounter every day. It occurs when there is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. Static electricity can be generated by varous sources, such as friction, pressure, or separation. While static electricity is generally harmless, it can potentially be lethal under certain circumstances.
Electric shock is the most common danger posed by static electricity. A shock occurs when a current of electricity passes through the body, causing anything from a mild discomfort to serious injury or death. If a current of 50 mA passes through the heart, it can cause cardiac arrest.
The heart is a muscle that beats to pump blood through the body. The rhythm of our heartbeat is controlled by electric impulses. Any disruption to these impulses can cause the heart to stop beating, leading to cardiac arrest. This is why even a small amount of current passing through the heart can be fatal.
Fires or explosions due to the ignition of flammable or explosive mixtures are also potential dangers of static electricity. When a spark jumps between two objects, it can ignite any nearby flammable materials, such as gasoline or propane. This is why it is important to avoid using electronic devices in areas where flammable materials are present.
To prevent static electricity, there are several measures that you can take. One of the most effective ways is to reduce the buildup of static charges by using conductive materials. For example, wearing clothes made of natural fibers or using anti-static mats can help to dissipate static charges.
Another way to prevent static electricity is to avoid rubbing or touching materials that are likely to generate static charges. For example, when refueling your car, avoid touching the nozzle or the gas tank. Instead, hold onto the metal part of the car to discharge any static electricity that may have built up in your body.
Static electricity can potentially be lethal under certain circumstances. The most common danger posed by static electricity is electric shock, which can cause cardiac arrest. To prevent static electricity, it is important to reduce the buildup of static charges and avoid touching or rubbing materials that are likely to generate static charges. By taking these precautions, we can ensure that we stay safe from the potential dangers of static electricity.
Can Excessive Static Electricity Harm Humans?
Static electricity is a common occurrence, especially during the winter months when the air is dry. While the sudden shock or pop caused by static discharge can be uncomfortable, it is generally not harmful. However, if you are exposed to too much static electricity, it could potentially cause harm to your body.
In rare cases, exposure to high levels of static electricity can lead to a condition called electrostatic discharge (ESD) which can cause minor to severe injuries. The risk of injury increases when working with sensitive electronic devices or in environments where flammable materials are present. In such cases, it is important to take necessary precautions, such as grounding yourself and using anti-static equipment to prevent ESD.
Excessive exposure to static electricity can also cause skin irritation, such as dryness, itching, and redness. This is becuse static electricity can disrupt the natural moisture balance of the skin, leading to dehydration and irritation. While this is not a serious condition, it can be uncomfortable and annoying.
To avoid the potential harm of excessive static electricity exposure, it is important to take preventative measures. This can include wearing natural fibers instead of synthetic materials, using a humidifier to add moisture to the air, and grounding yourself before touching sensitive electronic equipment.
While the occasional static shock is not harmful, excessive exposure to static electricity can cause harm to your body. It is important to take necessary precautions to prevent electrostatic discharge and skin irritation.
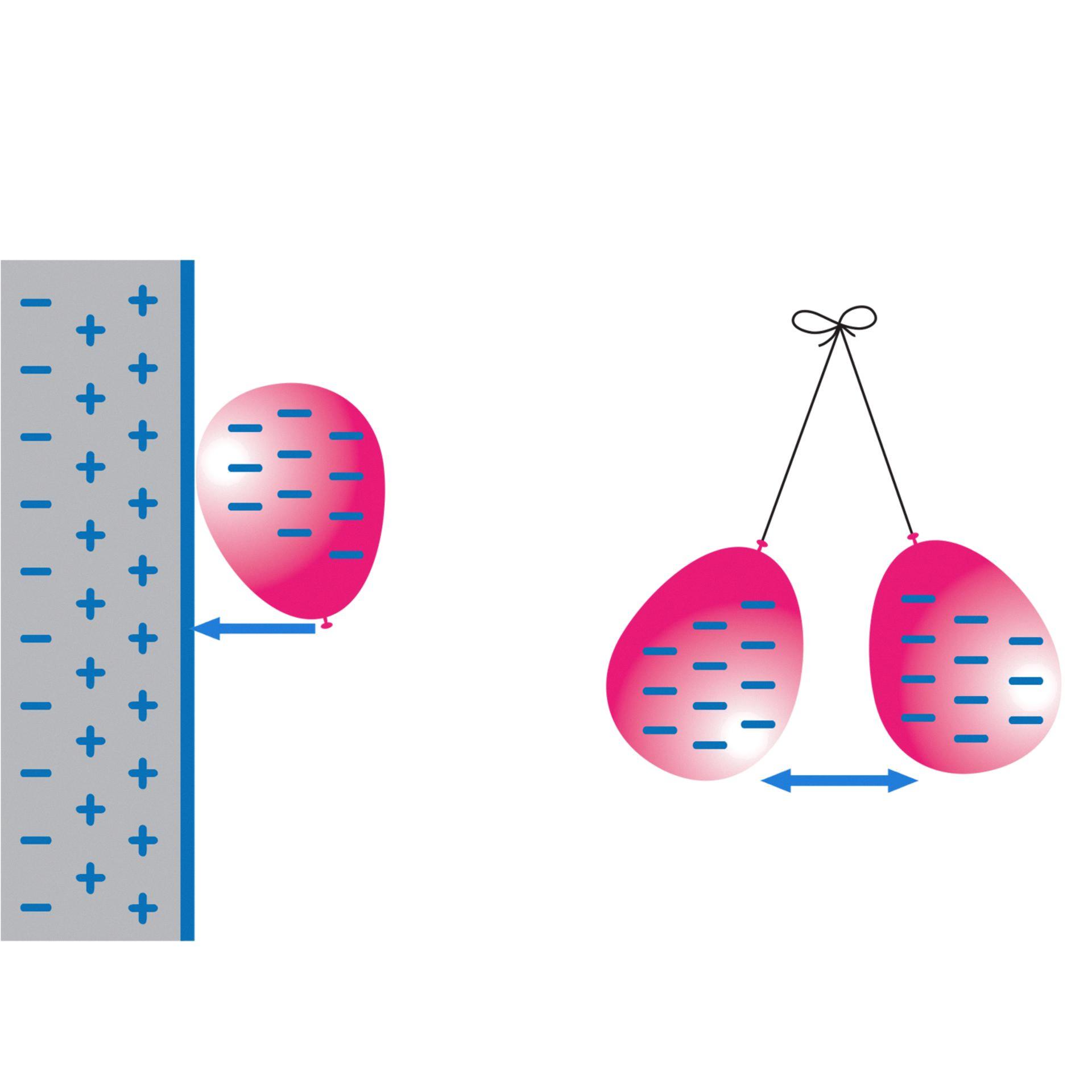
Source: dkfindout.com
Can Static Shock Cause Cardiac Arrest?
Static shocks are common occurrences in our daily lives, and they usually happen when we touch a metal object after walking on a carpet or when we exit a car. While static shocks can be annoying and someimes even painful, they are not usually harmful to our health.
There is no evidence to suggest that a static shock can stop your heart or cause cardiac arrest. A static shock is a sudden discharge of electricity, but it is not strong enough to affect the electrical impulses that control the rhythm of our heartbeat.
However, it is important to note that electric shocks of a certain intensity can be dangerous, and they can cause harm to our bodies. Electrical shocks that are strong enough to affect our heart can cause cardiac arrest, which is a life-threatening condition.
If you are exposed to an electrical shock, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately, even if you feel fine. Electrical shocks can cause internal injuries that may not be immediately apparent, and they can also cause long-term health problems.
While static shocks are not harmful to our health, it is essential to be aware of the dangers of electrical shocks and to take precautions to avoid them. It is also important to seek medical attention if you are exposed to an electrical shock, as it can be a serious medical emergency.
To summarize, here are some key points to remember:
– Static shocks are not harmful to our health
– Electrical shocks of a certain intensity can be dangerous and cause cardiac arrest
– Seek medical attention immediately if you are exposed to an electrical shock
– Take precautions to avoid electrical shocks.
The Dangers of Static Electricity
Static electricity may seem harmless, but it can pose serious dangers to people and property. Here are two dangers of static electricity that you should be aware of:
1. Electric shock: Static electricity can cause an electric shock, which occurs when the body becomes part of an electrical circuit. The severity of the shock depends on the voltage, current, and duration of the shock. Even a small shock can be uncomfortable, while a strong shock can cause burns, muscle contractions, and even death. Electric shocks can occur when touching a charged object or when moving from one surface to another.
2. Fire or explosion: Static electricity can also cause fires or explosions if it ignites flammable or explosive substances. When a static charge builds up on a surface, it can create a spark that can ignite gases, vapors, dust, or other combustible materials. This can be particularly dangerous in industrial settings whee there are many flammable materials present. Static electricity can also cause fires or explosions when refueling vehicles or handling chemicals.
To avoid these dangers, it’s important to take precautions when working with static electricity. This can include grounding equipment, using antistatic materials, and avoiding working in environments with flammable or explosive materials. By being aware of the dangers of static electricity, you can help ensure your safety and the safety of those around you.
Can Static Electricity Affect Heart Health?
Static electricity is the build-up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. It can be generated by rubbing two objects together or by the separation of electric charges. While static electricity is typically harmless, there have been reports of people experiencing heart-related symptoms after being exposed to static shocks.
The electric shock from static electricity is typically very low in voltage and amperage. In fact, most static shocks are not strong enough to cuse any harm to the human body. However, in certain rare cases, a static shock can cause a person to experience heart palpitations or arrhythmias.
This happens because the electric shock can disrupt the normal electrical signals that control the heart’s rhythm. In some cases, this disruption can cause the heart to beat irregularly or even stop beating altogether. However, it’s important to note that these cases are extremely rare and usually only occur in people who have pre-existing heart conditions.
To avoid the potential risk of heart-related symptoms from static electricity, it’s important to take certain precautions. For example, avoid rubbing your feet on the carpet or wearing clothes made of synthetic materials, which can generate static electricity. You can also use an anti-static spray or dryer sheets to reduce static buildup on your clothes and in your home.
While static electricity is typically harmless, it can in rare cases cause heart-related symptoms. By taking certain precautions, such as avoiding static-generating materials and using anti-static products, you can reduce your risk of experiencing these symptoms.
The Effects of Static Electricity on the Brain
Static electricity is a type of electrical charge that remains in a fixed position on an object. It is generated by the buildup of electric charge on the surface of an object, typically caused by friction or contact with another charged object. Static electricity is commonly experienced as a mild shock when touching a metal object after walking on a carpet, for example.
The question of whether static electricity can affect the brain is a difficult one to answer. There is currently no clear evidence to suggest that static electricity has a direct impact on the brain. However, there is some research to suggest that static magnetic fields can exert an influence on the gating processes of membrane channels in the brain.
Membrane channels are essential for the functioning of neurons in the brain. They are responsible for regulating the flow of ions into and out of the cell, which is critical for the generation and transmission of electrical signals. Static magnetic fields have been shown to induce effects on these membrane channels, which could potentially affect the functioning of neurons in the brain.
It is important to note that the effects of static magnetic fields on the brain are still beig studied, and there is no conclusive evidence to suggest that they have a significant impact on cognitive function or behavior. However, some studies have suggested that exposure to moderate static magnetic fields may have some beneficial effects on the brain, such as improving memory and attention.
While there is no clear evidence to suggest that static electricity has a direct impact on the brain, static magnetic fields may potentially affect the functioning of neurons in the brain. Further research is needed to better understand the potential effects of these fields on cognitive function and behavior.
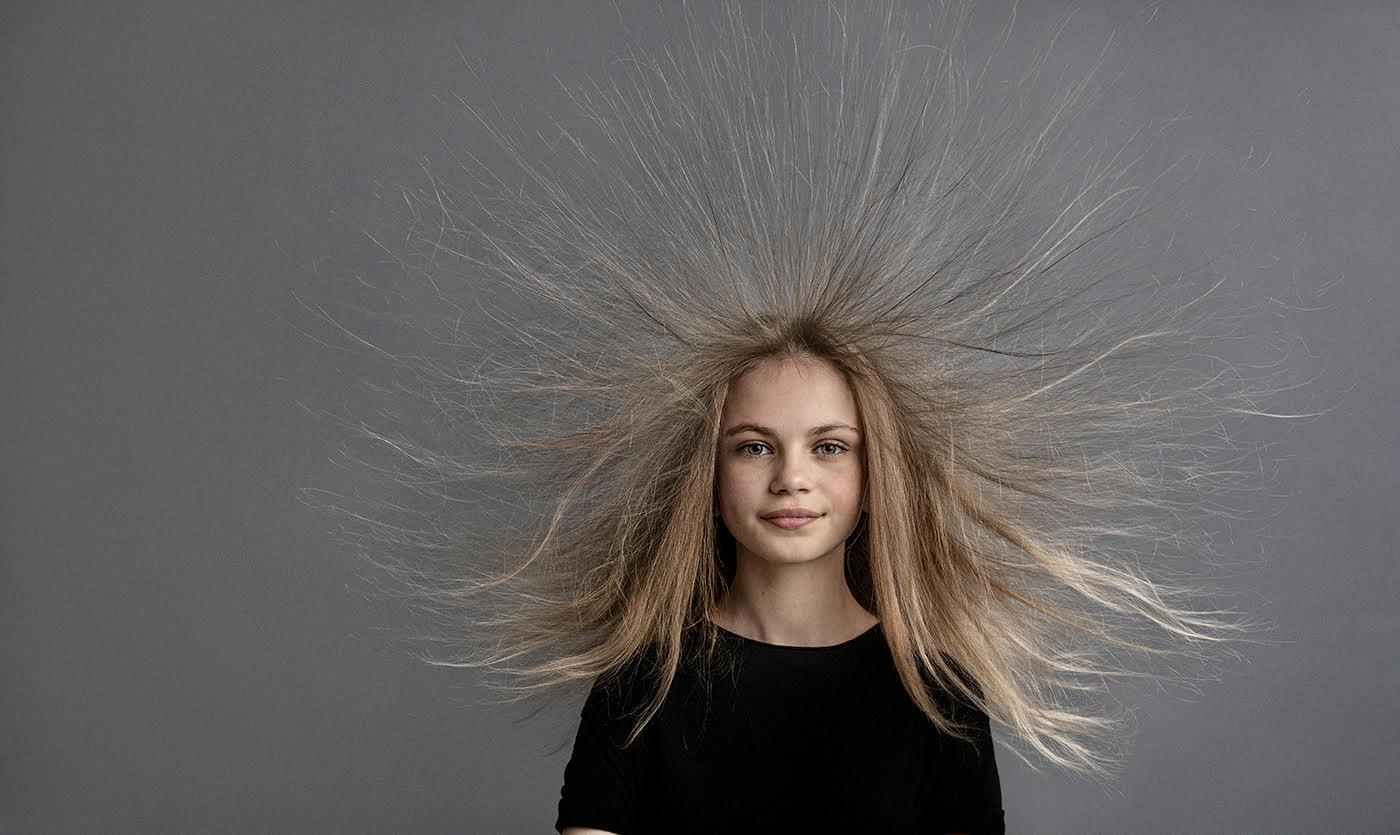

Source: brickellmattress.com
Can Static Electricity Damage Skin?
Static electricity can indeed break the skin. Even the tiniest spark can measure around 500 volts, and a longer spark can measure several thousand volts. When this spark cmes into contact with the skin, it can burn a tiny hole. This is because the energy from the spark is concentrated in a small area, causing a high level of heat to be generated.
In addition to causing burns, static electricity can also cause discomfort and pain. When a person experiences a static shock, they may feel a sharp, stinging sensation or a tingling feeling. This is because the electrical charge disrupts the normal functioning of the nerves in the skin.
It’s worth noting that the severity of the injury caused by static electricity depends on a number of factors, such as the duration and intensity of the spark, as well as the sensitivity of the person’s skin. In most cases, a small static shock is not harmful and will not cause any lasting damage. However, in rare cases, a severe electric shock can cause serious injuries, such as burns, nerve damage, and even cardiac arrest.
To protect against static electricity, it’s important to avoid situations where static electricity is likely to build up, such as wearing synthetic clothing or walking on carpets. You can also use anti-static products, such as sprays or dryer sheets, to reduce the amount of static electricity in your environment.
The Mystery of Electric Shocks: Why Is Everything I Touch Zapping Me?
If you have ever experienced a shock when touching smething metal, you may be wondering why this happens. The answer lies in static electricity, which is generated whenever two materials are in contact with each other.
All materials are made up of electrically charged atoms, which means that they have either a positive or negative charge. When two materials come into contact, their charges can interact with each other, causing electrons to transfer from one material to the other.
This transfer of electrons can result in a buildup of static electricity, which can be discharged when you touch something metal. The shock you feel is caused by the sudden flow of electrons from your body to the metal object.
There are several factors that can influence the buildup of static electricity, including the materials involved, temperature, and humidity. For example, dry air can increase the buildup of static electricity, while humid conditions can help to dissipate it.
To avoid experiencing shocks, there are several steps you can take. These include:
– Moisturizing your skin, as dry skin can increase the buildup of static electricity
– Wearing natural fibers, such as cotton, which are less likely to generate static electricity than synthetic materials
– Using anti-static products, such as sprays or wipes, to help dissipate static electricity
– Avoiding rubbing or shuffling your feet on carpet, as this can generate static electricity
By taking these steps, you can reduce the likelihood of experiencing shocks when touching metal objects.
The Amount of Static Electricity a Person Can Hold
When it comes to static electricity, the amount a person can hold varies. The maximal potential commonly achieved on the human body ranges between 1 and 10 kV (kilovolts). However, in optimal conditions, it is possible to reach as high as 20-25 kV.
It is important to note that the amount of static electricity a person can hold depends on several factors. These include the humidity in the air, the type of clothing worn, and the type of shoes worn. For example, when the air is dry, it is easier to build up a static charge. Wearing clothing made of synthetic materials and shoes with rubber soles can also increase the amount of static electricity a person can hold.
It is also worth mentioning that the human body is capable of discharging static electricity on its own. This can happen through actions such as touching a grounded object or another person. However, in some cases, static electricity can build up to dangerous levels, whih can lead to electric shocks or even explosions in certain environments.
To prevent the buildup of static electricity, it is recommended to wear clothing made of natural fibers, avoid wearing shoes with rubber soles, and ensure that the environment has adequate humidity levels. Additionally, grounding oneself by touching a grounded object can help to discharge any static charge that has built up.
The amount of static electricity a person can hold varies between 1 and 10 kV, with a potential to reach as high as 20-25 kV in optimal conditions. Factors such as humidity, clothing type, and footwear can affect the amount of static electricity a person can hold. It is important to take precautions to prevent dangerous buildup of static electricity.
The Consequences of Unintentionally Shocking Others
Static electricity is responsible for the shock you experience when you touch someone or an object. This is caused by the buildup of electrical charge on the surface of insulating materials, which do not conduct electricity well. When you come into contact with an object or person that has a positive charge, such as from touching a doorknob or walking on a carpet, the excess electrons in your body are released, resulting in a shock.
The buildup of static electricity is most commonly caused by friction between two materials, such as rubbing your feet on a carpet or wearing synthetic clothing. This friction causes electrons to be transferred from one material to another, resulting in a buildup of charge.
To prevent static shocks, you can take seveal measures. One way is to wear clothing made of natural materials, such as cotton or wool, which do not generate as much static electricity as synthetic materials. Additionally, you can use a humidifier to add moisture to the air, which can help to reduce the buildup of static electricity.
Static electricity is the main cause of the shock you experience when you touch someone or an object. By understanding the causes of static electricity and taking preventative measures, you can reduce the frequency and intensity of static shocks.
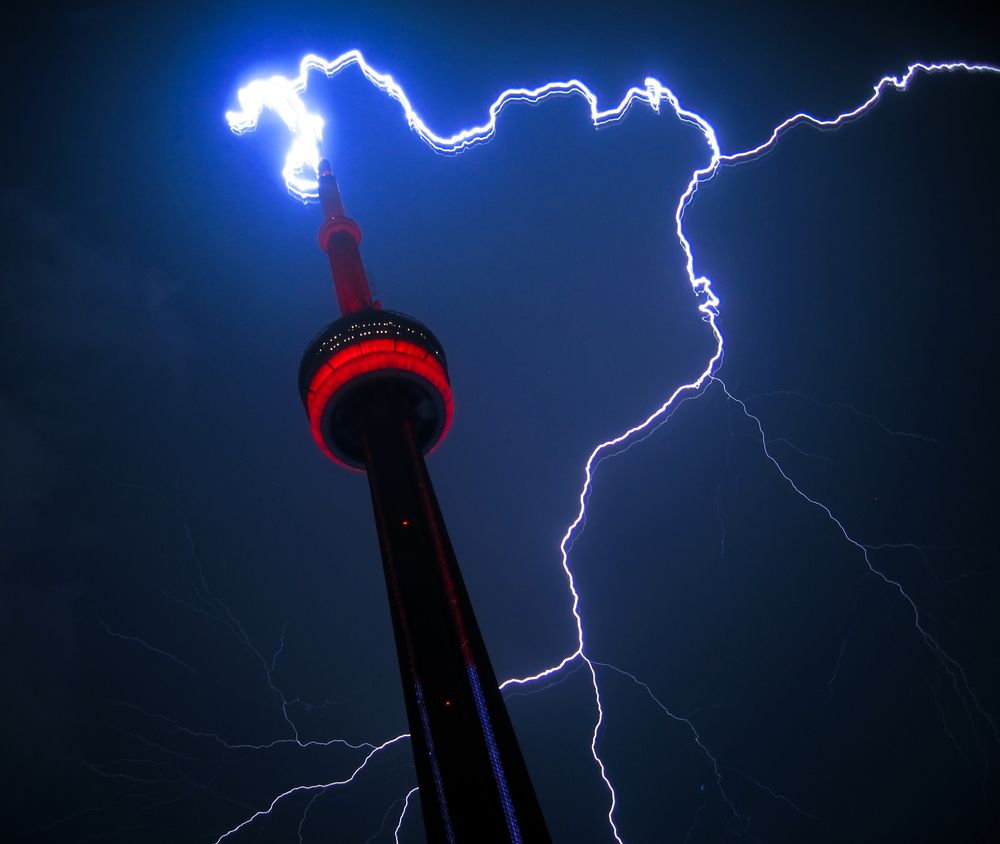

Effects of Excessive Static Electricity
Static electricity is a phenomenon where an object accumulates an excess amount of electric charge. This buildup of charge can be caused by a variety of factors such as friction, pressure, or separation of different materials. If an object has too much static electricity, it can lead to various hazards and dangers.
One of the most common dangers of too much static electricity is the risk of electrical shock. When an object becomes charged, it can release a high voltage shock when touched or approached by another conductive object. This shock can cause serious injury or even death, depending on the strength of the charge and the individual’s physical condition.
Another danger of static electricity is that it can damage electronic devices. When an object with a high amount of static electricity comes into contact with an electronic device, it can discharge the built-up charge and cause damage to the device’s internal components. This can lead to malfunctions, data loss, or even complete failure of the device.
Additionally, static electricity can pose a fire hazard in certain environments. If a spark is generated from an object with a high charge, it can ignite flammable materials such as gas, oil, or chemicals. This can lead to explosions or fires that can cause significant damage and harm to individuals in the vicinity.
To prevent thse hazards, it is important to take proper precautions when dealing with objects that may have a high amount of static electricity. This may include wearing protective gear, using grounding straps or conductive mats, or using anti-static agents to reduce the buildup of charge. By taking these measures, individuals can avoid the dangers associated with static electricity and work safely in their environment.
Can Static Electricity Ignite a Fire in a Bed?
Static electricity is a common phenomenon that occurs when two objects come into contact and then separate, resulting in an imbalance of electrons. This imbalance can create a spark, which can be seen and felt as a small shock.
While it is true that static electricity can be a nuisance, causing clothes to cling or hair to stand on end, it is highly unlikely that it could start a fire in your bed. This is because there are no flammable materials btween the static and the fabric, such as gasoline, chemicals, or other highly flammable substances.
Furthermore, most bedding materials are not highly flammable, and are often treated with flame-retardant chemicals to reduce the risk of fire. Even if a spark were to occur, it would need to be strong enough and sustained enough to ignite the bedding material, which is highly unlikely.
Some other factors that can increase the risk of fire in the bedroom include smoking in bed, using candles or other open flames, and leaving electrical devices plugged in and turned on for extended periods of time. It is important to be mindful of these risks and take appropriate precautions to prevent fires from starting.
While static electricity can be a nuisance, it is highly unlikely that it could start a fire in your bed. However, it is important to be aware of other factors that can increase the risk of fires in the bedroom and take appropriate precautions to prevent them from occurring.
The Reality of Static Electricity Shocks
Static electricity is a real phenomenon that many people experience on a daily basis. It occurs when two objects come into contact and exchange electrons, which can result in an imbalance of electrical charge. This charge can build up on the surface of an object, creating a static charge.
When a person comes into contact with a statically charged object, they may experience a small shock, known as static shock. This can feel like a mild jolt or a small spark, and is typically harmless. However, it can be surprising or uncomfortable for some people.
It is important to note that static electricity is different from electrical shock, which occurs when a person comes into contact with an electrical current. Electrical shock can be dangerous and even life-threatening, depending on the severity of the shock and the amount of current involved.
To avoid static shock, it is recommended to discharge any static charge by touching a grounded object before touching sensitive electronics or other objects that may be affected by static electricity. Additionally, wearing clothing made of natural fibers and usng humidifiers can help reduce the buildup of static electricity.
While static electricity can result in a small shock or spark, it is not the same as electrical shock and is typically harmless.
Can Static Electricity Cause Illness?
Static electricity is a common occurrence in our daily lives. It is created when two surfaces come into contact and then separate, causing a buildup of electrical charge. This can happen when we walk across a carpet, rub a balloon on our hair, or touch a metal object.
There have been reports of static electricity causing physical discomfort, such as headaches, dry mucosa, itchy skin, and other similar ailments. However, the scientific evidence linking static electricity to these symptoms is limited, and there is no clear mechanism by which static electricity cold cause them.
It is important to note that static electricity is not harmful in itself. It is the discharge of static electricity that can be dangerous, such as when it causes a spark that ignites flammable materials. However, the amount of static electricity generated in our daily lives is generally too low to cause any harm.
That being said, there are some situations where static electricity can be a nuisance, such as in industrial settings where it can interfere with sensitive electronic equipment or cause sparks that could ignite flammable materials. In these cases, measures can be taken to reduce static electricity, such as using anti-static materials, grounding equipment, or increasing humidity levels.
While static electricity may cause some physical discomfort, there is no clear evidence that it can make you sick. It is important to take precautions in situations where static electricity can be dangerous, but in most cases, it is simply a harmless annoyance.
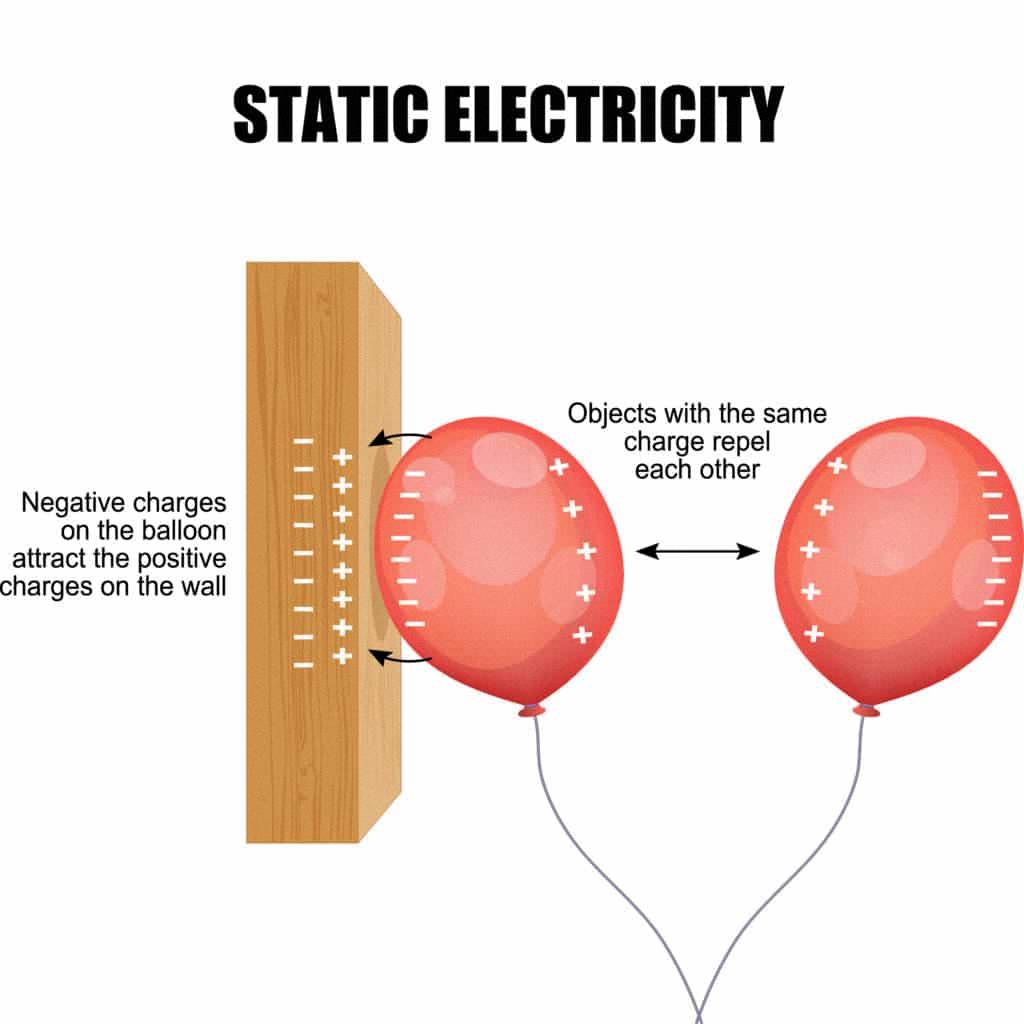
Source: science-sparks.com
The Effects of Static Electricity on Anxiety
Static electricity is a common phenomenon that occurs when two objects with different electrical charges come into contact or are separated. This type of electricity can sometimes build up and discharge through a person, causing a shock or a spark. While the shock or spark itself may not cause anxiety, electrical injuries can cause imediate neuropsychological disorders sequelae such as changes in orientation, anxiety, temporary emotional instability, and memory disorders, resembling traumatic brain injury.
Anxiety is a psychological condition characterized by excessive worry, fear, and nervousness. While there is no direct link between static electricity and anxiety, electrical injuries can cause anxiety as a result of the physical and psychological trauma caused by the shock or spark. In some cases, individuals may develop a fear of experiencing electrical shocks or sparks, which can lead to anxiety and avoidance behaviors.
It is important to note that anxiety caused by electrical injuries is typically temporary and can be treated with the help of a mental health professional. If you or someone you know is experiencing anxiety as a result of an electrical injury, it is important to seek medical attention and discuss treatment options with a qualified healthcare provider.
While static electricity itself may not cause anxiety, electrical injuries can result in immediate neuropsychological disorders sequelae that can include anxiety. It is important to understand the potential risks of electrical injuries and seek medical attention if necessary to prevent or treat any associated psychological conditions.
Conclusion
Static electricity is a natural phenomenon caused by the buildup of electric charge on the surface of materials. While it can be a nuisance and even uncomfortable, the pop and shock associated with static electricity are generally not dangerous. However, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with static electricity, such as electric shock and fires or explosions. It is crucial to take precautions to minimize tese risks, such as grounding yourself or using antistatic materials in certain situations. By understanding the nature of static electricity and taking necessary precautions, we can prevent harm and safely enjoy the benefits of modern technology.
