Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is a highly corrosive and strong acid that is widely used in various industrial processes such as the production of fertilizers, dyes, detergents, and explosives. It is also used in laboratories for various purposes. In this blog post, we will discuss the properties of H2SO4 that make it a strong acid.
Firstly, H2SO4 is a strong acid because it completely ionizes or dissociates in water. This means that when H2SO4 is dissolved in water, it breaks down into hydrogen ions (H+) and sulfate ions (SO42-). This dissociation is essential in maintaining the high acidity of the solution.
Secondly, even in dilute solutions, the hydrogen sulfate ions also dissociate to form more hydronium ions (H3O+) and sulfate ions (SO42-). This further reinforces the strong acidic properties of H2SO4.
Furthermore, H2SO4 is a highly reactive acid that can react with a wide range of substances, including metals, organic compounds, and inorganic compounds. This reactivity is due to the high concentration of hydrogen ions in H2SO4, which makes it a powerful oxidizing agent.
It is important to note that while H2SO4 is a strong acid, it also poses significant health and safety risks. It can case severe burns and is highly toxic if ingested or inhaled. Therefore, it must be handled with extreme caution and proper safety measures must be taken when working with H2SO4.
H2SO4 is a strong acid due to its complete ionization in water, high reactivity, and ability to dissociate even in dilute solutions. However, its strong acidic properties also make it a hazardous substance that must be handled with care.
The Strength of H2SO4 as an Acid
Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is considered a strong acid due to several reasons. Firstly, when it is dissolved in water, it completely ionizes or dissociates to form H+ and SO42- ions. This means that all molecules of H2SO4 break down into their constituent ions, resulting in a high concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
In addition, even in dilute solutions, the hydrogen sulfate ions further dissociate to form more hydronium ion H3O+ and sulfate ions SO42-. This results in an even higher concentration of hydrogen ions, making the solution highly acidic.
Another reason why H2SO4 is considered a strong acid is its low pKa value. The pKa value is a measure of the strength of an acid, with lower values indicating stronger acids. The pKa value of H2SO4 is -3, which is very low compared to oher acids.
Furthermore, H2SO4 is a highly reactive compound and can easily donate its hydrogen ions to other molecules, making it a strong acid. It is widely used in various industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers, detergents, and dyes.
H2SO4 is considered a strong acid due to its complete ionization, high concentration of hydrogen ions, low pKa value, and reactivity. Its strong acidic properties make it a valuable chemical compound in many industries.
Is Dilute Hydrogen Sulfate a Strong Acid?
Dilute H2SO4, also known as sulfuric acid, is considered a strong acid due to its ability to completely ionize in water. When sulfuric acid is added to water, it dissociates into hydrogen ions and sulfate ions. The hydrogen ions are responsible for the high acidity of the solution, giving it a low pH value.
The strength of an acid is determined by its ability to donate hydrogen ions in water. Strong acids like sulfuric acid completely dissociate in water, whie weak acids only partially dissociate. This means that strong acids have a higher concentration of hydrogen ions in solution, making them more acidic.
Sulfuric acid has a wide range of applications in various industries, including fertilizers, batteries, and detergents. It is also used in laboratory settings as a strong acid for various chemical reactions.
It is important to handle dilute sulfuric acid with care as it can be corrosive and cause skin and eye irritation. Proper safety precautions such as wearing gloves and goggles should be taken when working with sulfuric acid.
Dilute H2SO4 is considered a strong acid due to its complete ionization in water, resulting in a high concentration of hydrogen ions and low pH value.
Is H2PO4 a Strong Acid?
H2PO4‾, also known as dihydrogen phosphate, is a weakly acidic anion. Its acidity is due to the presence of two hydrogen ions that can dissociate in water, releasing H+ ions. This process is also known as ionization.
The strength of an acid is determined by its tendency to donate protons (H+ ions) in water. A strong acid completely ionizes in water, meaning that all of its hydrogen ions are released. In contrast, a weak acid only partially ionizes, meaning that only a fraction of its hydrogen ions are released.
H2PO4‾ is considered a weak acid because it does not completely ionize in water. Instead, it undergoes partial ionization, meaning that only some of its hydrogen ions are released. The extent of ionization can be quantified by the acid dissociation constant, Ka.
The Ka value for H2PO4‾ is 6.2 x 10^-8, which is relatively small compared to strong acids such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This means that only a small fraction of H2PO4‾ molecules will dissociate in water, resulting in a relatively low concentration of H+ ions.
Although H2PO4‾ is a weak acid, it is still acidic enough to be used in some baking powders. Baking powders typically cotain a mixture of baking soda (NaHCO3) and a weak acid such as H2PO4‾. When the baking powder is mixed with water or another liquid, the acid and the baking soda react to release carbon dioxide gas, which causes the dough or batter to rise.
H2PO4‾ is a weakly acidic anion with a small Ka value. It does not completely ionize in water, but it is still acidic enough to be used in some baking powders.
Weakness of H2SO4 as an Acid
In fact, H2SO4 ionizes completely in water and is considered a strong acid.
To provide a more detailed answer, it is important to understand the concept of acid strength. The strength of an acid is determined by its ability to donate a proton (H+) to a water molecule. In other words, a strong acid readily gives away its proton, while a weak acid holds onto its proton more tightly.
H2SO4, also known as sulfuric acid, is a diprotic acid, meaning it has two hydrogen ions (protons) to donate. When it is added to water, it completely ionizes into H+ and SO4 2- ions. This means that all of the H+ ions are released into the solution, making it a strong acid.
It is important to note that the strength of an acid is not the same as its concentration. While sulfuric acid may be highly concentrated, it is still considered a strong acid.
H2SO4 is considered a strong acid bcause it ionizes completely in water, releasing all of its hydrogen ions.
Strength of H2SO4 as a Base
Sulfuric acid, also known as H2SO4, is a common industrial chemical and a strong acid. As a strong acid, it completely dissociates in water, meaning that it readily releases hydrogen ions when it is dissolved in water. This is because the sulfuric acid molecule has a high affinity for water molecules, and readily reacts with them to form hydrated hydrogen ions (H+) and sulfate ions (SO4 2-).
The strength of an acid is typically determined by its ability to donate hydrogen ions (protons) in solution. In the case of sulfuric acid, it is considered a strong acid because it fully dissociates in water and has a high acidic strength. This means that it has a low pH value, typically around 1, and is highly reactive with other substances.
It is important to note that sulfuric acid is not a base, but rather an acid. A base is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions in solution, whie an acid is a substance that can donate hydrogen ions. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid and not a base, as it readily donates hydrogen ions in solution and does not accept them.
Sulfuric acid is a strong acid and not a weak base, as it readily dissociates in water and donates hydrogen ions. Its high acidity and reactivity make it a common industrial chemical that is used in a variety of applications.
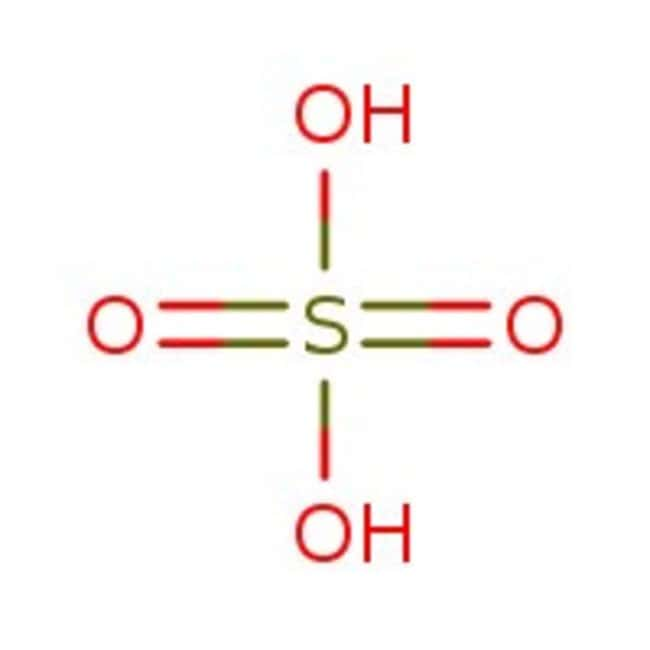
Which Acid is Stronger: H2SO4 or HCl?
When it comes to comparing the strength of two acids, it is important to look at their acid dissociation constants or pKa values. The pKa value of an acid is a measure of its strength – the lower the pKa value, the stronger the acid.
In this case, HCl (hydrochloric acid) is stronger than H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) beause its pKa value is much lower. The pKa value of HCl is around -6.3, while the pKa value of H2SO4 is around -3.0.
To put this into perspective, a difference of just one unit in pKa value represents a tenfold difference in acid strength. In other words, HCl is roughly 100 times stronger than H2SO4.
The reason for this difference in strength lies in the chemical structure of the two acids. HCl is a simple binary acid composed of hydrogen and chlorine, while H2SO4 is a polyprotic acid composed of hydrogen, sulfur, and oxygen. This means that H2SO4 can donate more than one hydrogen ion, making it a weaker acid overall.
HCl is a stronger acid than H2SO4 due to its lower pKa value, which is a result of its simpler chemical structure.
Which Acid is Stronger: Hso4 or H2SO4?
The strength of an acid is determined by its ability to donate hydrogen ions (H+). When an acid is dissolved in water, it dissociates into ions, and the more ions it produces, the stronger the acid is. In the case of HSO4- and H2SO4, the ltter is the stronger acid.
HSO4- is a conjugate base of sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which means it can accept a proton to become H2SO4. However, HSO4- only partially dissociates in water, producing a fewer number of H+ ions.
On the other hand, H2SO4 dissociates completely and furnishes a larger number of H+ ions in the aqueous solution. Therefore, it is considered a stronger acid than HSO4-.
It is essential to note that the strength of an acid can also be affected by its concentration, solvent, and temperature. However, in general, H2SO4 is a stronger acid than HSO4-.
To summarize, H2SO4 is a stronger acid than HSO4- due to its ability to dissociate completely and furnish a larger number of H+ ions in the aqueous solution.
Comparing the Acidity of H2SO4 and HNO3
Sulphuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid (HNO3) are both strong acids, meaning they completely dissociate in water to form hydrogen ions (H+) and their respective anions. However, when it cmes to comparing the strength of these two acids, sulphuric acid is considered to be stronger than nitric acid.
There are a few reasons for this. Firstly, sulphuric acid has two ionizable hydrogen atoms (able to donate protons) per molecule, while nitric acid has only one. This means that sulphuric acid can potentially release more hydrogen ions into a solution than nitric acid, making it a stronger acid.
Additionally, sulphuric acid has a higher tendency to attract electrons towards itself (electronegativity) than nitric acid. This results in a greater polarization of the H-O bond in sulphuric acid, making it easier to break and release hydrogen ions.
Furthermore, sulphuric acid is also a dehydrating agent, meaning it can remove water molecules from other substances. This property is due to the strong affinity of sulphuric acid for water molecules, and can further enhance its acidity.
While both sulphuric acid and nitric acid are strong acids, sulphuric acid is considered to be stronger due to its higher number of ionizable hydrogen atoms, greater electronegativity, and dehydrating properties.
Is HSO4 a Strong Acid?
HSO4, also knwn as bisulfate or hydrogen sulfate, is a weak acid. It can donate one proton to water, forming the bisulfate ion (HSO4-) and a hydronium ion (H3O+). However, the bisulfate ion can also donate another proton to water, forming the sulfate ion (SO42-) and another hydronium ion.
To determine the strength of an acid, we look at its dissociation constant, also known as its acid dissociation constant (Ka). The Ka is a measure of how readily the acid donates a proton in water. Strong acids have a high Ka value, while weak acids have a low Ka value.
The Ka value of HSO4 is 1.2 x 10^-2, which is relatively low compared to strong acids such as hydrochloric acid (Ka = 1.3 x 10^6) or sulfuric acid (Ka1 = 1.0 x 10^3, Ka2 = 1.2 x 10^-2). This means that HSO4 is a weak acid, as it does not readily donate protons to water.
HSO4 is a weak acid that can donate some protons to water, but its dissociation constant is relatively low compared to strong acids.

Which Acid is Stronger: H3PO4 or H2SO4?
When it comes to comparing the acidity of H3PO4 and H2SO4, it is important to consider teir dissociation in water. H2SO4, also known as sulfuric acid, is a strong acid and dissociates completely in water to form H+ and SO4^-2 ions. On the other hand, H3PO4, also known as phosphoric acid, is a weak acid and only partially dissociates in water to form H+ and H2PO4^- ions.
The strength of an acid is often measured by its pKa value, which is a measure of the acidity of a compound. A lower pKa value indicates a stronger acid. In the case of H2SO4, it has a pKa value of approximately -3, making it a very strong acid. H3PO4, on the other hand, has a pKa value of approximately 2.1, making it a weak acid.
It is important to note that the strength of an acid is also dependent on the concentration of the solution. At high concentrations, even weak acids can exhibit strong acidic properties. However, when considering the pure form of H3PO4 and H2SO4, it is clear that H2SO4 is a stronger acid than H3PO4.
H2SO4 is a stronger acid than H3PO4 due to its complete dissociation in water and lower pKa value.
Comparing the Strength of H2SO4 and H2PO4 Acids
When comparing the strength of two acids, it is important to consider their chemical properties. In this case, we are comparing sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and phosphoric acid (H2PO4). Both of these acids contain hydrogen ions (H+) that can dissociate in water, making them acidic. However, sulfuric acid is generally considered to be stronger than phosphoric acid.
One reason for this is that sulfur and phosphorus are located in the same period on the periodic table, meaning they have similar chemical properties. However, sulfur is more electronegative than phosphorus, which means it is better able to hold onto its electrons. This makes sulfuric acid more stable than phosphoric acid.
Another factor to consider is the pKa values of the two acids. The pKa is a measure of acidity, with lower values indicting stronger acids. The pKa of sulfuric acid is -3, while the pKa of phosphoric acid is 2.14. This means that sulfuric acid is a much stronger acid than phosphoric acid.
Sulfuric acid is considered to be stronger than phosphoric acid due to its chemical properties and lower pKa value. It is important to note that both of these acids can be dangerous and should be handled with care. Here are some key points to remember:
– Sulfuric acid is more electronegative than phosphoric acid, making it more stable.
– The pKa of sulfuric acid is -3, while the pKa of phosphoric acid is 2.14.
– Sulfuric acid is considered to be a stronger acid than phosphoric acid.
– Both sulfuric acid and phosphoric acid can be dangerous and should be handled with care.
The Acidity of H2SO4
H2SO4, also known as sulfuric acid, is a mineral acid and is considered to be highly acidic in nature. The chemical formula of sulfuric acid is H2SO4 which inicates the presence of two hydrogen atoms, one sulfur atom, and four oxygen atoms.
When sulfuric acid is dissolved in water, it dissociates into hydrogen ions (H+) and sulfate ions (SO4 2-). This dissociation process makes sulfuric acid an acidic compound.
The pH scale is used to measure the acidity or basicity of a substance. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most basic. A pH of 7 is considered neutral.
Sulfuric acid has a very low pH, usually around 1, which indicates that it is highly acidic. This acidic nature of sulfuric acid is due to the presence of hydrogen ions which readily donate protons in aqueous solution.
It is worth noting that the strength of sulfuric acid is dependent on its concentration. The higher the concentration of sulfuric acid, the more acidic it is, and the lower its pH.
H2SO4 or sulfuric acid is an acidic compound with a low pH, making it highly corrosive and dangerous to handle.
The Strongest Strong Acid
Acids are substances that can donate hydrogen ions (H+) to a solution, making it more acidic. The strength of an acid is determined by its ability to donate these H+ ions. The strongest of all acids is fluoroantimonic acid. It is a superacid mixture of antimony pentafluoride and hydrofluoric acid.
Fluoroantimonic acid is considered the strongest acid because it has the ability to donate a proton (H+) more easily than any other acid. This is due to the high electronegativity of fluorine and the high oxidation state of antimony in the compound. The acid has a Hammett acidity function of -31, making it over 10^19 times stronger than 100% sulfuric acid.
Other strong acids include sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and hydrochloric acid. These acids are strong because they have the ability to donate H+ ions to a solution. However, they are not as strong as fluoroantimonic acid.
It is important to note that superacids like fluoroantimonic acid are extremely dangerous and should only be handled by trained professionals wearing proper protective gear. Contact with even small amounts of the acid can cause severe burns and lead to other serios health issues.
Fluoroantimonic acid is the strongest of all acids due to its ability to donate H+ ions more easily than any other acid. Its high reactivity and danger make it a rare and highly specialized substance, only handled by trained professionals.
Conclusion
Sulphuric acid is a highly important and widely used chemical compound in various industries. It is known as a strong acid due to its ability to completely ionize in water, forming hydrogen ions and sulfate ions. This high acidity makes it useful in many chemical processes and applications, such as in the production of fertilizers, detergents, and dyes.
Furthermore, the complete ionization of sulfuric acid allows for it to react readily with other substances, making it an effective catalyst in many industrial processes. However, this strong acidity also means that it must be handled with care, as it can case severe burns and other injuries.
Sulfuric acid is a crucial compound in the chemical industry, thanks to its strong acidic properties. Its ability to completely ionize in water makes it a powerful reactant and catalyst, but also means that it must be handled with caution. the importance of sulfuric acid in various industries cannot be overstated, making it a vital component of modern society.
