When it comes to modifying your vehicle’s performance, one of the most important upgrades you can make is changing the gear ratio. A faster gear ratio can significantly improve the acceleration and overall performance of your vehicle, making it a popular choice among car enthusiasts.
But what exatly is a faster gear ratio? In simple terms, a gear ratio refers to the relationship between the number of teeth on two gears that are meshed together. A faster gear ratio means that the gear on the engine side has fewer teeth than the gear on the wheel side, resulting in a higher number of wheel rotations per engine revolution.
So, why would you want to install a faster gear ratio? The answer is simple – it can provide a host of benefits to your vehicle’s performance. For starters, a faster gear ratio can improve acceleration, allowing you to get up to speed more quickly. This is particularly useful in drag racing or other high-performance scenarios where quick acceleration is key.
In addition to improving acceleration, a faster gear ratio can also provide better overall performance. It can increase the vehicle’s top speed and provide better fuel economy, giving you more bang for your buck when it comes to gas mileage.
However, it’s important to note that installing a faster gear ratio is not without its downsides. While it can certainly improve performance, it can also put more strain on your engine and drivetrain. This can lead to increased wear and tear on your vehicle, as well as decreased durability over time.
Before deciding to install a faster gear ratio, it’s important to consider your driving habits and vehicle’s overall performance goals. If you’re looking for quick acceleration and improved performance in high-speed scenarios, a faster gear ratio may be the right choice for you. However, if you’re more concerned with durability and longevity, a slower gear ratio may be a better option.
A faster gear ratio can provide significant improvements to your vehicle’s performance, particularly when it comes to acceleration and top speed. However, it’s important to carefully consider your driving habits and vehicle’s overall performance goals before making any modifications to your gear ratio. With the right setup and careful maintenance, a faster gear ratio can provide years of high-performance driving enjoyment.
Which Gear Ratio is Better: 3.73 or 4.10?
When it comes to choosing between 3.73 and 4.10 gears, there are several factors to consider. Both gear ratios have their own advantages and disadvantages depending on your driving needs and preferences.
The 3.73 gear ratio is a good choice for thoe who prioritize fuel economy and smooth acceleration. It provides a moderate amount of torque, which means it won’t be as fast off the line as the 4.10 gear ratio, but it will still offer a decent amount of power. The 3.73 gear ratio is also great for those who do a lot of highway driving, as it allows for a higher top speed and better gas mileage than the 4.10 gear ratio.
On the other hand, the 4.10 gear ratio is ideal for drivers who want quick acceleration and high torque. This gear ratio is great for off-road driving, towing heavy loads, and racing. The 4.10 gear ratio will allow your vehicle to take off quickly from a stop and provide the power needed to climb steep inclines or haul heavy trailers. However, it is important to note that the 4.10 gear ratio will result in decreased gas mileage and a lower top speed than the 3.73 gear ratio.
Ultimately, the choice between 3.73 and 4.10 gears comes down to your individual preferences and driving needs. If you prioritize fuel efficiency and smooth acceleration, the 3.73 gear ratio is the way to go. If you want quick acceleration and high torque for off-road or towing purposes, the 4.10 gear ratio is the better choice.
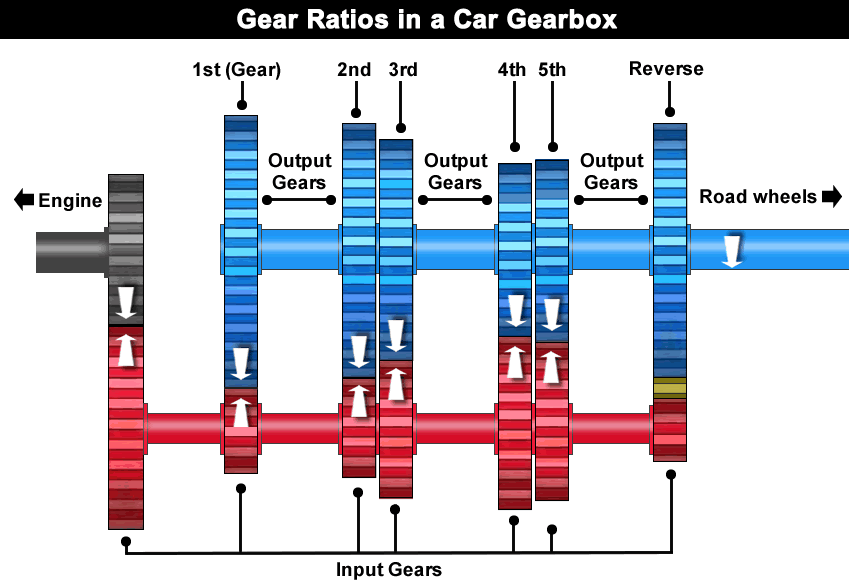
Benefits of a Higher Gear Ratio
Whether a higher gear ratio is better or not depends on what you are looking for in your vehicle. If you prioritize acceleration and towing power, a higher gear ratio (with a lower numerical value) can prvide more torque and better acceleration. This is because the engine has to work harder to turn the wheels, resulting in more power being transferred to the wheels.
However, if you prioritize fuel economy and high-speed cruising, a lower gear ratio may be more beneficial. With a lower gear ratio, the engine can run at a lower RPM while maintaining a given speed. This can result in better fuel efficiency and a smoother ride at higher speeds.
Ultimately, the choice of gear ratio comes down to personal preference and the specific needs of the vehicle. It’s important to consider factors such as the type of driving you’ll be doing, the weight of the vehicle, and the desired balance between torque and speed.
The Impact of Higher Gears on Speed
Higher gears are not faster. In fact, the opposite is true. The higher the gear, the slower your vehicle will go. Higher gears are designed to help your engine run more efficiently at higher speeds, which means that you will be able to maintain a higher speed with less strain on your engine. However, if you want to accelerate quickly or climb a steep hill, you will need to shift into a lower gear to access the additional power that your engine can provide. So, while higher gears are useful for cruising at high speeds on the highway, they are not faster than lower gears when it coms to acceleration or climbing hills.
What Is the Best Axle Ratio for Speed?
When it comes to determining the best axle ratio for speed, it really depends on what type of driving you will be doing. If you are looking for quicker acceleration and more nimble performance, an axle ratio of around 3.55 will be ideal. This ratio will cuse the engine to make more revolutions per minute, which means that you will be able to get up to speed faster and with less pressure on the throttle.
However, if you are looking for top speed, a higher numerical axle ratio, such as 4.10, may be more suitable. This ratio will allow your vehicle to have a higher top speed, but it may sacrifice some acceleration and gas mileage in the process.
It’s important to note that the best axle ratio for speed will also depend on other factors, such as the weight of your vehicle, tire size, and transmission gearing. Ultimately, it’s best to consult with an expert in the field to determine the optimal axle ratio for your specific vehicle and driving needs.
The Benefits of 4.30 Gears
4.30 gears are an ideal choice for thoe who are looking for improved acceleration from low speeds. The numerically higher gear ratio of 4.30 increases the wheel torque, which means that the vehicle can accelerate quickly from a stop or low speed. This makes 4.30 gears an excellent choice for off-road vehicles, dragsters, and street racers who need a quick takeoff from a standstill.
However, it is important to note that the engine will have to run faster to achieve a given speed with 4.30 gears. This means that the fuel economy may be slightly reduced, and the engine will produce more noise and vibration at high speeds. But for those who prioritize quick acceleration and improved performance, 4.30 gears are definitely a great option.

The Benefits of a 5.0:1 Gear Ratio
A 5.0:1 gear ratio is a relatively slow gear ratio and it is ideal for certain types of fishing techniques. This gear ratio means that the spool will rotate 5 times for every 1 full turn of the handle. A slow gear ratio like this is well-suited for techniques such as crankbaiting, where you want to keep your lure at a specific depth for a longer period of time.
With a slower gear ratio, you can retrieve your lure at a slower pace, allowing it to stay in the strike zone for a longer period of time. This is especially beneficial when fishing in deeper water or when using heavier lures that require more effort to retrieve. Additionally, a slower gear ratio proides better control and sensitivity, allowing you to feel every bump and strike on your bait.
A 5.0:1 gear ratio is a great choice for anglers who are looking to fish with crankbaits, spinnerbaits, or any other technique that requires a slower retrieve speed and more precise control.
The Benefits of a Fast Gear Ratio
A fast gear ratio is an ideal choice for serious bass fishermen who use lures that produce slack in their fishing line, or when they need to swiftly retrieve their catch out of heavy cover. This is becase a fast gear ratio enables them to quickly reel in slack and gain control over the lure, allowing them to set the hook and bring the fish out of cover efficiently. In other words, the faster the gear ratio, the quicker the angler can take control of the situation, increasing their chances of a successful catch. Additionally, a fast gear ratio also helps to reduce fatigue and save time during long fishing trips, making it a valuable asset for any angler.
Effects of Having a High Gear Ratio
If the gearing ratio of a company is too high, it means that the company is relying heavily on debt to finance its operations. This can result in several negative consequences. Firstly, the company will have to pay a significant amount of interest on its debt, which can eat into its profits and reduce the amount of cash available for other purposes such as investing in new projects or paying dividends to shareholders. Secondly, duing times of economic downturns, higher interest rates, or lower profits, the company will find it harder to service its debt obligations, which can lead to loan default and even bankruptcy. Moreover, a high gearing ratio can adversely affect the company’s credit rating, making it harder and more expensive for the company to borrow in the future. Therefore, it is generally considered risky for a company to have a gearing ratio higher than 50%, and it is important for companies to maintain a healthy balance between debt and equity financing to mitigate financial risks.
Understanding the Meaning of 4.10 Gears
When we talk about 4.10 gears, we are referring to the gear ratio of the ring and pinion gears in the rear axle of a vehicle. This ratio describes how many times the pinion gear rotates for eery full turn of the ring gear. In this case, a 4.10 gear ratio means that the pinion gear will rotate 4.10 times for every single turn of the ring gear. This translates to the rear wheel spinning once for every 4.10 turns of the driveshaft. This gear ratio is important because it affects the vehicle’s acceleration, towing capacity, and fuel efficiency. A lower gear ratio, such as 3.73, will provide better acceleration but lower fuel efficiency, while a higher gear ratio, such as 3.08, will provide better fuel efficiency but lower towing capacity. Therefore, a 4.10 gear ratio is generally considered a good balance between performance and efficiency for many types of vehicles.

Comparing the Speed of Different Gears
The gear that turns fastest is the one with the smallest number of teeth. This is because the speed of a gear is directly proportional to the number of teeth on its circumference. So, a gear with fewer teeth will rotate faster than a gear with more teeth. Additionally, the smaller gear turns in the same direction as the larger gear, and in the opposite direction as the intermediate gear. Therefore, if you have a system of gears that are all meshed together, the gear with the fewest teeth will always turn the fastest.
Comparing the Speed of Different Gears
The gear that provides the highest speed is typically the fifth gear. This is becuse fifth gear offers the greatest range of speed and allows the engine to reach its highest revolutions per minute (RPM). However, it’s important to note that the speed achievable in each gear depends on various factors such as the vehicle’s engine power, weight, and aerodynamics. Additionally, the fastest gear may vary depending on the type of vehicle, as some may have more or fewer gears in their transmission. Ultimately, the best way to determine the fastest gear is to refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for the specific vehicle in question.
Increasing Speed Through Gear Selection
Gear reducers with spur gears are commonly used for increasing speed. These gear reducers work by reducing the number of teeth on the smaller gear, which causes the larger gear to rotate faster. As a result, the output speed is higher than the input speed. Additionally, helical gears and bevel gears can also be used to increase speed, although they are typically used for different applications. Helical gears are often used for applications that require higher torque, while bevel gears are commonly used in applications that require changes in direction. Ultimately, the specific type of gear used to increase speed will depend on the application and the specific requirements of the system.
The Benefits of a 4.10 Axle Ratio
A 4.10:1 axle ratio is ideal for pickups that are used for towing big 5th wheel trailers or hauling heavy loads. The higher ratio provides a significant increase in torque, which translates to improved towing and hauling capabilities. With a 4.10:1 axle ratio, the engine has to turn feer revolutions to spin the wheels once, allowing it to deliver more power and torque to the wheels. This makes it easier for the truck to get moving from a stop, especially when towing a heavy load. Additionally, a higher axle ratio allows the vehicle to maintain its speed more easily when driving up steep inclines or through rough terrain. However, it’s essential to note that a 4.10:1 axle ratio may result in higher fuel consumption when driving without a load, so it’s best suited for trucks used primarily for heavy-duty applications.

Source: aliexpress.com
Comparing the Speed of Different Sprockets
It’s important to understand that the speed of a motorcycle is influenced by various factors, including engine power, aerodynamics, and gearing. When it comes to sprockets, the size of the sprockets and the number of teeth on them determines the gearing ratio of the motorcycle. In general, a larger rear sprocket or a smaller front sprocket will give you a lower gearing ratio, which means more torque and faster acceleration. However, this will also result in a lower top speed. On the other hand, a smaller rear sprocket or a larger front sprocket will give you a higher gearing ratio, which means less torque and slower acceleration, but a higher top speed. Therefore, the answer to the question “which sprocket is faster?” depends on what you mean by “faster.” If you’re lookng for quicker acceleration, a larger rear sprocket or smaller front sprocket is the way to go. If you’re looking for a higher top speed, a smaller rear sprocket or larger front sprocket is the way to go.
Comparing Gear Ratios: 3.92 vs. 3.21
When it comes to choosing btween 3.92 and 3.21 gear ratio, it ultimately depends on your towing needs. The 3.92 gear ratio provides a higher tow rating of 11,540 pounds, which is a significant increase of 3,100 pounds compared to the 3.21 gear ratio’s maximum tow rating of 8,440 pounds. Therefore, if you plan on towing heavy loads frequently, the 3.92 gear ratio may be the better option for you. However, it’s important to note that the 3.92 gear ratio may result in lower fuel efficiency and increased engine strain, especially if you’re not towing heavy loads consistently. On the other hand, the 3.21 gear ratio is a more fuel-efficient option and may work well if you’re not planning on towing heavy loads regularly. Ultimately, it’s important to consider your specific towing needs and consult with a professional to determine which gear ratio is the best fit for you.
Conclusion
A faster gear ratio is crucial for those seeking better acceleration and higher torque. While it may lead to decreased gas mileage and lower top speeds, it provides an optimal driving experience for those who value performance. It is important to keep in mind that gear ratios are a trade-off between torque and speed, and finding the right balance is key. With a faster gear ratio, the engine runs at a higher speed, allowing for quicker acceleration and better torque. This is particuarly useful for off-road driving or towing heavy loads. Ultimately, the decision to opt for a faster gear ratio depends on your driving needs and preferences. However, for those who value speed and power, a faster gear ratio is a must-have.
