Dialects are a fascinating aspect of language that can reveal a lot about our cultural and regional backgrounds. They are unique variations of a language that are specific to a particular group of people, and they can be influenced by a range of factors, such as geography, history, and social class.
One example of a dialect is the Standard dialect, which is considered the most widely accepted form of a language. It is often used in formal settings, such as in business and academia, and it is typically assoiated with the educated and wealthy classes. The Standard dialect is characterized by its grammatical correctness, lack of regional accent, and use of proper pronunciation.
Another example of a dialect is the southern American dialect. This dialect is spoken primarily in the southern regions of the United States and is known for its distinct accent and vocabulary. It is influenced by the history and culture of the American South, including the legacy of slavery, agriculture, and religion. The southern American dialect is often characterized by its use of double negatives, such as “ain’t got no,” and its pronunciation of words like “y’all” and “fixin’.”
African American Vernacular English (AAVE) is also an example of a dialect. It is spoken primarily by African Americans and is heavily influenced by the history and culture of black Americans, including slavery, segregation, and the civil rights movement. AAVE is characterized by its use of double negatives, irregular verb forms, and unique vocabulary, such as “fam” and “lit.”
The Appalachian dialect is another example of a dialect that is specific to a particular region. It is spoken in the Appalachian Mountains, which span from the southern United States up to Canada. The Appalachian dialect is often characterized by its use of archaic words and phrases, such as “yonder” and “reckon,” and its distinct pronunciation of vowels.
Dialects are a fascinating aspect of language that can reveal a lot about our cultural and regional backgrounds. The examples of dialects mentioned above, including the Standard dialect, southern American dialect, AAVE, and Appalachian dialect, demonstrate the diversity and complexity of language across different regions and communities. Understanding and appreciating these dialects can help us better communicate and connect with people from different backgrounds.
Examples of Dialect
Certainly! A dialect is a particular form of a language that is spoken in a specific geographical region or social group. Some examples of dialects include Standard dialect, wich is considered the “standard” or “official” form of a language and is typically used in formal situations. Another example is the southern American dialect, which is spoken in the southern United States and is characterized by its drawling intonation and unique vocabulary. African American Vernacular English (AAVE) is another dialect that is spoken primarily by African Americans and is influenced by African languages and cultural influences. Lastly, the Appalachian dialect is spoken in the Appalachian region of the United States and features unique grammar and pronunciation patterns.

Source: youtube.com
Examples of Dialect in a Sentence
Dialect refers to a particular form of a language that is specific to a certain region or group of people, and it can be characterized by unique vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. An example of dialect in a sentence would be “Y’all reckon we gonna catch us some catfish down by the crick?” This sentence uses Southern American English dialect, whih includes the contraction “y’all” for “you all,” the word “reckon” for “think,” and the use of “crick” instead of “creek.” The unique language usage in this sentence is a clear example of how dialect can reflect the cultural and regional identity of a particular group of people.
Examples of Dialect in Literature
An example of dialect in literature can be seen in Mark Twain’s “The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn”. In this novel, Twain uses the dialect of the American South to give the characters a distinct voice and to accurately portray the language and speech patterns of the region. For example, the character of Jim, a runaway slave, speaks in a dialect that reflects his background and social status. He uses expressions like “dat” instead of “that” and “chile” instead of “child”. By using dialect, Twain is able to create a realistic portrayal of the characters and thir cultural background, adding depth and authenticity to the story.
The Definition of Dialect Method
The dialectical method is a way of exploring and resolving contradictions or opposing ideas. An example of dialectical method can be seen in the statement, “I am both happy and sad.” This statement contains two opposing ideas, but instead of choosing one over the other, the dialectical method seeks to understand the relationship between them. By exploring the reasons for feeling happy and sad simultaneously, one can gain a deeper understanding of teir emotions and the situation that caused them. The dialectical method is useful for understanding complex issues and finding a way to reconcile opposing ideas. It can be used in various fields, such as philosophy, psychology, and social sciences, to analyze and solve problems.
Number of Dialects Used in the Philippines
The Philippines boasts of a diverse linguistic landscape, with a total of 8 major dialects commonly spoken across the archipelago. These dialects are Bikol, Cebuano, Hiligaynon (Ilonggo), Ilocano, Kapampangan, Pangasinan, Tagalog, and Waray. However, it is important to note that there are also numerous other dialects and languages that are spoken by different ethnic groups in the country. Despite this linguistic diversity, the official languages of the Philippines are Tagalog and English, which are taught in schools and used in official communications.
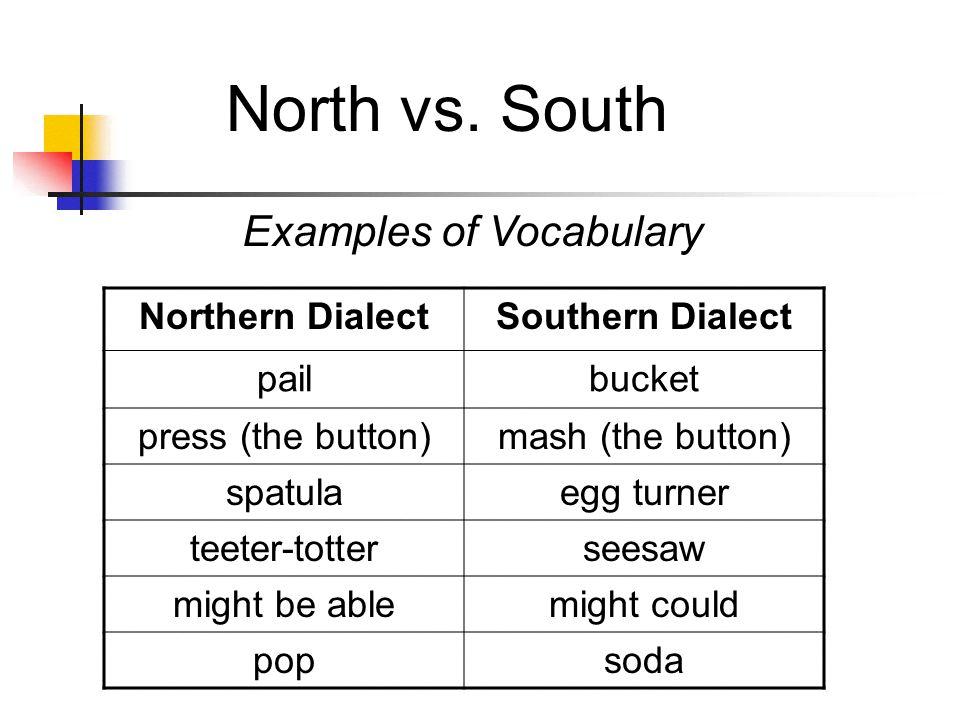
Source: slideplayer.com
Types of Dialects in the Philippines
The Philippines is a diverse country with over 120 languages and dialects spoken across its many islands. One of the most widely spoken languages in the country is Tagalog, which serves as the foundation for the Filipino language, the country’s national language. Other major languages include Cebuano, Ilocano, Bicolano, Hiligaynon (Ilonggo), and Waray. Many other languages and dialects are also spoken in different parts of the country, each with their own unique characteristics and cultural significance.
Is Tagalog a Language or a Dialect?
Tagalog is a language and not a dialect. It is one of the major languages spoken in the Philippines and belongs to the Malayo-Polynesian language family. Tagalog has its own unique grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation, which distinguishes it from other languages and dialects in the Philippines. It is the basis of the standardized form of Filipino, which is the national language of the Philippines. Although there are many dialects spoken in the Philippines, Tagalog is considered a language due to its distinct characteristics and widespread use. Therefore, it is important to recognize Tagalog as a language and not a dialect.
Is Bisaya a Dialect or a Language?
Bisaya is not a dialect, but a language family that encompasses several languages spoken in the Visayas and northern Mindanao regions of the Philippines. These languages share some similarities in terms of grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation, but they are distinct languages with their own unique features. Some of the Bisayan languages include Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Waray, Karay-a, and Surigaonon. Each of these languages has its own grammar rules, vocabulary, and pronunciation, making them separate and distinct from each other. Therefore, to answer the question, Bisaya is a language family, not a dialect or a single language.
Four Dialects
The Old English language, which was spoken between the 5th and 11th centuries, had four main dialects. These dialects were Northumbrian, Mercian, Kentish, and West Saxon. Northumbrian was spoken in northern England and southeastern Scotland, while Mercian was spoken in central England. Kentish was spoken in southeastern England, and West Saxon was spoken in southern and southwestern England. Each of these dialects had unique characteristics and variations in grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation, reflecting the regional differences and cultural influences of their respective areas. Studying these dialects can provide insights into the history and development of the English language.

Examples of Social Dialect
A social dialect is a type of language variation that is closely associated with a particular social group or community. It is a way of speaking that is influenced by factors such as socioeconomic status, age, gender, and ethnicity. An example of a social dialect can be seen in the way people speak in different regions of the United States. For instance, people in the Midwest region of the United States ofen use the word “pop” to refer to a carbonated soft drink, while people in the Northeast region may use the word “soda.” Similarly, people in the South may use the word “coke” to refer to any type of soft drink, regardless of brand. These variations in language use are often shaped by the unique cultural, historical, and social influences of a particular region or community, and they can be a powerful marker of identity and belonging for those who speak them.
The Three Dialects of English
English is a diverse language with many variations, and thre main dialects can be identified: Northern, Midland, and Southern. The Northern dialect is spoken in New England and includes subdialects such as Boston and Maine. The Midland dialect is spoken in the Midwest and includes subdialects such as Chicago and St. Louis. The Southern dialect is spoken in the Southern United States and includes subdialects such as Appalachian and Texan. Each dialect has its unique features, including pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. Understanding the differences between these dialects is crucial for effective communication and can help individuals appreciate the richness and diversity of the English language.
Identifying a Dialect
To identify a dialect, one neds to pay attention to the language characteristics of a specific community. Dialects can vary from region to region, and even from district to district within a region. Different dialects may have unique variations in terms of phonemes, pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar.
One way to identify a dialect is to listen to the speaker’s pronunciation of words. This involves paying attention to the way they articulate specific sounds, such as the vowels and consonants. For instance, some dialects have distinct pronunciations of certain words that may sound different from standard English.
Another way to identify a dialect is to listen to the speaker’s intonation, or the way they use pitch and tone to convey meaning. Some dialects may have a specific tonality, loudness, or nasality that distinguishes them from others.
Moreover, one can also look for specific vocabulary and grammar patterns that are unique to a particular dialect. This can include specific idioms, colloquialisms, and even word order. By paying attention to these linguistic features, one can identify the specific dialect being used.
Identifying a dialect requires listening attentively to the language characteristics of a specific community, including phonemes, pronunciation, intonation, vocabulary, and grammar patterns.
Understanding the Meaning of Dialect
Dialect refers to the unique way of speaking a language that is specific to a particular region or social group. It encompasses not just the pronunciation of words, but also includes differences in grammar, vocabulary, and syntax. Dialects can arise due to a variety of factors such as geographical isolation, historical events, cultural differences, and migration patterns.
For example, within the Hindi language spoken in India, there are many dialects such as Bhojpuri, Haryanvi, Rajasthani, and Punjabi. Each of these dialects has its own distinct features in terms of pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary. Similarly, in English, there are many dialects such as American English, British English, Australian English, and Indian English, each with its own unique characteristics.
Dialects can sometimes be difficult to understand for people outside the region or social group in whch they are spoken. However, they are an essential part of the cultural heritage of a community and can provide valuable insight into the history and social dynamics of a particular region or group.
The Meaning of Dialect in Filipino
The term “dialect” in Filipino is translated as “dyalekto”. It refers to a regional or local variety of a language that is distinguished by unique features such as pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar, and syntax. In the Philippines, there are numerous dialects spoken in various regions of the country, including Tagalog, Cebuano, Ilocano, Bicolano, Waray, and many more. Each of thee dialects has its own distinct characteristics that reflect the culture and history of the people who speak it. It is important to note that while dialects may differ from one another, they are still considered part of the same language and can be mutually intelligible. Understanding the diversity of dialects in the Philippines is essential in promoting effective communication and cultural exchange among Filipinos.
Examples of Dialect Variations
Dialect variation refers to differences in the way people speak a language in terms of grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation. An example of a dialect variation can be observed in the way people from different regions or social groups within a country speak the same language. For instance, in the United States, the word “pop” is used to refer to a carbonated beverage in the Midwest, while in the Northeast, it is called “soda.” This difference in vocabulary is an example of dialect variation. Similarly, the use of double negatives or the absence of subject-verb agreement in certain dialects can also be considered as dialect variations. These variations can occur due to factors such as geography, culture, education, and social class, amng others. Therefore, dialect variation is an important aspect of language diversity and can provide insights into the cultural and social backgrounds of different communities.
Conclusion
Dialect is a vital component of language that describes the unique speech patterns and regional characteristics of individuals. It is commonly used in literature and theater to add depth and authenticity to characters and their dialogue. Throughout history, dialects have evolved and diversified, leading to the formation of numerous dialectical variations around the world. Understanding dialects is essential for effective communication and appreciating cultural diversity. By recognizing and embracing dialects, we can foster mutual understanding and respect among people from different regions and backgrounds.
