Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a colorless, non-flammable, volatile organic compound that has a sweet smell similar to chloroform. It is used in many industries, such as cleaning and firefighting, as well as being found in some household products. Carbon tetrachloride is classified as a VOC (Volatile Organic Compound).
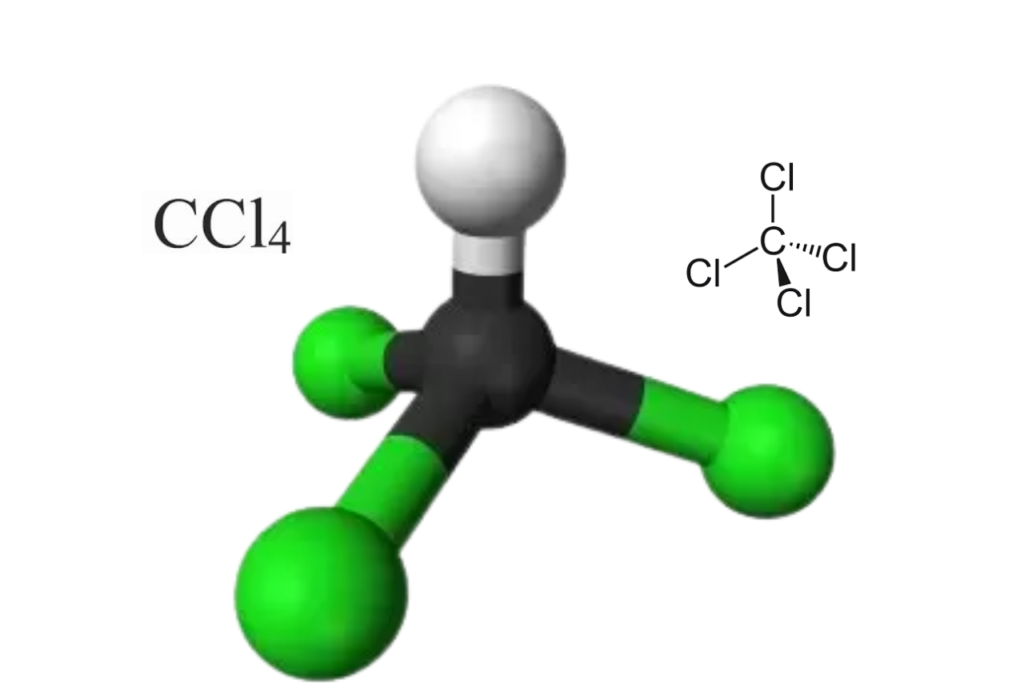
This chemical compound is made up of one carbon atom and four chlorine atoms which are connected together by covalent bonds. The carbon atom forms four covalent bonds with the four chlorine atoms to form a tetrahedral shape molecule. This molecule does not have any extra electrons that cause it to be electrically charged and so it does not interact with other molecules easily.
Due to its low boiling point and high vapor pressure, carbon tetrachloride evaporates quickly when exposed to air. This makes it useful for removing grease from surfaces quickly without having to use harsh chemicals or scrubbing. It can also be used in firefighting as Halon-104 because its vapors can smother flames and reduce the risk of fire spreading.
Unfortunately, carbon tetrachloride has been linked to health risks such as skin irritation, eye irritation, lung irritation, nausea, dizziness and headaches when inhaled in large concentrations. In addition, long-term exposure can lead to liver damage and cancer. For this reason it should only be used in well-ventilated areas with appropriate safety equipment such as masks and gloves.
Fortunately, due to the health risks associated with carbon tetrachloride tere have been steps taken by regulatory authorities to reduce its use in products where possible. For example, the European Union has banned the use of this chemical in aerosol products while other countries are looking into alternatives that are safer for both people and the environment.
Overall, carbon tetrachloride has many useful properties but care must be taken when using or handling it due to its potential health hazards. If you use this chemical or think you may have been exposed then please consult your doctor or seek medical advice immediately.
What Is Cci4 Element?
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is an organochlorine compound composed of one carbon atom and four chlorine atoms. It is a colorless, nonflammable, liquid chemical with a sweet odor similar to that of chloroform. CCl4 has a wide range of uses, including as a solvent, in fire extinguishers, and as a refrigerant. It is also used in the production of pesticides and various other chemicals. However, due to its toxicity and ozone-depleting potential, its use has been restricted or phased out in many countries.
The Name of CCl4
The name of the compound CCl4 is carbon tetrachloride. It is also known by many other names, such as tetrachloromethane (recognised by the IUPAC), carbon tet in the cleaning industry, Halon-104 in firefighting, and Refrigerant-10 in HVACR.
What Does Cci4 Stand For?
CCI4 stands for Carbon Tetrachloride, an organic compound with the chemical formula CCl4. Carbon tetrachloride is also known as tetrachloromethane and is composed of one carbon atom and four chlorine atoms. It is a colorless, volatile liquid that has a wide variety of uses ranging from solvents to refrigerants. It is also used in fire extinguishers and in some cases as a pesticide. Though it has many practical applications, it can also be dangerous when inhaled or ingested.
What Is Cci4?
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a covalent compound composed of one carbon atom and four chlorine atoms, bound together by four non-polar covalent bonds. It has a molar mass of 153.8 g/mol and is a colorless, volatile liquid with an ether-like odor. In addition to its use as a solvent, carbon tetrachloride is also used as a fire extinguishing agent and aerosol propellant.
Is the Cci4 Bond Polar?
No, Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) does not have a polar bond. CCl4 is a covalent compound, meaning it is composed of non-polar covalent bonds between carbon and chlorine atoms. This means that the electrons in the covalent bond are equally shared between both atoms, resulting in no net dipole moment, and thus making it a non-polar molecule.
What is the Shape of CCI4?
CCl4 is a tetrahedral molecule with four equal C-Cl bond lengths and a bond angle of 109.8 degrees between the lone pairs of electrons. The molecule has four regions of electron density, which results in its sp3 hybridization and tetrahedral shape.
Is CCI4 a Gas?
Yes, CCl4 is a gas. It is a colorless and odorless gas at room temperature and pressure, and it evaporates into the air easily. It has a sweet smell that can be detected at low levels. CCl4 is also known as carbon tetrachloride, and it is frequently used in fire extinguishers and dry cleaning solutions.
Is Cc14 Organic?
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is an organic compound, meaning it contains carbon and hydrogen atoms bonded together. It is a synthetic chemical that does not occur naturally in the environment. CCl4 has a wide range of uses, such as in the production of aerosol propellants, cleaning solvents, refrigerants, and fire extinguishing agents. Although it is considered to be an organic compound, it should be noted that it is toxic and can cause severe health effects if inhaled or ingested.
Why Is CCL4 Banned?
CCl4, or carbon tetrachloride, is a synthetic compound that was widely used in the 1980s as a solvent and industrial cleaning agent. However, scientists soon discovered that it was contributing to the depletion of the ozone layer, which protects us from harmful UV radiation. Due to its ozone-depleting properties, CCl4 was added to the list of substances that governments around the world agreed to phase out of production.
The reason for this ban is that CCl4 molecules are able to reach the stratosphere, where they break down into chlorine atoms. Chlorine atoms are able to catalyze the breakdown of ozone molecules into oxygen atoms, leading to a decrease in overall ozone levels. This loss of ozone can lead to increased ultraviolet radiation exposure, which can cause skin cancer and other health issues. Furthermore, it can lead to environmental damage such as crop losses and reduced fish populations in certain areas due to changes in ocean temperatures caused by increased UV radiation.
To reduce thee risks and protect our environment and health, governments around the world agreed that CCl4 should be phased out of production and replaced with safer alternatives.
Formation of the CCI4 Index
Carbon tetrachloride (CCI4) is formed through a process of chlorination of low molecular weight hydrocarbons. This can be achieved through two different methods: chlorination of hydrocarbons such as carbon disulphide, methane, ethane, propane or ethylene dichloride; or by thermal chlorination of methyl chloride. The chlorination process involves the addition of chlorine atoms to the hydrocarbon molecules, resulting in the formation of four chlorine atoms attached to a single carbon atom – hence the name Carbon Tetrachloride (CCI4).
Conclusion
In conclusion, Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a covalent compound composed of four non-polar covalent bonds between carbon and chlorine atoms. It is a clear, nonflammable, heavy liquid with a sweet odor similar to chloroform. Carbon tetrachloride is classified as a volatile organic compound (VOC) and has multiple uses including firefighting and HVACR. It should be handled with caution due to its toxicity and potential health hazards.
