Diarrhea is a common digestive problem that occurs when the body has difficulty absorbing fluid and nutrients from food. It usually results in frequent, loose stools and can be uncomfortable and inconvenient. In some cases, it may be a symptom of an underlying medical condition.
When it cmes to food-related causes of diarrhea, eating moldy cheese is one potential culprit. Moldy cheese can contain harmful bacteria like salmonella, E. coli and listeria, which can cause gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhea if consumed. Additionally, certain types of molds contain toxins that can irritate the lining of your digestive tract and lead to diarrhea.
If you’ve eaten moldy cheese, it’s important to monitor your symptoms for several days afterwards. If you experience persistent diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, contact your doctor as soon as possible for advice on how to treat it. It’s also a good idea to avoid eating any more moldy cheese in the future in order to reduce your risk of long-term health problems associated with consuming contaminated foods.
Ultimately, if you suspect that you may have eaten moldy cheese and are experiencing diarrhea or other gastrointestinal symptoms, it’s best to contact your doctor for further advice on how to manage the situation.
The Consequences of Accidentally Eating Moldy Cheese
If you accidentally eat moldy cheese, you may experience some symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, shortness of breath and possibly an allergic reaction. It is important to note that the severity of the symptoms will depend on a variety of factors such as the type of cheese consumed, how much was eaten and if there are any underlying health conditions. If you experience any of these symptoms after eating moldy cheese, it is best to seek medical attention.
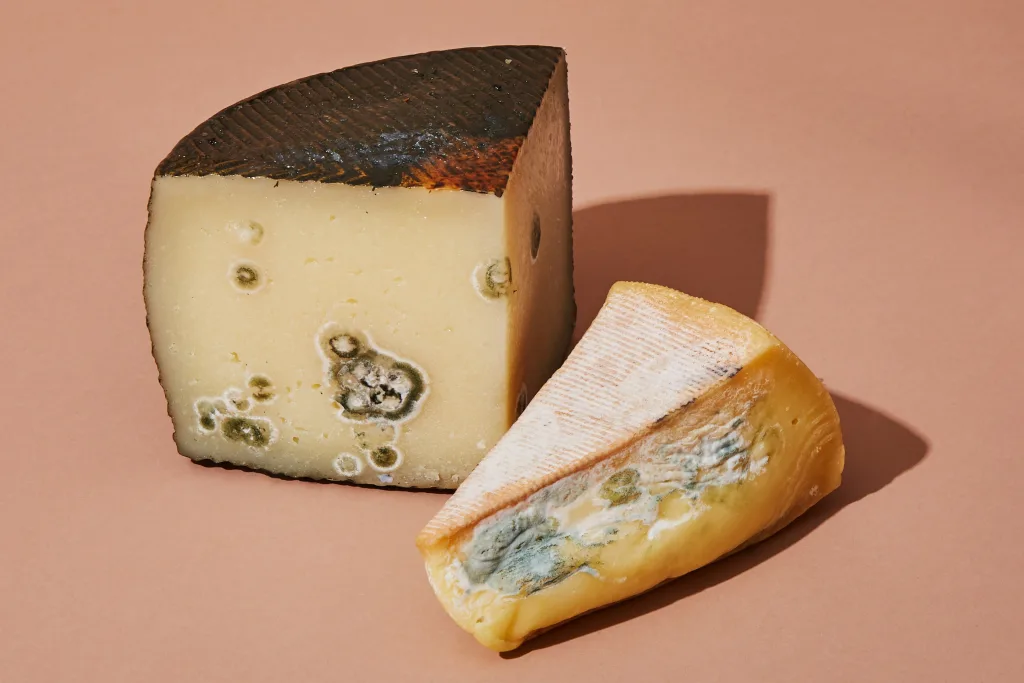

Can Eating Mold Lead to Diarrhea?
Yes, eating mold can cause diarrhea. The toxin in the mold can irritate the stomach and cause gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach cramps. In some cases, eating moldy food can cause more severe reactions such as nausea, fever, and headaches. If you think you may have eaten moldy food and are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important that you seek medical attention as soon as possible.
How Long Does It Take to Become Ill After Eating Moldy Food?
It depends on the type of mold you ate, but some reactions may occur right away while others may be delayed. If you develop any symptoms – such as shortness of breath, nausea, fever or diarrhea – seek medical attention immediately. It is also important to note that some people may not experience any symptoms at all.
Can Eating Moldy Cheese Make You Sick?
No, a small amount of mold on cheese will not make you sick. The molds that are likely to grow on cheese are not dangerous, and in fact, some cheeses have a specific type of mold as part of thir production process. For example, Brie and Camembert have a white rind due to the presence of Penicillium candidum, while Gorgonzola is made with Penicillium glaucum. While these molds can affect the flavor of the cheese, they will not make you sick.
However, it’s important to remember that large amounts of mold on any food can cause food poisoning or other illnesses. If you notice an excessive amount of mold on your cheese (or any other food), it’s best to throw it away and not take any chances.
Is Eating Slightly Moldy Cheese Safe?
It is generally safe to eat hard and semisoft cheeses, such as cheddar, colby, Parmesan and Swiss, even if they have a little bit of mold on them. The key is to cut away the moldy part and an additional inch around it to ensure that no mold remains. If you see any spots that look abnormal or the cheese smells bad, it should be discarded. Remember to always store cheese properly in the refrigerator and use it within its expiration date for best results.
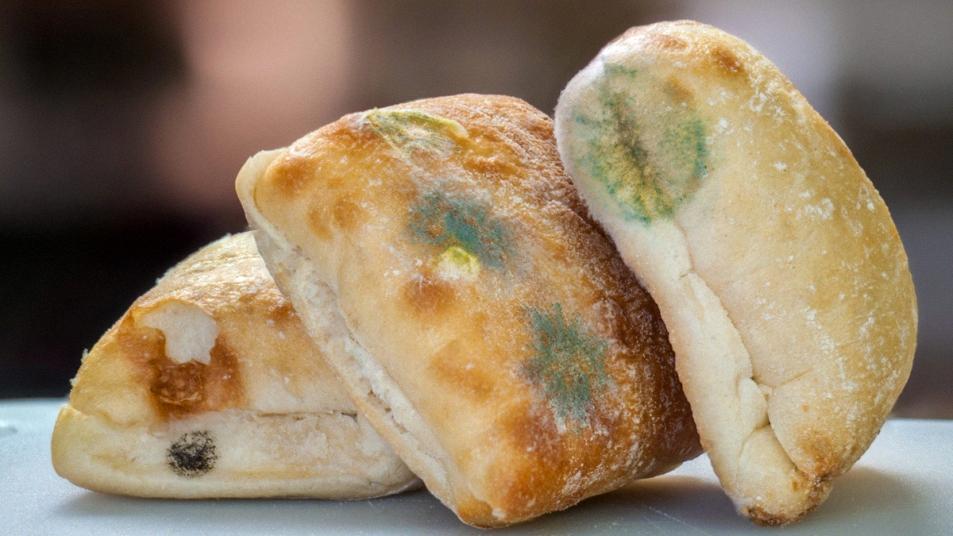

Source: firstforwomen.com
Dealing with Eating Moldy Food
If you’ve eaten moldy food, the best thing to do is to monitor your body for any adverse reactions. Pay close attention to your breathing and othr symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or headaches. If you start to experience any of these symptoms or feel unwell in general, seek medical advice right away. Depending on your individual condition and the type of mold you consumed, the doctor may recommend treatment.
Although some molds are harmless and won’t cause any serious health problems, it’s important to take precautions after eating moldy food. Be sure to wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling moldy food. If you have consumed a large amount of moldy food, drink plenty of fluids to help flush out toxins from your system. Additionally, drinking probiotic-rich beverages such as kefir or kombucha may also help boost your digestive health and reduce the risk of any complications associated with eating moldy food.
The Effects of Mold on Diarrhea
Diarrhea can be caused by a number of molds, with two of the most common being Aspergillus Versicolor and Aspergillus Fumigatus. Both species of mold are found in damp environments, and produce toxins that can case gastrointestinal distress when ingested. Symptoms of infection include abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. In some cases, ingestion of these toxins may also lead to more serious health problems such as kidney and liver cancer. It is important to note that molds other than these two may also cause similar symptoms; however, these are the two most commonly found in areas where a person may be exposed. To reduce the risk of infection or illness from these molds, it is important to avoid contact with damp areas or materials that may contain them.
Signs of Mold Poisoning
Mold poisoning can cuse a wide range of symptoms, depending on the type of mold and the length of exposure. Common signs of mold poisoning include respiratory symptoms, such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, or nasal stuffiness. Other potential signs include eye irritation, skin rashes or itching, fatigue, headaches, and memory loss. In severe cases, it may even cause fever and difficulty breathing. It is important to note that some people may be more sensitive to mold than others and may experience more severe reactions. If you think that you have been exposed to mold and are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Signs of Mold Toxicity
Mold toxicity can cause a variety of symptoms, including: respiratory issues such as coughing, sneezing, chest tightness and shortness of breath; skin irritation such as rashes and hives; eye irritation such as redness, watery eyes and blurred vision; fatigue; headaches; memory problems; and general malaise. In more extreme cases, it can lead to fever and difficulty breathing. People with mold allergies or asthma may experience more severe reactions when exposed to molds.
Can Stomachs Be Prone to Mold Growth?
No, mold cannot grow in the stomach. Although mold can be found in the gastrointestinal tract of immunocompromised patients, it typically does not cause infection unless the person’s immune system is severely weakened. In this case, a patient may experience disseminated invasive mold infection (IMI), which is a serious complication that carries a high mortality rate. As such, it is important to seek medical care if one experiences any symptoms of IMI or other systemic fungal infections.
Is Eating Green Moldy Cheddar Cheese Safe?
It is not recommended to eat cheddar cheese with green mold on it. Green mold can sometimes contain toxins that can be harmful to humans. Eating the cheese could cause allergic reactions, including vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, and internal bleeding. In rare cases, these reactions can be serious and even life-threatening. Therefore, it is best to discard any cheddar cheese that has green mold on it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diarrhea is a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors and causes. It can be acute or chronic, mild or severe, and last for days or weeks. Many cases of diarrhea can be treated with simple lifestyle changes such as increasing water intake, eating small meals more frequently, and avoiding dairy or spicy foods. However, if the diarrhea persists for more than two weeks or becomes severe, it is important to seek medical attention. With proper diagnosis and treatment, most cases of diarrhea can be quickly resolved.
