The concept of average velocity is quite simple – it’s the rate at which an object moves from one place to another. It can be used to measure how fast a car is travelling, or how quickly a ball is moving. But what about when it comes to average velocity being negative? Can it really be negative?
The answer is yes – average velocity can indeed be negative. To understand why, it’s important to first understand the difference between speed and velocity. Speed is the rate at which distance is covered, while velocity includes both magnitude and direction. This means that an object can have a positive or negative velocity depending on its direction of motion. And this in turn means that average velocity can also be eiter positive or negative depending on the direction of motion over time.
For example, imagine a plane flying from point A to point B – if its displacement (the distance between points A and B) is in the north-east direction and its average speed is 300 km/h, then its average velocity would be 300 km/h in a north-east direction (positive). However, if instead of flying from A to B it was flying from B to A (in other words, south-west), then it would have an average velocity of 300 km/h in a south-west direction (negative).
It’s also possible for an object or system to have an average acceleration that’s either positive, negative, or zero depending on whether it speeds up, slows down, or maintains constant speed over time. An example of a situation where an object’s acceleration might be negative would be if an airplane was flying southwest and suddenly crashed somewhere before reaching its destination; in this case the airplane’s acceleration would have been in the opposite direction (negative) of its original path.
Overall, while speed itself cannot ever be negative, the change in speed over time (velocity) and the rate of change in speed (acceleration) can both have either positive or negative values depending on their directions relative to each other.
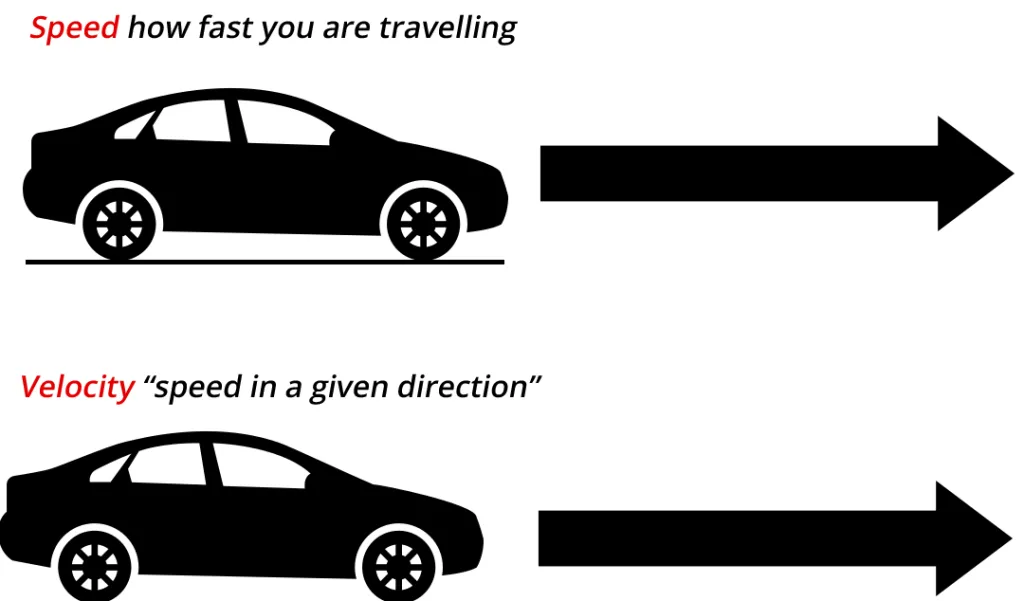
The Difference Between Velocity and Speed
Velocity is a vector quantity and is different from speed, which is a scalar quantity. Velocity measures the rate of change in an object’s position, so it has both magnitude (speed) and direction (east, west, north, or south). When the direction of motion changes, the velocity changes accordingly. If an object moves in the opposite direction of its original motion, then its velocity will be negative. For example, if an object is moving east at 10 m/s and then reverses its course and moves west at 10 m/s, then its velocity is -10 m/s. However, speed does not take direction into account; it only considers magnitude. Therefore, it can nver be negative.
Can Velocity Be Negative in Calculus?
Yes, velocity can be negative in calculus. Velocity is a vector quantity that measures both the magnitude and direction of motion. In calculus, velocity can be positive or negative depending on the direction of motion. Positive velocities indicate motion in one direction, while negative velocities indicate motion in the opposite direction. For example, if an object moves to the right with a speed of 5 meters per second, its velocity wuld have a positive value of 5 m/s; however, if it then reverses course and moves to the left with the same speed, its velocity would have a negative value of -5 m/s.
Can Average Speed and Average Velocity Have Opposite Signs?
Yes, it is possibe to have a positive average speed and a negative average velocity. Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the total time elapsed. Average velocity, on the other hand, is the displacement (change in position) divided by the time elapsed. If an object moves in one direction for some time, then reverses its direction and moves in the opposite direction for an equal amount of time, its displacement will be zero but its average speed will still be greater than zero. In this case, the average velocity would be negative because it would be calculated as a displacement of 0 divided by a non-zero amount of time.
Negative Average Acceleration: Is It Possible?
Yes, you can have a negative average acceleration. This occurs when an object’s velocity decreases over time. In other words, the object is decelerating. The magnitude of the acceleration is equal to the rate of change of velocity, so if the velocity decreases, then its magnitude will be negative. This would lead to a negative average acceleration for that time period.
The Impact of Negative Average Velocity
Your average velocity is negative when the displacement of your object is in the negative direction. This means that your object has moved from a higher position to a lower position, or from a rightward position to a leftward position. For example, if you were driving in a car and you moved 5 kilometers to the north and then 10 kilometers to the south, your displacement would be -5 kilometers because you ended up 5 kilometers south of where you started. This would result in an average velocity of -5 km/hr because your change in position was in the negative direction.
Can Average Velocity Be Equal to Zero?
Yes, average velocity can be zero. Average velocity is a measure of the rate of change of an object’s position over a period of time. It is calculated by dividing the total displacement (change in position) by the total time elapsed. If an object’s displacement is zero, then its average velocity will also be zero, regardless of the time elapsed. For example, if an object starts and ends in the same location, then its displacement and velocity are both zero no matter how much time has passed.
Understanding Velocity’s Ability to Be Negative, Positive, or Zero
Velocity is a vector quantity which has both magnitude and direction. It is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time. It can be positive, negative or zero depending on the direction of displacement with respect to the reference frame chosen.
A positive velocity indicates an object travelling in the same direction as the reference frame, a negative velocity indicates an object travelling in the opposite direction to that of the reference frame and a zero velocity indicates an object at rest relative to the reference frame. Therefore, velocity can be negative, positive or zero depending on whether an object is travelling in the opposite, same or no direction compared to that of a givn reference frame.
Impossibility of Negative Velocity
Velocity cannot be negative because it is a vector quantity that describes both the magnitude and direction of an object’s movement. It is measured in units such as meters per second (m/s), feet per second (ft/s), or kilometers per hour (km/h). Since velocity has both magnitude and direction, a negative velocity would imply that an object was moving in the opposite direction of its original starting point. Therefore, it is impossible for a velocity to be negative.
Can Relative Velocity Be Negative?
Yes, relative velocity can be negative. Relative velocity is the difference between two velocities, and it does not matter if one velocity is larger or smaller than the other. So, even if one of the velocities is greater than the other, the difference could still be a negative number and thus, relative velocity can be negative.
Source: youtube.com
Average Velocity Under What Conditions
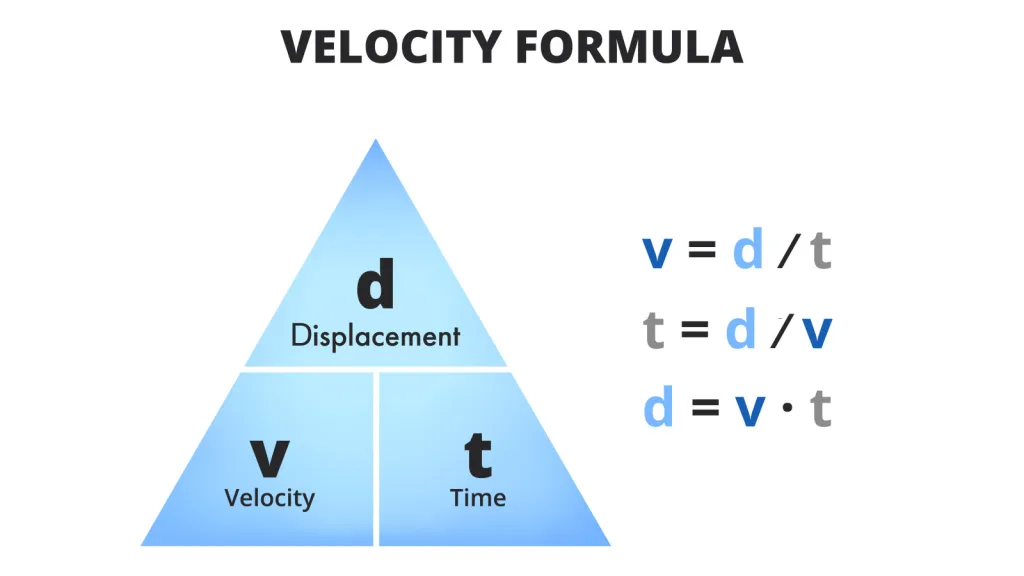
Average velocity is a measure of the rate at which an object changes its position in a given direction over a period of time. It is the displacement (change in position) divided by the time taken for the change to occur.
To calculate average velocity, two conditions must be met:
1. The object must move in a straight line and not turn back. If the object moves in a curved path or turns back, then its average velocity cannot be found, as it cannot be described by just one linear equation.
2. The distance covered by the object must equal its displacement over a given period of time. This means that if an object moves for 2 minutes and covers 2 kilometers, then its average velocity wuld be 1 kilometer per minute (km/min). In this case, its speed and average velocity are equal.
In conclusion, average velocity is calculated when an object moves along a straight line without turning back and when the displacement of the object is equal to the distance covered by it in a given time interval.
Can Velocity Have a Negative Value While Acceleration is Positive?
Yes, velocity can be negative and acceleration positive. Velocity is the rate of change of an object’s position in a certain direction, and it is measured in meters per second (m/s). When the object is moving in the negative direction, the velocity is negative. On the other hand, acceleration is a vector quantity that measures how quickly an object’s speed or direction changes over time. This means that even if the object’s velocity is negative, its acceleration can sill be positive if its speed or direction are increasing. For example, if an object starts moving towards the left at -5 m/s and then increases its speed to -3 m/s after two seconds, then its acceleration would be positive because it has increased its speed in a given amount of time.
Can Negative Values Be Achieved for Average Angular Velocity?
Yes, average angular velocity can be negative. This is because angular velocity is a measure of the rate of change of an object’s angular position over time, and this can increase or decrease. If the angular position decreases over time, then the average angular velocity will be negative. This can happen if an object rotates clockwise in a given amount of time, which would cause the average angular velocity to be negative.
Can Velocity Have a Negative Value?
Yes, velocity can be negative in physics. Velocity is a vector quantity that describes the change in an object’s position over time. It includes both speed (the magnitude of the change) and direction (whether it is accelerating or decelerating). Since direction can be positive or negative, velocity can also be positive or negative. For example, if an object is moving in the positive direction at a certain speed, its velocity would be positive. On the other hand, if an object is moving in the negative direction at a certain speed, its velocity would be negative.
Is Average Acceleration Always Positive?
No, average acceleration is not always positive. Acceleration is a measure of the rate of change of velocity, and can be positive, negative, or zero. Positive acceleration indicates an increase in velocity, negative acceleration indicates a decrease in velocity, and zero acceleration indicates no change in velocity. Therefore, average acceleration can be any of these values depending on the situation.
Negative Velocity and Negative Acceleration
Yes, it is possible to have negative velocity and negative acceleration. This occurs when the position of an object changes away from the direction of motion, and its velocity decreases with time. For example, if a car is traveling east at 10 m/s and then turns around and starts heading west at 7 m/s, the car will have a negative velocity of -7 m/s and a negative acceleration of -3 m/s2.
Conclusion
In conclusion, average velocity is a vector quantity that takes into account both the magnitude and direction of an object’s motion. It is the rate at which an object’s position changes over time and is measured in distance per unit of time (e.g. meters per second). Average velocity can be negative, positive, or zero depending on the direction of motion. Negative velocities describe motion in the opposite direction to positive velocities and average acceleration can be negative, positive, or zero.
