Hernias are one of the most common medical conditions, affecting millions of people worldwide. But what is a hernia, and can it be dangerous?
A hernia occurs when part of an organ or fatty tissue protrudes through a weak spot or tear in the muscle wall that holds it in place. This can cause pain and discomfort, but if left untreated, a hernia can lead to more serious health complications.
Most hernias occur in the abdomen, specifically in the groin area. While there are many types of hernias, they all have certain risk factors in common such as obesity, heavy lifting, and straining. Hernias can also be present at birth due to congenital defects.
When it comes to treating a hernia, surgery is usually necessary to repair the weakened area and prevent further damage or complications. Depending on the type and severity of the hernia, there are both open and laparoscopic surgeries available. Open surgeries involve making an incision in order to access and repair the affected area while laparoscopic procedures involve inserting a small camera into the body to guide surgeons during repairs without large incisions.
But can a hernia kill you? While rare, it is possible for an untreated hernia to become life-threatening. If left untreated for too long, a hernia can become strangulated which means that blood flow is cut off from the tissue trapped within it – this can lead to sepsis or tissue death which requires emergency surgery intervention. It’s important that if you experience any symptoms related to a possible hernia that you seek medical attention right away so that treatment can begin quickly before any further damage is done.
If you tink you may have a hernia it’s important not to ignore your symptoms as waiting too long could be life-threatening! Talk with your doctor about diagnosis and treatment options so that you can get back on track quickly with minimal risks involved!
Consequences of Not Treating a Hernia
If a hernia is left untreated, it can lead to serious health complications. The intestine or organ that is protruding through the weakened area of the abdominal wall may become larger and more uncomfortable over time. Without treatment, the intestine can become twisted or “strangulated,” meaning the blood supply to that part of the intestine is cut off. This can case severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and even tissue death. If left untreated for too long, hernias can also lead to infection in the area of the hernia. In rare cases, an untreated hernia can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. It is important to speak with your doctor about treatment options for hernias so that you can avoid these serious health issues.
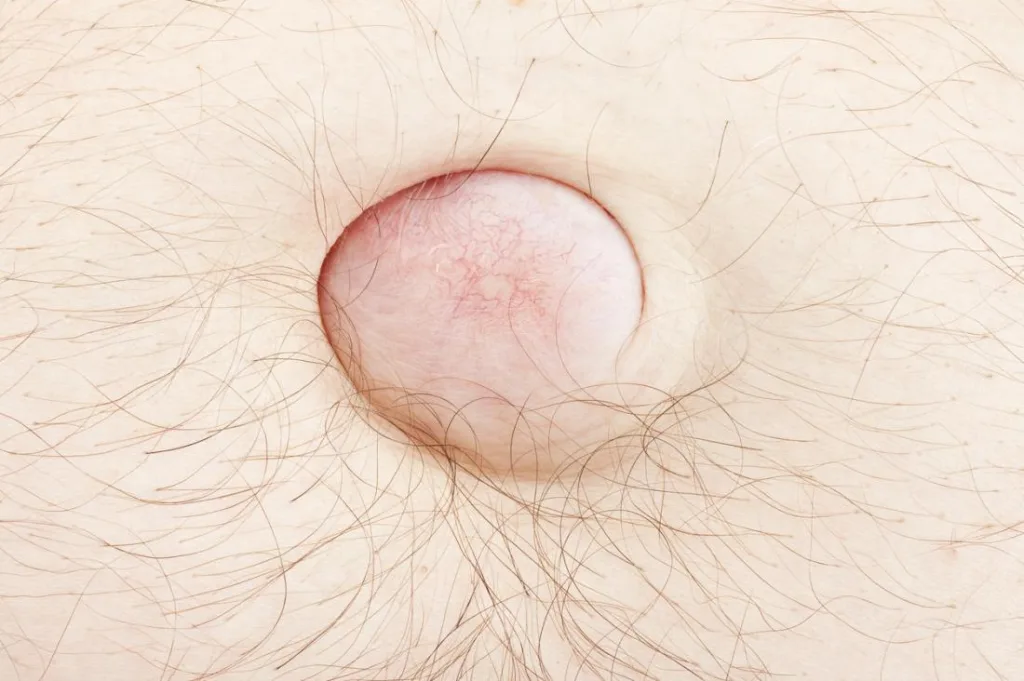
Risks of a Burst Hernia
If your abdominal hernia bursts, it is a medical emergency and you should seek immdiate medical attention. A hernia rupture can lead to further obstruction of the intestines, as well as strangulation of the bowel, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. During surgery, your surgeon will repair the hernia and replace any protruding tissue back into its original position. Additionally, they may use sutures or synthetic mesh to reinforce the weakened area in order to prevent future ruptures. After surgery, you may need to take antibiotics for several days and engage in light activities for a few weeks in order to allow adequate healing.
Risk of Sudden Death Associated with Hernia
No, hernia typically does not cause sudden death. However, if the hernia becomes incarcerated (trapped) and then strangulated (cut off from its blood supply), it can lead to life-threatening complications and even death if not treated promptly. Strangulation of a hernia is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. If the intestine or other organs in the hernia become deprived of oxygen for too long, they can become gangrenous and eventually die, leading to serious health issues and possibly death. Therefore, seeking medical help as soon as symptoms appear is essential to prevent further complications.
Living with a Hernia without Surgery
Yes, it is possible to live with a hernia without surgery. While surgery is the only way to permanently repair a hernia, some people are able to manage their condition without having surgery. This can include taking steps to reduce the strain on the affected area and avoiding activities that may worsen the hernia.
If you choose to manage your hernia without surgery, you should monitor it closely for any changes in size or symptoms. It’s important to see your doctor regularly and discuss any new pains or discomforts that occur as well as lifestyle changes that may help reduce symptoms. Additionally, if you experience severe pain, fever, redness or swelling in the affected area, you should seek medical help immediately as these can be signs of an incarcerated hernia, which requires emergency care.
Signs of a Serious Hernia
If you are experiencing any of the followig symptoms related to a hernia, it is important to seek immediate medical attention:
1. Severe pain, tenderness, or burning around the area of the bulge that does not subside with rest.
2. Nausea and/or vomiting.
3. Difficulty urinating or bowel movements.
4. A feeling of heaviness, weakness, or pressure in the affected area.
5. Fever and/or chills.
6. Skin discoloration in the affected area that can be red, blue, or purple in color.
7. Rapid heart rate or irregular heartbeat that does not go away with rest or medications for an extended period of time (more than 24 hours).
8. Difficulty breathing and/or difficulty swallowing.

When is a Hernia Considered an Emergency?
A hernia is considered an emergency when the hernia bulge is growing quickly, the hernia site is swollen and/or red, and there is severe pain. If any of these symptoms are present, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Other signs of an emergency hernia include nausea and/or vomiting. If a person experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
The Urgency of Hernia Surgery
Hernia surgery can range from being very urgent to moderately urgent depending on the severity of the hernia. Patients with a hernia that cannot be pushed back in, combined with severe pain, will likely need emergency surgery and should seek evaluation in an emergency room. Patients without severe pain may have their hernia surgically repaired within a few weeks, but should still seek medical attention as soon as possible to avoid further complications.
The Impact of Hernia Surgery on Major Surgery
Yes, hernia surgery is a major surgery. It is typically performed with the aid of either general anesthesia or local anesthesia and sedation. During the procedure, the surgeon will make one or two standard-sized incisions (three to six inches in length) to be able to access the affected area and repair the hernia. The surgery can take anywhere from one to three hours, depending on its complexity. After the operation, you will be required to stay in the hospital for a few days for observation and monitoring before being discharged.
The Dangers of Leaving a Hernia Untreated
It is not recommended to leave a hernia untreated for any length of time. The longer a hernia is left untreated, the bigger and more painful it can become. To prevent serious complications, it is important to seek medical attention wthin six hours of recognizing any signs or symptoms of a hernia. If you experience any kind of pain in your abdomen or difficulty performing everyday activities due to a lump, it is essential to see your doctor as soon as possible. Untreated hernias can cause serious problems such as tissue damage, obstruction in the intestines, and even strangulation which can be life threatening.
Death Rate from Hernia
The death rate from hernia is typically very low, ranging from 0.4 to 11%. Strangulated groin hernias, which involve the intestines becoming trapped in the hernia and cutting off blood supply, pose the greatest risk of death, as the mortality rate for this type of hernia has been reported to be as high as 11%. However, the majority of hernias are not strangulated, and therefore the overall mortality rate for all types of hernias is much lower. In addition, with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most patients can expect full recovery with no long-term complications or increased risk of mortality.
Types of Hernias
The three main types of hernias are umbilical hernia, inguinal hernia, and femoral hernia. An umbilical hernia occurs when there is a weak spot in the abdominal wall near the belly button that allows fat or part of the intestine to push through. An inguinal hernia is caused by a weakness in the lower abdomen near the groin that can allw fatty tissue or part of the intestine to protrude through. A femoral hernia occurs in the upper thigh area when fatty tissue or part of the intestine pushes through a weakened area in the abdominal wall. All three types of hernias require medical attention and can be treated with either surgery or medications depending on severity and individual circumstances.
How Long Does Hernia Surgery Take?
Hernia surgery typically takes between 30 and 45 minutes to complete, depending on the complexity of the hernia. Generally, you can expect to be able to go home on the same day after a successful hernia repair. However, some people may need to stay in hospital overnight if they have other medical conditions or if they live alone.
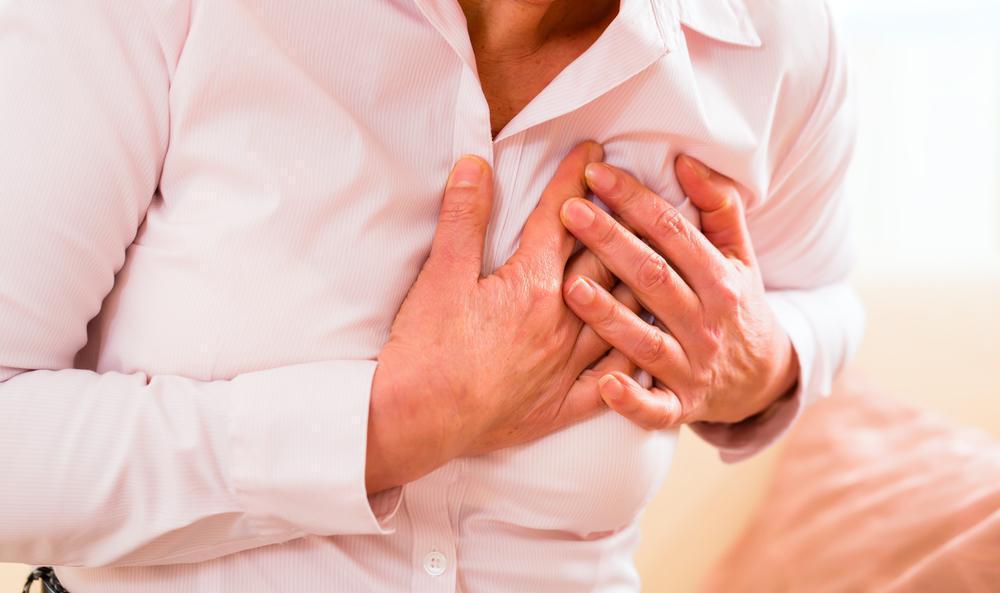
The Impact of Hernias on the Heart
Yes, a hernia can affect the heart. A large hiatal hernia is a type of hernia that can cause cardiac compression, as it can press on the posterior side of the heart. This compression may cause changes in the lower left ventricular wall, which may lead to arrhythmia pathogenesis. It is important to note that these changes usually resolve after hernia repair. It is also important to be aware of any symptoms that may indicate a hiatal hernia, such as chest pain or difficulty swallowing, so that it can be treated in a timely manner.

Living with a Hernia: Is It Possible?
It is possible to live with a hernia for your entire life, however, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with a hernia. If your hernia is not causing pain or discomfort, you may be able to manage it without surgical intervention. However, there is always the chance that the hernia cold become incarcerated or strangulated – which can be life-threatening. It is important to monitor any changes in size, shape, or pain and seek medical attention if any of these occur. If left untreated, a hernia can lead to complications such as infection and tissue death. To minimize the risk of complications, it is important to follow up with your doctor regularly and discuss any new symptoms you may experience.
Causes of Hernia
The main cause of a hernia is an increase in pressure combined with an opening, weakness, or defect in the muscle or fascia surrounding the organs or tissues. This increased pressure can be caused by a variety of factors, such as heavy lifting, obesity, pregnancy, straining during bowel movements or urination, chronic coughing, and previous surgery. In some cases, the muscle weakness that leads to a hernia is present from birth. In others, it develops over time due to aging or lifestyle activities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hernias are treatable conditions that do not go away on their own. If left untreated, the size of protruding intestine can get bigger and become strangulated which can lead to reduced blood flow to surrounding tissue and even life-threatening complications. Surgery is necessary to repair a hernia and many people are able to delay surgery for months or even years depending on the size of the hernia. In any case, it is important to consult a doctor if you suspect you may have a hernia in order to prevent further complications.
