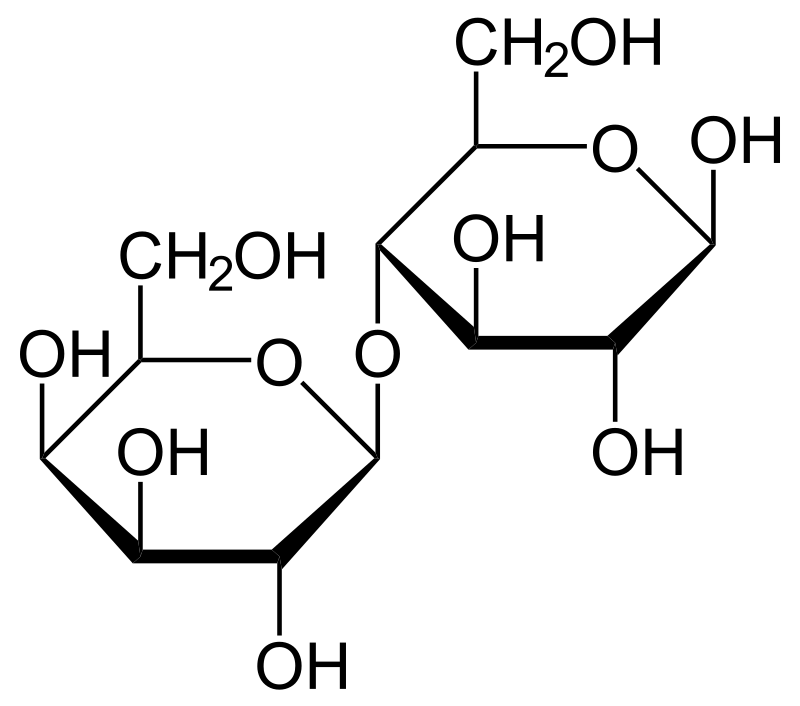
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar that is commonly found in milk and dairy products. It is composed of glucose and galactose, which are joined togethr by a β-glycosidic bond. The structure of lactose makes it a reducing sugar, which means that it has the ability to donate electrons and reduce other substances.
The reducing properties of lactose come from the presence of a hemiacetal group in the glucose moiety. This hemiacetal group can open up and form an aldehyde group, which is capable of reducing other substances. When lactose is hydrolyzed, the β-glycosidic bond is broken, and glucose and galactose are released. The glucose molecule still retains its hemiacetal group and can act as a reducing sugar.
The reducing properties of lactose have important implications in food chemistry and biochemistry. Lactose can react with amino acids and proteins in a process called the Maillard reaction. This reaction can lead to the formation of brown pigments and the development of flavor and aroma compounds in baked goods, roasted coffee, and other foods.
In addition, the reducing properties of lactose can be used in analytical chemistry to detect the presence of lactose in food and biological samples. The most common method for measuring lactose is the Fehling’s test, which involves the reduction of copper ions to cuprous oxide in the presence of lactose. The amount of cuprous oxide formed is proportional to the amount of lactose present in the sample.
Lactose is a reducing sugar because of the presence of a hemiacetal group in the glucose moiety. This property has important implications in food chemistry, biochemistry, and analytical chemistry. Understanding the reducing properties of lactose is essential for the development of new food products, the analysis of food and biological samples, and the understanding of carbohydrate metabolism in the human body.
Is Lactose A Reducing Or Nonreducing Sugar?
Lactose is a reducing sugar. A reducing sugar is a carbohydrate that undergoes a chemical reaction which reduces another molecule. In the case of lactose, it has a free aldehyde or ketone group that can react with another molecule. This reduction reaction can be detected using a simple laboratory test called the Benedict’s test, which turns from blue to red when a reducing sugar is present. Therefore, lactose can be classified as a reducing sugar.
Why Lactose Is Reducing Sugar And Sucrose Is Not?
Lactose and sucrose are two different types of disaccharides. Lactose is composed of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose linked together by a beta-glycosidic bond. On the other hand, sucrose is composed of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose linked together by an alpha-glycosidic bond.
The difference in their chemical structure is what makes lactose a reducing sugar and sucrose a non-reducing sugar. Lactose has a hemiacetal group on the glucose molecule, which can undergo oxidation to form an aldehyde group. This aldehyde group is responsible for the reducing property of lactose. Sucrose, on the other hand, has two acetal groups that cnnot be oxidized to form an aldehyde group. Therefore, it cannot act as a reducing sugar.
The presence of a hemiacetal group in lactose allows it to act as a reducing sugar, while the absence of a hemiacetal group in sucrose makes it a non-reducing sugar.
Is Lactose Or Sucrose A Reducing Sugar?
Lactose is a reducing sugar, while sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. Reducing sugars are those which can donate electrons to other molecules, while non-reducing sugars cannot. Lactose contains a free aldehyde group which can donate electrons and undergoes a reduction reaction. On the other hand, sucrose does not contain a free aldehyde or ketone group and therefore cannot donate electrons and undergo a reduction reaction. Hence, lactose is considered a reducing sugar while sucrose is classified as a non-reducing sugar.
Why Is Lactose The Reducing Sugar?
Lactose is considered a reducing sugar due to the presence of a specific functional group in its molecular structure. This functional group is a hemiacetal, which is formed when a carbonyl group (in this case, the carbonyl group of glucose) reacts with a hydroxyl group (in this case, the hydroxyl group of galactose) in the presence of an acid catalyst. The hemiacetal group is capable of donating electrons, which can reduce oter compounds by transferring electrons to them. This property of lactose is what makes it a reducing sugar. Additionally, lactose can be detected using common reducing sugar tests such as the Benedict’s test, which involves the reduction of copper ions to copper oxide in the presence of reducing sugars.
Conclusion
Lactose is a reducing sugar that is commonly found in milk and dairy products. It is composed of galactose and glucose joined togeter as a beta-glycoside, with the glucose moiety containing a hemiacetal function that allows it to act as a reducing agent. Lactose intolerance, which affects a significant portion of the population, occurs when individuals lack the enzyme lactase needed to break down lactose into its component sugars. However, lactose-free dairy products and lactase supplements are available to help individuals with lactose intolerance enjoy the nutritional benefits of milk and dairy without experiencing digestive discomfort. lactose is an important carbohydrate that plays a significant role in human nutrition and health.
