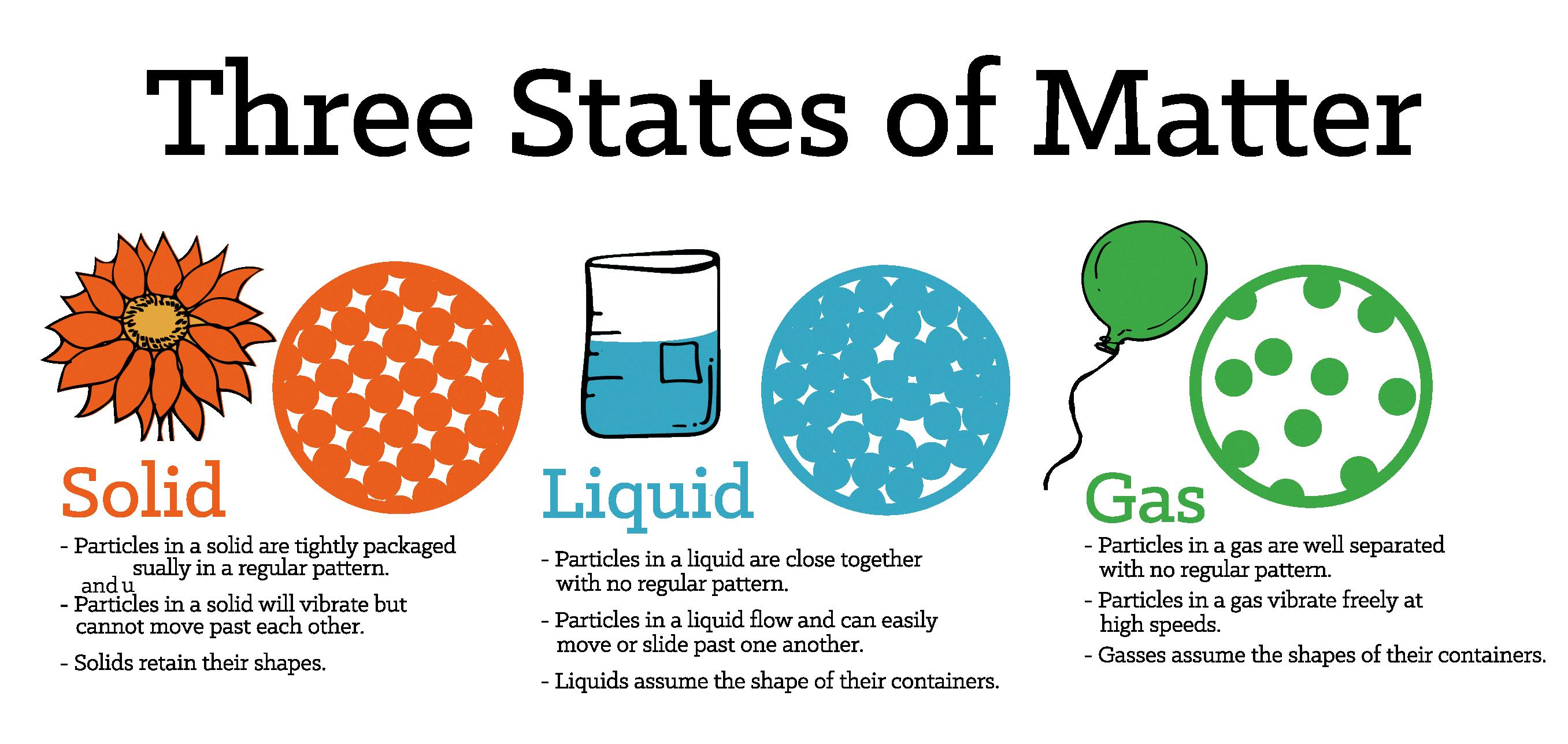
Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. It is the physical substance that makes up everything around us. There are three states of matter – solid, liquid, and gas. Each of these states has unique properties that can be explained by looking at the arrangement of their particles.
One of the most common examples of matter is the apple. When you hold an apple in your hand, you are holding matter. The apple is a solid object that has a definite shape and volume. The particles that make up the apple are tightly packed together, giving it a strong structure.
Another example of matter is a person. Just like an apple, a person is made up of matter. Our bodies are composed of different types of matter, including bones, organs, and muscles. These different types of matter work together to create a functioning human body.
A table is another example of matter. Tables are usually made of wood, which is a solid material. The particles that make up the wood are tightly packed together, giving the table a strong structure. Tables are also a good example of how matter can be shaped and molded into different forms.
Air is an example of matter that is often overlooked. Air is a gas that we can’t see or touch, but it is still matter. The particles that make up air are constantly in motion, bouncing off each other and the surfaces around them. This movement gives air its unique properties, including its ability to fill any space it is given.
Water is another example of matter that is essential to our daily lives. Water is a liquid that can take on different forms, including ice and steam. The particles that make up water are loosely packed together, giving it a fluid structure. This allows water to flow and take on the shape of its container.
A computer is an example of matter that has revolutionized the way we live and work. Computers are made up of many different types of matter, including metals, plastics, and silicon chips. The arrangement of these particles allows computers to perform complex calculations and store vast amounts of information.
Paper is another example of matter that has had a significant impact on human society. Paper is made from wood pulp, which is a solid material. The particles that make up paper are tightly packed together, giving it a strong structure. Paper can be used for many different purposes, including writing, printing, and packaging.
Iron is an example of matter that has been used for thousands of years. Iron is a solid metal that is knwn for its strength and durability. The particles that make up iron are tightly packed together, giving it a strong, rigid structure. Iron has been used to create tools, weapons, and buildings throughout human history.
Matter is all around us, and it comes in many different forms. From the apple to the computer, everything we interact with is made up of matter. Understanding the properties of matter is essential to our understanding of the world around us.
Examples of Matter
Matter refers to aything that has mass and takes up space, such as solids, liquids, and gases. Here are five examples of matter:
1. Water: Water is a liquid that takes up space and has a definite mass. It is composed of hydrogen and oxygen atoms and is essential for life.
2. Iron: Iron is a solid metal that has a definite mass and takes up space. It is one of the most commonly used metals in construction and manufacturing.
3. Air: Air is a mixture of gases that takes up space and has a definite mass. It is composed mainly of nitrogen, oxygen, and small amounts of other gases.
4. Paper: Paper is a thin material that takes up space and has a definite mass. It is made from wood pulp and is commonly used for writing, printing, and packaging.
5. Apple: An apple is a solid fruit that takes up space and has a definite mass. It is composed of various nutrients and is commonly consumed as a source of food.
Source: lsintspl3.wgbh.org
Examples of Matter
Certainly! Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Here are ten examples of matter:
1. An apple – This fruit is made up of matter, including the sugar, water, and nutrients that make it up.
2. A person – Our bodies are made up of matter, including bones, muscles, organs, and blood.
3. A table – The wood, plastic, or metal that make up a table are all examples of matter.
4. Air – Even though it’s invisible, air is composed of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide, all of which are forms of matter.
5. Water – Whether it’s in liquid form or frozen into ice, water is a type of matter.
6. A computer – All the components of a computer, from the silicon chips to the plastic casing, are examples of matter.
7. Paper – Whether it’s made from wood pulp or recycled materials, paper is a type of matter that we use evey day.
8. Iron – This metal is an example of matter, and is used in everything from construction to manufacturing.
9. Plastic – Whether it’s a water bottle or a toy, plastic is a type of matter that we encounter all the time.
10. Soil – The ground beneath our feet is made up of matter, including minerals, organic matter, and water.
I hope this helps!
Types of Matter
The three types of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. Solids are characterized by a fixed shape and volume, with particles closely packed together in a rigid structure. Liquids, on the oher hand, have a fixed volume but can take the shape of their container, with particles that are close together but able to move past one another. Gases have neither a fixed shape nor volume, with particles that are widely spaced and move independently of one another. The properties of each type of matter can be explained by looking at the arrangement of its particles, and understanding these differences is essential to understanding many aspects of the physical world around us.
Examples of Things That Do Not Matter
Matter refers to anthing that has mass and takes up space. Therefore, things that do not have mass and do not take up space are considered to be not matter. Here are 10 examples of things that are not matter:
1. Time: Time is a concept that measures the duration of events but does not have any physical presence.
2. Sound: Sound is a form of energy that travels through matter but is not matter itself.
3. Sunlight: Sunlight is a form of electromagnetic radiation that has no mass or volume.
4. Rainbow: A rainbow is an optical illusion that does not have any physical presence.
5. Love: Love is an emotion that exists in the mind and has no physical form.
6. Thoughts: Thoughts are mental processes that do not have any physical manifestation.
7. Gravity: Gravity is a force that exists between objects with mass but is not considered to be matter itself.
8. Microwaves: Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation that has no mass or volume.
9. Electricity: Electricity is a form of energy that flows through conductors but is not matter itself.
10. Magnetism: Magnetism is a force that exists between magnetic materials but is not matter itself.
Types of Matter
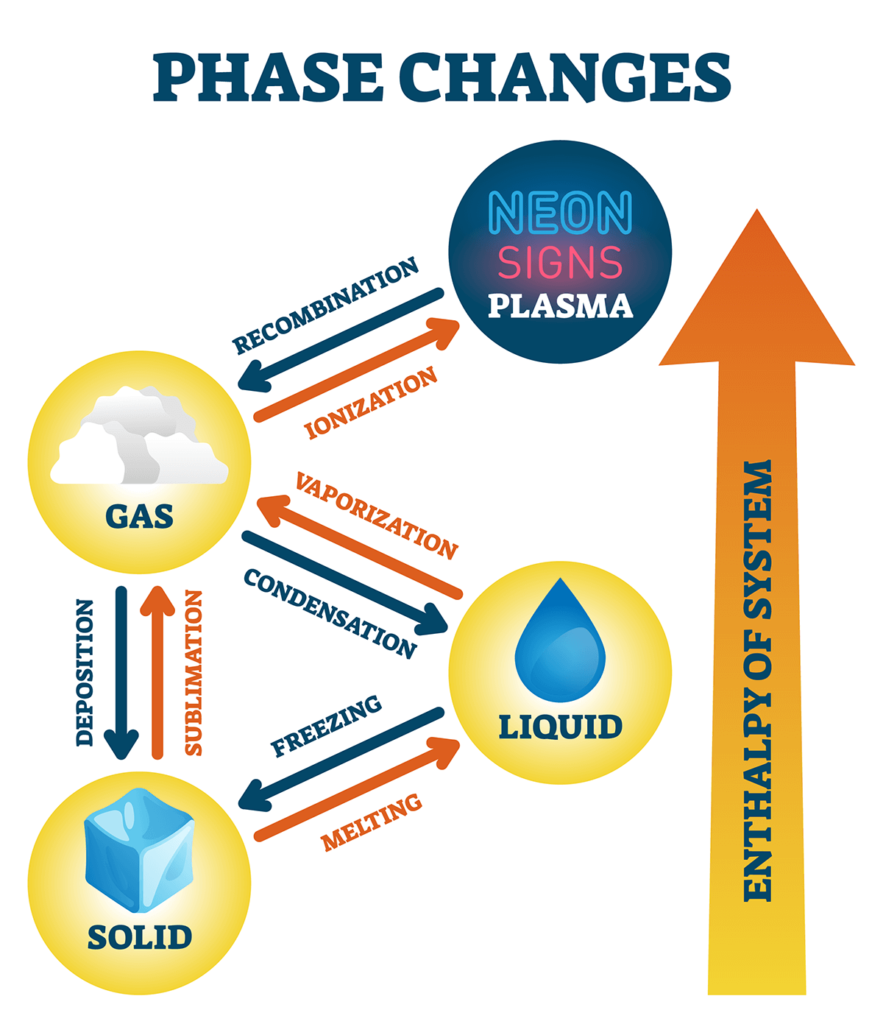
There are actually five main states of matter: solid, liquid, gas, plasma, and Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC). However, if we include two other types, we can say that there are sven types of matter. Solids are generally rigid and have a fixed shape and volume. Liquids have a fixed volume but can change shape. Gases, on the other hand, can change both their shape and volume. Plasma is an ionized gas that has free electrons and positive ions. BEC is a state of matter that occurs when atoms are cooled to near absolute zero, causing them to combine and act as a single entity. Two other types of matter that can be included are dark matter, which is thought to make up most of the matter in the universe, and antimatter, which is the opposite of regular matter and is rarely seen in nature.
Examples of Liquid
Liquids are one of the three fundamental states of matter, alongside solids and gases. They are characterized by their ability to flow and take the shape of their container. Here are 20 examples of liquids:
1. Water – a colorless, tasteless, and odorless liquid that is essential for life
2. Oil – a viscous liquid used in cooking, lubrication, and fuel
3. Petrol – a volatile liquid used as fuel for motor vehicles
4. Diesel – a heavy liquid fuel used in diesel engines
5. Mercury – a dense, silvery liquid metal that is toxic and used in thermometers and barometers
6. Blood – a red liquid that circulates in the veins and arteries of animals
7. Urine – a yellow liquid waste product excreted by the kidneys
8. Tea – a hot or cold beverage made by steeping dried leaves in water
9. Milk – a white liquid produced by female mammals for feeding their young
10. Soy sauce – a dark, salty liquid used as a seasoning in Asian cuisine
11. Vinegar – a sour liquid made from fermented alcohol
12. Lemon juice – a tangy liquid squeezed from lemons, used as a flavoring
13. Beer – an alcoholic beverage made from fermented grains and hops
14. Wine – an alcoholic beverage made from fermented grapes
15. Soda – a carbonated beverage with vaious flavors
16. Perfume – a fragrant liquid used to enhance personal scent
17. Ink – a colored liquid used for writing or printing
18. Bleach – a liquid used for cleaning and disinfecting
19. Shampoo – a liquid used for cleaning hair
20. Mouthwash – a liquid used for rinsing the mouth to freshen breath.
Examples of Gases
Sure, I’d be happy to proide a detailed answer to your question “What are 20 examples of gases?”.
Gases are one of the three states of matter, along with solids and liquids. They are substances that have no fixed shape or volume, and they can expand to fill any container they are put in. Here are 20 examples of gases:
1. Oxygen: a gas that makes up about 21% of the Earth’s atmosphere and is essential for respiration in most living organisms.
2. Nitrogen: the most abundant gas in the Earth’s atmosphere, making up about 78% of it.
3. Carbon dioxide: a gas that is produced by combustion and respiration, and is a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change.
4. Helium: a light, non-toxic, and non-flammable gas that is commonly used in balloons.
5. Hydrogen: a highly flammable gas that is used in fuel cells and as a rocket propellant.
6. Neon: a gas that is used in neon lights and is also present in the Earth’s atmosphere in trace amounts.
7. Argon: a gas that is used in welding and as a filler gas in incandescent light bulbs.
8. Methane: a gas that is produced by natural processes and is a potent greenhouse gas.
9. Chlorine: a highly reactive gas that is used as a disinfectant and in the production of chemicals.
10. Fluorine: a highly reactive gas that is used in the production of chemicals and in dental care.
11. Xenon: a gas that is used in lighting, medical imaging, and anesthesia.
12. Krypton: a gas that is used in lighting and as a filler gas in windows.
13. Radon: a gas that is radioactive and can accumulate in buildings, increasing the risk of lung cancer.
14. Sulfur dioxide: a gas that is produced by volcanic activity and by burning fossil fuels, and is a major contributor to acid rain.
15. Ammonia: a gas that is used in fertilizer production and as a refrigerant.
16. Ozone: a gas that is present in the Earth’s atmosphere and protects us from harmful UV radiation.
17. Water vapor: a gas that is present in the Earth’s atmosphere and is essential for the water cycle.
18. Carbon monoxide: a poisonous gas that is produced by incomplete combustion and can be deadly in high concentrations.
19. Nitrous oxide: a gas that is used as an anesthetic and as a propellant in whipped cream canisters.
20. Propane: a gas that is commonly used as a fuel for heating and cooking.
I hope this answer helps you better understand the wide range of gases that exist in our world!
Types of Matter
Actually, there are not 13 types of matter. However, there are 13 states of matter. The three most common states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. But there are other states of matter that exist under specific conditions. The other states of matter are:
1. Plasma: A highly ionized gas that conducts electricity.
2. Bose-Einstein condensate: A state of matter that occurs at extremely low temperatures, where particles lose their individuality and behave as one entity.
3. Fermionic condensate: A state of matter that is formed by fermions, particles with half-integer spin, under specific conditions.
4. Supersolid: A state of matter that combines the properties of a solid and a superfluid.
5. Superfluid: A fluid that has zero viscosity and can flow without resistance.
6. Quark-gluon plasma: A state of matter that is believed to exist in the first few microseconds after the Big Bang.
7. Quantum spin liquid: A state of matter that occurs in magnetic materials where the magnetic moments cnnot form a long-range order.
8. Strange matter: A hypothetical form of matter that is made up of strange quarks.
9. Photonic matter: A state of matter that is formed by photons, particles of light, under specific conditions.
10. Rydberg matter: A state of matter that is formed by Rydberg atoms, highly excited atoms, under specific conditions.
11. Dark matter: A type of matter that does not interact with light and can only be detected through its gravitational effects.
12. Antimatter: A type of matter that is composed of antiparticles, which have opposite charges to their corresponding particles.
13. Neutronium: A hypothetical form of matter that is made up of neutrons and exists in the cores of neutron stars.
Types of Matter
The nine types of matter are superconductor, superfluid, Bose-Einstein condensate, fermionic condensate, Rydberg molecule, quantum Hall state, photonic matter, dropleton, and dark matter.
Superconductors are materials that can conduct electricity with zero resistance at very low temperatures, making them useful for applications such as MRI machines and particle accelerators.
Superfluids are liquids that can flow without any friction, even at very low temperatures, and are used in experiments to study quantum mechanics.
Bose-Einstein condensates are a state of matter where a group of bosons (particles with integer spin) collapse into the same quantum state, resulting in a single entity with remarkable properties such as coherence and interference effects.
Fermionic condensates are similar to Bose-Einstein condensates, but they are made up of fermions (particles with half-integer spin), whih are subject to the Pauli exclusion principle.
Rydberg molecules are formed by binding a Rydberg atom (an atom in an excited state) to another atom or molecule, resulting in a molecule with unusual properties.
Quantum Hall states are a phenomenon that occurs in two-dimensional systems under strong magnetic fields, where electrons start to behave as if they are divided into “quanta” of charge, resulting in a quantized Hall resistance.
Photonic matter is a type of matter made up of photons, the particles that make up light. Photonic matter has been used in experiments to create new types of materials and to study quantum mechanics.
Dropletons are a type of quasiparticle that can form in semiconductors under special conditions, consisting of a hole (a missing electron) and a cloud of electrons.
Dark matter is a hypothetical type of matter that does not interact with light or any other form of electromagnetic radiation, but is thought to make up a significant portion of the universe’s mass.

Examples of Solids
Certainly! Solids are one of the three common states of matter, alog with liquids and gases. They are characterized by having a definite shape and volume, meaning they maintain their shape and occupy a fixed amount of space. Here are three examples of solids:
1. Diamond: This is a naturally occurring mineral that is made up of carbon atoms arranged in a crystalline structure. Diamond is one of the hardest substances known to man, making it ideal for use in cutting tools and other applications.
2. Iron: This metal is commonly found in the earth’s crust and is used in a wide variety of applications, from construction to manufacturing. It is known for its strength and durability, making it an ideal material for use in buildings, bridges, and other structures.
3. Salt: This is a crystalline solid that is commonly used in cooking and food preservation. It is made up of sodium and chloride ions and is typically found in the form of small white crystals. Salt is also used in a number of industrial applications, such as water treatment and chemical production.
Types of Matter
The four most common types of matter are solids, liquids, gases, and plasma. Solids are defined as having a definite shape and volume, with particles that are closely packed together and have a fixed position. Liquids, on the other hand, have a definite volume but not a definite shape, with particles that are more loosely packed and able to move around each other. Gases have neither a definite shape nor a definite volume, with particles that are widely spaced and in constant random motion. plasma is a state of matter that occurs at very high temperatures, where the atoms become ionized and the gas becomes electrically conductive. While these are the most common states of matter, thee are other, more exotic states that can occur under extreme conditions, such as Bose-Einstein condensates and superfluids.
Is Air a Form of Matter?
Air is matter. It has physical properties such as weight, takes up space, and is composed of particles that are too small and too spread apart to see. Air is a mixture of gases, which shares properties with water vapor, the gaseous form of water that is also part of the air. Therefore, air can be considered matter like solids and liquids.
Is Light Considered Matter?
Light is not an example of matter. Matter is made up of particles that have mass and volume, while light exists in the form of tiny packets called photons. Photons have no rest mass and do not occupy any volume, which means they do not exhibit the characteristics of matter. Additionally, matter can be classified into vrious categories based on their physical and chemical properties, but light cannot be classified in this way as it does not possess these properties. Therefore, light is not considered as matter, but instead, it is a form of energy that can travel through space in a wave-like manner.
Is Water a Form of Matter?
Water is a form of matter. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Water is a substance that has mass and occupies space, which makes it a form of matter. It is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, and it can exist in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. In its solid state, water is kown as ice and has a fixed shape and volume. In its liquid state, water takes the shape of its container and has a fixed volume. In its gaseous state, water is known as water vapor and can fill any container it is placed in. Therefore, water is a form of matter that can exist in different states depending on its temperature and pressure conditions.
Conclusion
Matter is all around us and can be defined as anything that has mass and takes up space. It exists in three states- solid, liquid, and gas, which can be explained by looking at the arrangement of their particles. Examples of matter include everyday objects like an apple, a table, and iron, as well as substances like water and air. It is important to note that there are also things that are not considered matter, such as time, sound, and thoughts. Understanding the properties and states of matter is crucial in many fields, including chemistry and physics, and helps us beter understand the world we live in.
