Water is a vital molecule for all living organisms on this planet. It is crucial for various biological processes like hydration, transportation of nutrients, and even for the production of energy. However, did you know that water is also produced during a process called cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process that occurs in all living cells, including plants and animals. The process involves the breakdown of glucose to produce energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). The energy produced during cellular respiration is essential for various biological processes that occur in living organisms.
During cellular respiration, water is produced in the final stage, knwn as the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. It is responsible for the transfer of electrons from NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and FADH2 (flavin adenine dinucleotide) to oxygen. This transfer releases energy, which is used to produce ATP.
The process of water production during cellular respiration is simple. NADH and FADH2 pass the electrons they carry as hydrogen atoms onto the electron transport chain in mitochondria. These electrons are then passed down the chain, and as they do so, they release energy. This energy is used to pump protons (H+) across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating an electrochemical gradient.
The protons that are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane then flow back into the mitochondrial matrix through an enzyme called ATP synthase. As the protons flow through the ATP synthase, they cause the enzyme to rotate, which in turn, causes the production of ATP. The oxygen that was transferred to the electron transport chain combines with the protons and electrons to form water (H2O).
Water production is a crucial part of cellular respiration. It occurs during the final stage of the process, known as the electron transport chain. The electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 are passed down the chain, releasing energy, which is used to produce ATP. As a result, protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane, creating an electrochemical gradient. The protons then flow back into the mitochondrial matrix through the ATP synthase, causing the production of ATP, and the oxygen combines with protons and electrons to produce water. This process is essential for the production of energy, which is vital for various biological processes in living organisms.
Production of Water During Cellular Respiration
Water is produced in the final stage of cellular respiration, which is known as the electron transport chain. This process takes place in the mitochondria of cells. During the earlier stages of respiration, glucose is broken down into pyruvate, which is then converted into acetyl-CoA. This molecule is then used in the Krebs cycle, which generates energy in the form of ATP.
However, the electron transport chain is were the majority of ATP is produced, and it is also where water is formed. NADH and FADH, which are molecules that carry electrons and protons, pass these along to the electron transport chain. The electrons are then used to generate a proton gradient, which ultimately powers the production of ATP.
As the electrons are passed along the chain, they combine with oxygen molecules to form water. Specifically, two electrons and two protons combine with an oxygen molecule to form two molecules of water. This reaction is crucial for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis, as it helps to regulate both the pH and the overall fluid balance of the cell. Therefore, water production during cellular respiration is a critical process for the survival of all living organisms.
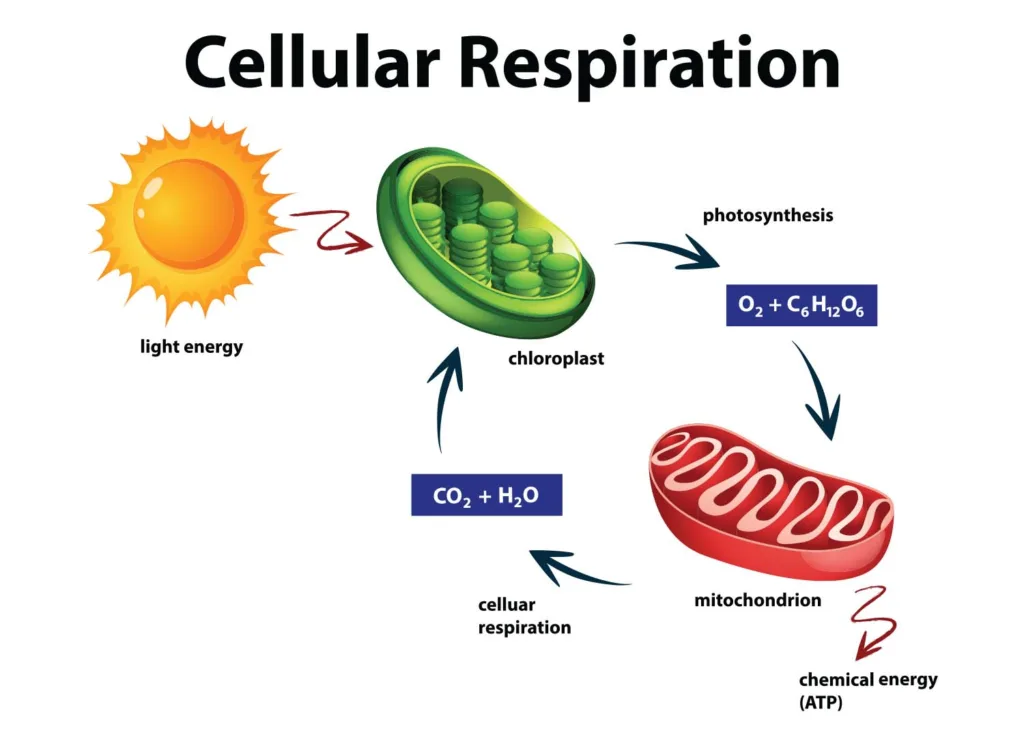
Does Anaerobic Respiration Produce Water?
Water is not produced in anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration is a metabolic process that occurs in the absence of oxygen. During anaerobic respiration, glucose is broken down to release energy without the involvement of oxygen. The end product of anaerobic respiration is typically lactic acid or ethanol, depending on the organism. Unlike aerobic respiration, which produces water as a byproduct, anaerobic respiration does not involve the reduction of oxygen to form water. Therefore, no water is produced in the process of anaerobic respiration.
Is Glycolysis a Source of Water?
Water is a product of glycolysis. During the process of glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, whih results in the production of four molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Additionally, two molecules of NAD+ are reduced to NADH, which releases two hydrogen ions (H+) into the cytoplasm. These hydrogen ions combine with two molecules of oxygen (O2) to form two molecules of water (H2O). Therefore, the net equation for glycolysis is: glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi → 2 pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 ATP + 2 H2O. As we can see, the production of water is an integral part of the glycolytic pathway.
The Role of Water in Cellular Respiration
Water is a by-product of cellular respiration. During the process of cellular respiration, glucose and oxygen are combined in a series of chemical reactions that release energy. One of the by-products of these reactions is water. Specifically, during the electron transport chain, oxygen molecules are used to produce water molecules, which are released as waste products. Therefore, water is an essential by-product of cellular respiration, and its production is critical to the proper functioning of living organisms.
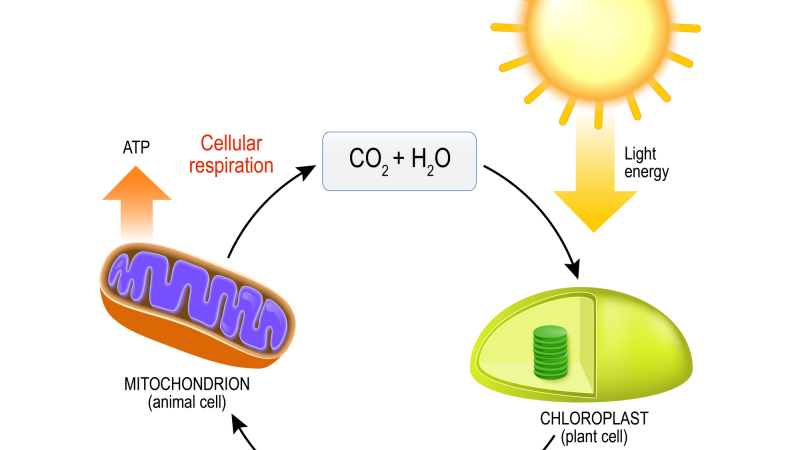
The Production of Water in Photosynthesis and Respiration
Water is produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis, not respiration. During photosynthesis, plants use energy from sunlight to combine carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen gas. The oxygen gas is released into the atmosphere as a waste product, whie the glucose is used by the plant as a source of energy. As a result of this process, water molecules are broken down and their hydrogen atoms are incorporated into the glucose molecule, while the oxygen atoms are released as a gas. On the other hand, during respiration, glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen to release energy, carbon dioxide, and water as byproducts. Therefore, while both photosynthesis and respiration involve the use and production of water, water is produced only during photosynthesis as a byproduct of the chemical reaction.
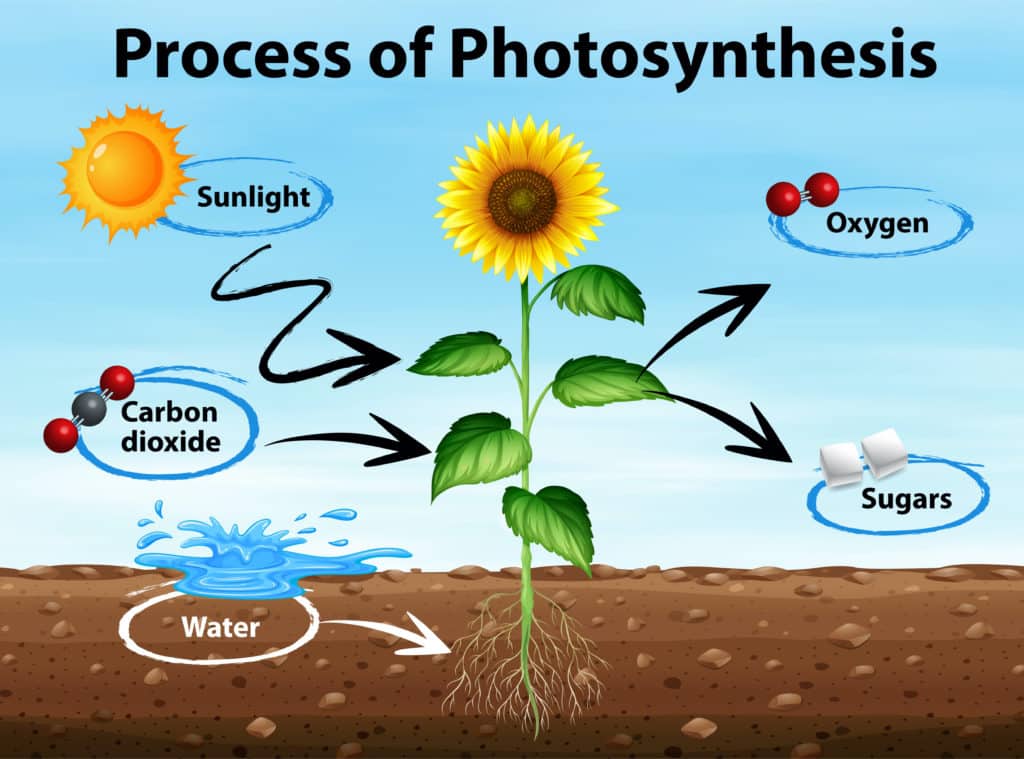
Production of Water During Photosynthesis
The stage of photosynthesis that produces water is the light-dependent reactions, wich occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. During this stage, light energy is absorbed by pigments called chlorophyll, which initiates a series of chemical reactions that ultimately split water molecules into oxygen, protons (H+), and electrons. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere, while the protons and electrons are used to create energy-rich molecules such as ATP and NADPH. This process, known as photolysis, is essential for providing the electrons needed to power the subsequent stages of photosynthesis. Therefore, it can be concluded that water is a crucial ingredient for the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, as it provides the electrons necessary to generate energy and convert carbon dioxide into organic molecules.
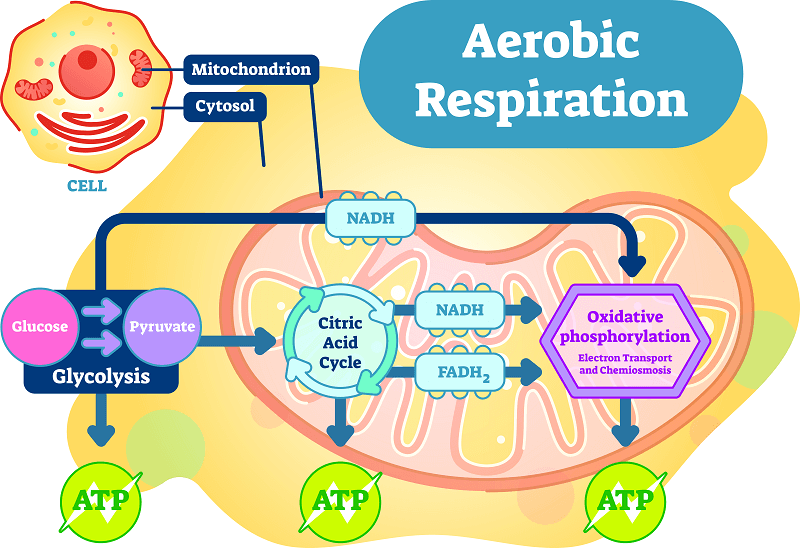
Does Aerobic Respiration Produce Water?
Water is produced durig aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is a metabolic process that occurs in the presence of oxygen and involves the breakdown of glucose to form carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (adenosine triphosphate)- the energy currency of cells. During the process, the oxygen is used to accept electrons from the glucose molecule, forming water molecules as a byproduct. The chemical equation for aerobic respiration is C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (ATP). Therefore, the production of water is an essential part of aerobic respiration, and it plays a crucial role in the maintenance of cellular homeostasis.
Does Aerobic Respiration Produce Water?
Water is produced as a byproduct of aerobic respiration. During the process, oxygen combines with electrons and hydrogen ions produced in the electron transport chain to form water molecules. This reaction is known as oxidative phosphorylation and occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotic cells. Specifically, the electrons and hydrogen ions combine with oxygen to form water in the final step of the electron transport chain. Thus, the oveall equation for aerobic respiration can be written as:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP
Therefore, water is an essential byproduct of aerobic respiration and plays a critical role in maintaining the cell’s homeostasis.
Does Aerobic Respiration Use Water?
Water is used in aerobic respiration. During the process of aerobic respiration, glucose is oxidized, and its energy is used to power the production of ATP. One of the by-products of this process is water, which is generated when oxygen molecules accept electrons at the end of the electron transport chain. Specifically, oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, and its reduction to water is a critical step in the process of aerobic respiration. Therefore, water is an essential component of aerobic respiration, and its production is necessary for the efficient generation of ATP.
Does Fermentation Produce Water?
Fermentation produces water. During the process of fermentation, glucose is converted into energy (in the form of ATP) and waste products such as ethanol and CO2. However, water is also produced as a byproduct of the reaction. This occurs because glucose is made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, and during fermentation, these atoms are rearranged to form ethanol, CO2, and water. Specifically, two molecules of water are produced for every molecule of glucose that undergoes fermentation. Therefore, water is an important byproduct of the fermentation process.
Glycolysis: What Is Produced?
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate. During this process, two ATP molecules are consumed, and in return, four ATP molecules are produced, resulting in a net gain of two ATP molecules. Additionally, two NADH molecules are produced, which can be used in the electron transport chain to generate more ATP molecules. two pyruvate molecules are produced, which can be utilized in the citric acid cycle to produce even more ATP or serve as a precursor for other metabolic pathways. glycolysis produces ATP, NADH, and pyruvate, which are essential for various cellular functions.
Glycolysis: Three Products
During glycolysis, three things are produced: two molecules of ATP, two molecules of NADH, and two molecules of pyruvate. ATP is the primary energy currency of the cell and is used for a variety of cellular processes. NADH is an electron carrier that is used to produce more ATP in later stages of cellular respiration. Pyruvate is a three-carbon molecule that can be further processed in the citric acid cycle to produce more ATP. Therefore, these three products of glycolysis play important roles in cellular energy production.
The Products of Cellular Respiration
During cellular respiration, glucose is broken down into smaller molecules such as pyruvate, whch then enter a series of chemical reactions that ultimately produce ATP. ATP is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells, and is used to power a wide range of biological processes, such as muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and biosynthesis. In addition to ATP, cellular respiration also produces carbon dioxide and water as waste products, which are eliminated from the body through breathing and other metabolic processes. cellular respiration is a crucial metabolic pathway that allows organisms to efficiently generate the energy they need to survive and thrive.
Formation of Products During Anaerobic Respiration
During anaerobic respiration, the product formed is lactic acid. Anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen. It involves the breakdown of glucose molecules to release energy for the cell’s metabolic processes. However, since thre is no oxygen available, the process does not proceed through the usual aerobic pathway. Instead, it uses an alternative pathway that involves the conversion of pyruvate into lactic acid. This process is commonly observed in muscles during strenuous physical activity when the oxygen supply cannot meet the energy demands of the body. So, lactic acid is the primary product of anaerobic respiration, and it can accumulate in the tissues, leading to muscle fatigue and soreness.
Conclusion
Water production is an essential process that occurs at the final stage of cellular respiration, known as the electron transport chain. This process involves the transfer of electrons carried by NADH and FADH to the electron transport chain in mitochondria, leading to the formation of water molecules. While water is a crucial by-product of cellular respiration, other by-products such as carbon dioxide also play a vital role in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. Understanding the process of water production is crucial in comprehending how living organisms derive energy from food and how they interact with their environment. water production is a remarkable process that highlights the intricate nature of cellular respiration and its role in sustaining life on earth.
