Welcome to a discussion on critical theory examples! Critical theory is an approach to studying and analyzing social, cultural, economic, and political structures. It is used to expose and challenge the power structures that exist in societies. The aim of critical theory is to bring about positive change through exposing the underlying assumptions that keep people from understanding how the world works.
One of the most commonly used critical theories is Marxism. This approach focuses on class struggle and aims to create an egalitarian society by eliminating inequality among classes. Another example of a critical theory is Postmodernism. This approach looks at culture and identity in a different way than traditional theories do by challenging existing definitions of culture, identity, and power. Finally, Feminism is another example of a critical approach which seeks to challenge gender inequalities that exist in society today.
The four major types of critical theories are Mimetic Theory, Pragmatic Theory, Expressive Theory, and Objective Theory. Each type of theory has its own unique focus and goals for analyzing society. For example, Mimetic Theory looks at how groups imitate one another in order to gain power or influence over others. Pragmatic Theory examines how language shapes our understanding of reality while Expressive Theory looks at how emotions shape our behavior and responses. Lastly, Objective Theory focuses on uncovering the truth behid social problems rather than attempting to explain them away with personal assumptions or biases.
Critical theory can be applied to various contexts such as politics, literature, sociology, philosophy, art and more. By using this approach we can gain insight into how certain power structures operate in society and come up with solutions for creating a more just society where everyone has equal rights and opportunities regardless of their background or identity.
We hope this blog post has provided you with some useful information on critical theory examples! If you would like to learn more about this topic please feel free to check out our other blog posts or contact us directly for more information!
The Principles of Critical Theory
An examle of critical theory is Marxism. Marxism is a form of social and economic thought developed by Karl Marx, which examines the relationship between power and production in society. It seeks to uncover the ways in which existing social and economic structures are oppressive and exploitative, as well as to identify solutions for creating a more equitable society. Marx’s theory argues that power relations between different classes (such as workers and capitalists) are the root cause of much of the world’s suffering and inequality, an idea that has been widely influential in the development of movements such as socialism and anarchism.

An Overview of the Four Major Critical Theories
Mimetic Theory: This literary theory suggests that literature should reflect the reality of life, and it is the author’s responsibility to accurately portray this reality. The author should strive to create a realistic representation of life, and the reader should be able to relate to the characters and situations presented in the text.
Pragmatic Theory: This critical theory suggests that literature has a purpose beyond merely entertaining its readers. Pragmatic theorists believe that literature can have an impact on society, and there should be an aim bhind a work of literature. This theory asserts that the author must consider how their work will affect their audience when creating a story.
Expressive Theory: This critical theory focuses on how authors use language as a tool for self-expression. It explores how authors use language to convey their emotions, thoughts, and beliefs about life and society. Expressive theorists also focus on how readers interpret these expressions through their own experiences, perspectives, and cultural backgrounds.
Objective Theory: This critical theory holds that literature exists independently from its creator or audience. The author’s intent or opinion is not important; instead, objective theorists focus on what is actually written in the text itself – exploring themes, symbols, characters, etc., without considering any outside factors such as the author’s background or personal opinions.
Exploring the Ideas of Critical Theory
Critical theory is a type of social philosophy that examines how power structures, such as those found in institutions, laws, and social practices, shape and influence our lives. It seeks to identify areas of injustice and oppression, challenge accepted norms and values, and ultimately work towards social transformation.
Core ideas of critical theory include the recognition that society is shaped by power dynamics which can lead to inequality; the importance of understanding history in order to beter understand the present; exploring how language shapes our understanding of reality; and that knowledge is socially constructed.
In addition, critical theorists examine how systems of domination are perpetuated through the media, education systems, politics, economics, and other aspects of society. They believe that people can work together to change oppressive systems through collective action and solidarity amongst oppressed groups. Critical theory also emphasizes creating more inclusive knowledge systems which recognize diverse perspectives from marginalized groups.
The Use of Critical Theory
Critical Theory is used to challenge the status quo and to promote social change. It seeks to uncover the hidden structures of power that shape our lives, oftn in ways we are unaware of or unable to see. Critical Theory attempts to bring light to the ways in which inequality and oppression shape our society and how these forces can be challenged. It is a tool for understanding how power works, both at an individual and group level, so that positive changes can be made. Critical Theory is also used to analyze language, culture, history, and politics in order to better understand our world. Through this analysis, we can gain insight into how societies are structured and maintained as well as identify potential areas for reform.
Types of Critical Theories
Marxism: This critical theory is based on the works of Karl Marx, who argued that society is divided into two classes: the bourgeoisie, who owns the means of production (capital), and the proletariat, who proide labor for production. Marxism seeks to explain how these two classes interact and how this interaction affects social and economic outcomes.
Postmodernism: This critical theory rejects grand narratives and essentialist beliefs in favor of a more nuanced understanding of power dynamics in society. Postmodernists view the world as fragmented and in constant flux, with each individual having their own unique experience. They also reject traditional notions of truth and objectivity in favor of emphasizing subjective interpretations.
Feminism: This critical theory examines how gender shapes our lives and relationships. Feminists believe that women have historically been excluded from social, economic, and political power structures, resulting in a patriarchal system that favors men over women. Feminists strive to create a more equitable world by challenging existing gender norms and advocating for women’s rights.

Applying Critical Theory in the Classroom
Critical theory can be applied to the classroom in a variety of ways. Teachers can encourage students to become aware of and question the societal status quo by using activities that help them recognize and challenge existing power structures, such as role play, discussion, and research projects. Critical pedagogy also encourages teachers to use their own enlightenment to facilitate critical reflection in their students, which involves asking questions that encourage students to consider why things are the way they are and what could be done differently. This could involve exploring topics such as gender roles, racial bias, or economic inequality in greater detail. Additionally, teachers can invite guest speakers or incorporate multimedia into their lessons to provide additional perspectives on these issues. Finally, teachers should also make sure that their classrooms provide an environment were all students feel safe and comfortable expressing themselves honestly without fear of judgment or ridicule.
The Role of Critical Theory in Education
Critical theory in education is an approach to teaching that focuses on challenging existing power structures and questioning assumptions about knowledge and learning. It uses a variety of methods to explore how social and cultural systems intersect with educational practices in order to ensure that people from all backgrounds have access to quality education. Critical theories of education bring attention to issues of power, privilege, and oppression, and seek to empower marginalized voices within the educational system. By examining these issues, critical theorists hope to create more equitable learning environments.
The core concepts of critical theory in education include:
– liberatory pedagogy: A focus on liberating learners from oppressive structures, promoting student agency and self-determination
– transformative praxis: Engaging in critical dialogue around the purpose of education, transforming values and practices based on this dialogue
– praxis cycle: A cycle of reflection and action that promotes transformative learning
– emancipatory discourse: Examining how language can be used for oppressive or emancipatory purposes
– cultural capital: Examining how knowledge is constructed through culture, race, gender, sexuality, class, etc.
– intersectionality: Examining the intersections between different forms of oppression
– decolonizing knowledge: Unpacking colonial narratives embedded within knowledge production
– critical literacy/media literacy: Examining the messages behnd texts/media consumed by students
Overall, critical theory in education is an approach that seeks to challenge existing power structures while providing students with the tools they need to become empowered agents in their own learning process.
Types of Theories
The first type of theory is classical literature in sociology. This includes the works of classic sociologists such as Karl Marx and Max Weber, wich provide a historical perspective on social issues and their evolution over time. It is primarily concerned with understanding how society functions and how it might be changed.
The second type of theory is sociological criticism. This approach looks at how social systems are flawed or oppressive and seeks to identify potential solutions or improvements. It is often used to critique existing power structures or inequalities in society, such as gender or racial discrimination.
The third type of theory is taxonomic theory. This type of theory examines the various categories of social phenomena and the relationships between them. It can be used to identify patterns and trends in society, as well as to develop more accurate models for predicting social outcomes.
Finally, there is scientific theory, which uses empirical data to test hypotheses about the causes and effects of different social events. Scientific theories are based on rigorous methods for collecting data, analyzing it, and drawing conclusions from it that can be tested against real-world evidence. This approach provides a more objective way to study social phenomena than the other types of theories mentioned above.
Exploring the Meaning of a Major in Critical Theory
A major in critical theory is an interdisciplinary field of study that examines the ways in which power, conflict, and crisis are constituted, reproduced, and transformed through various social and cultural practices. Students will explore the relationships between social conditions, power structures, and individual subjectivity. They will learn how to analyze the underlying mechanisms of domination and oppression in society and develop strategies for emancipation. Through thir studies, students become equipped with a deep understanding of how people understand their own identities within larger systems of oppression. In addition to core courses focused on critical theory, students may also take courses in literature, sociology, anthropology, history, gender studies, media studies and communication studies to gain a more holistic view of how power works in different contexts.
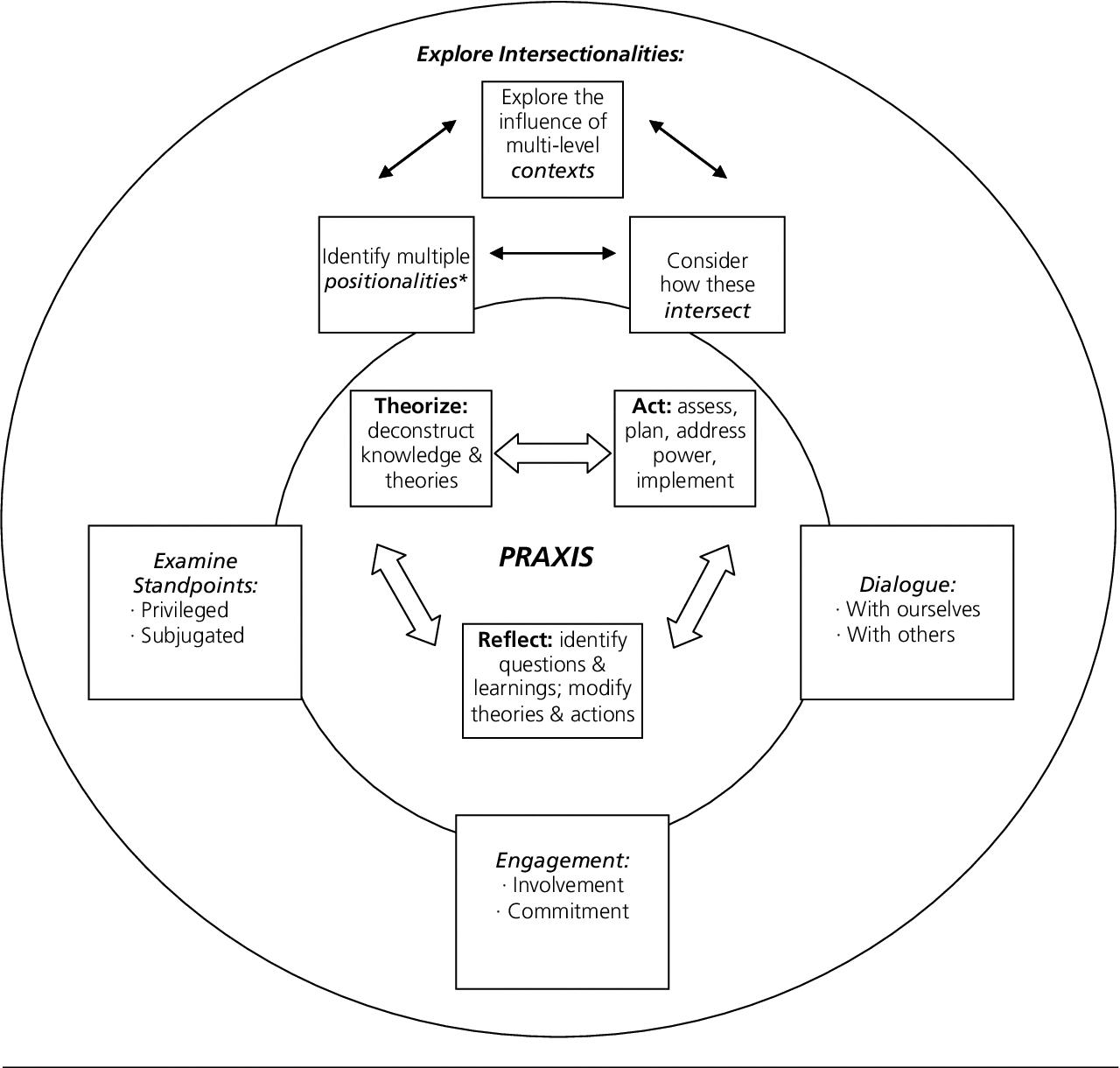
Source: semanticscholar.org
The Importance of Critical Theory to Students
The importance of critical theory to students lies in its ability to help them overcome educational barriers. Critical theory provides a framework for understanding educational, social, and economic inequalities, and how they can be addressed through equitable opportunities in the classroom. It emphasizes the importance of creating an environment where all students have access to the same resources and experiences, regardless of their background or circumstances. By doing so, it encourages students to think critically about their experience, reflect on their own perspectives, and develop strategies for improving their own performance. Ultimately, this helps students become more empowered and independent thinkers who are beter equipped to succeed in today’s increasingly complex world.
The Theory of Critical Thinking
Critical Thinking Theory is a philosophical approach to analyzing, understanding, and evaluating ideas and arguments. It involves the use of logic and reason to identify flaws, inconsistencies, and false assumptions in any argument or set of beliefs. Critical Thinking Theory seeks to challenge existing beliefs and assumptions in order to arrive at more accurate conclusions. This form of thinking encourages the exploration and questioning of knowledge, assumptions, and preconceptions about the world in order to develop a deeper understanding of how thngs work. The goal is to identify and evaluate evidence from multiple sources in order to make sound judgments about the truth or validity of any claim or statement. Critical Thinking Theory is an essential tool for problem solving, decision making, and creating new knowledge.
Exploring the Critical Theory Paradigm
Critical theory paradigm is an interdisciplinary approach to understanding the workings of power and domination in society. It seeks to uncover the underlying structures and processes that produce social inequality, injustice and oppression. This paradigm uses a variety of methods, including critical analysis, discourse analysis, psychoanalysis, and historical materialism to analyze social problems from a critical perspective. The goal of critical theory is to challenge existing power structures in order to create more equitable and just societies. Critical theorists often focus on how structures of race, class, gender, sexuality, nationhood and other axes of identity intersect with power dynamics in order to better understand the ways in which oppression works. They also examine how media representations contribute to the production of dominant ideas aout who is worthy or unworthy of respect, rights or privileges in society. Thus, critical theory is concerned with examining how existing social systems reproduce inequality and injustice while proposing solutions that can lead to a more just future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, critical theory is a powerful tool to challenge and critique the communication of dominant social, economic, and political structures. There are four major critical theories in literature which are Mimetic theory, Pragmatic theory, Expressive theory and Objective theory. Examples of critical approaches include Marxism, postmodernism, and feminism, all of which seek to expose and challenge the power structures that exist in society. By using critical theories to analyze our social life we can better understand the underlying assumptions that keep us from fully understanding our world. Ultimately, critical theory provides us with an invaluable resource for understanding and changing our society for the better.
