BD PROCHOT, also known as Thermal Control Circuit, is an important feature in Intel Pentium 4 processors that helps prevent the CPU from overheating. It works by underclocking the processor when it reaches a certain temperature, allowing it to maintain a safe operating temperature without sacrificing performance. While the feature is enabled by default on Intel Pentium 4 processors, some users may choose to disable it using software like Throttlestop.
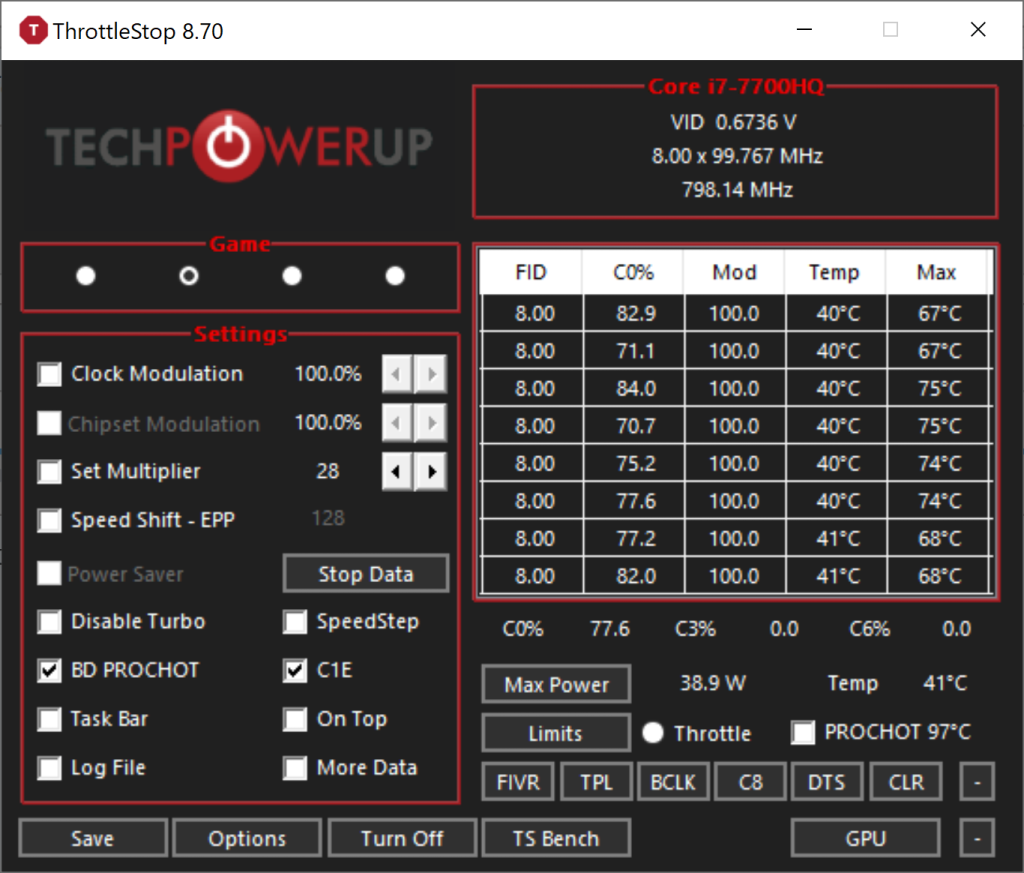
To disable BD PROCHOT using Throttlestop, open the program and click “CPU Cache” in the FIVR Control area in the top middle of the window. Then set the Offset Voltage to 0. This will clear MSR 0x1FC bit[0], which is the bit that controls BD PROCHOT. The value in MSR 0x1FC should be an even number before writing back to this same register.
Disabling BD PROCHOT can be beneficial for users who want to squeeze out maximum performance from their systems or those who are overclocking their CPUs. However, disabling this feature coms with some risks such as high temperatures and potential hardware damage if not done properly. So, if you decide to disable BD PROCHOT, make sure you understand how to do it correctly and keep an eye on your CPU’s temperatures at all times. Additionally, you should also consider undervolting your CPU with Throttlestop for better performance and power savings.
Overall, BD PROCHOT is an important safety feature that can help protect your processor from overheating and potential hardware damage caused by high temperatures. If you want to squeeze out maximum performance from your system or are interested in overclocking your CPU then disabling this feature might be beneficial but make sure you understand how to do it correctly before proceeding.
What is BD Prochot?
BD Prochot, or ‘Bi-Directional Processor Hot’, is a safety feature built into many CPUs. It helps to prevent overheating by monitoring the temperature of the CPU and reducing its clock speed when temperatures exceed a certan threshold. This helps to keep your system running in a safe environment and prevents any potential damage due to excessive heat. By reducing the clock speed, it also reduces the amount of energy consumed and improves system efficiency. Thus, BD Prochot can help you save power and money in the long run. All in all, it is an important feature for keeping your CPU running safely and efficiently.
What is Prochot and How Does It Work?
Prochot (PROcessor HOT) is a digital output pin on Intel’s Pentium 4 processors that indicates the internal Thermal Control Circuit has been activated. This occurs when the processor reaches its maximum safe operating temperature and is intended to protect the processor from heat-related damage. The Prochot signal activates a power throttling feature, whch reduces the power consumption of the processor in order to reduce its temperature. This helps to ensure that the processor does not overheat and allows it to operate safely.
Disabling BD Prochot in Ubuntu
In order to disable BD Prochot on Ubuntu, you’ll need to first open a terminal window and enter the folowing commands:
1. Execute the command `sudo su` to become root user.
2. Next, execute the command `rdmsr 0x1FC` which will read the value from MSR 0x1FC.
3. Subtract 1 from this value to make it an even number and then execute the command `wrmsr 0x1FC ` to write the new value back to MSR 0x1FC. This will clear bit[0] of MSR 0x1FC which controls BD Prochot and disable it.
4. Finally, exit from root user by executing the command `exit`.
Once all of these steps have been completed, BD Prochot should be disabled on your Ubuntu system.
Limiting CPU Speed with ThrottleStop
ThrottleStop is a great tool if you want to limit the speed of your CPU. To do this, first click on the “FIVR Control” tab at the top of the window. Next, set the ‘Turbo Ratio Limits’ to something lower than what it is currently set to. This will limit your processor speed. You can also use the ‘Power Saver’ option undr FIVR Control which will reduce your CPU voltage and prevent it from reaching its highest speeds. Lastly, you can use the ‘Limit Reasons’ tab to specify what types of tasks should be limited by ThrottleStop. Once you have configured these settings, click “Apply” or “OK” to save your changes. That’s all there is to it!
Should BD Prochot Be Enabled or Disabled?
It is not recommended to permanently disable BD Prochot as it is an important part of the OS. It helps prevent your CPU from burning out by causing it to throttle down when temperatures get too high. However, if you are uing a non-genuine battery or charger then Throttle Stop may be the best way forward. Ultimately, it’s up to you to decide what works best for your device and usage.
Understanding the Prochot Offset
PROCHOT Offset is a feature designed to reduce the maximum temperature of your CPU. It works by offsetting the maximum temperature that is specified by the chip manufacturer by a certain amount. For example, if Intel sets the maximum temperature to 100°C, setting a PROCHOT offset of 5 means that your CPU will try to maintain an upper limit of 95°C by throttling its performance. This helps to ensure that your CPU does not run too hot and risk thermal damage.
Raising Prochot
The PROCHOT (or Processor Hot) temperature is a thermal threshold that controls the maximum temperature of your CPU. When the processor reaches this temperature or higher, it throttles down to prevent damage to the components.
To raise your PROCHOT temperature, you’ll need to adjust a few settings in your computer’s BIOS. First, open up the BIOS and navigate to the Options menu. At the bottom of the main window, you’ll see two options relted to PROCHOT: one for setting the offset and one for enabling or disabling it.
Tick both options, then enter an offset value that is lower than your current PROCHOT temperature. For example, if your factory PROCHOT is set at 100C, entering a 10 would lower it to 90C. Once you have set the offset value, save your changs and exit out of BIOS. Your new PROCHOT target should now be active and take effect when needed.
The Benefits of Running ThrottleStop
Yes, you can and shoud keep ThrottleStop running if you are looking to maintain the voltage settings you have adjusted. It does not take up much CPU or memory usage so it is safe to leave running. Doing this will ensure that the voltage changes you make will stay in effect without needing to be reset after a sleep/resume cycle.
Stopping Thermal Throttling with ThrottleStop
To stop ThrottleStop thermal throttling, you will first need to identify whih of the power limits are being throttled. To do this, open ThrottleStop’s “TS Bench” and set the size to 1024M. Start the TS Bench and then open the “Limits” window. If any of the PL’s light up, then you are experiencing power limit throttling.
Once you have identified which power limits are being throttled, you can disable them by unchecking the boxes next to each power limit in the “Limits” window. This will disable those power limits and should prevent ThrottleStop from thermal throttling your system.
If disabling the power limits does not solve your issue, then you may need to look into additional cooling solutions for your system such as additional fans or a laptop cooler pad.
Turning Off Thermal Throttling
No, thermal throttling cannot be turned off as it is an important feature designed to protect your computer and its components from overheating. Thermal throttling works by reducing the power draw of the processor and othr components when they reach a certain temperature, thus preventing the system from overheating. To ensure optimal performance and prevent damage to your hardware, it is best to keep thermal throttling enabled.
The Benefits of Using DTS in ThrottleStop
DTS, or Degrees of ThrottleStop, is a feature in Intel CPUs that allows the user to set a specific temperature threshold for their processor. This is done by setting the maximum temperature (Tmax) and then setting the DTS value. When the CPU reaches this threshold, ThrottleStop will activate its failsafe profile, which can be set by the user. The lower the DTS value, the lower the temperature at which ThrottleStop will engage its failsafe profile. A DTS of 1 usually corresponds to Tmax (the maximum temperature of your CPU), while a DTS of 20 corresponds to 80C. This makes it easier to keep your CPU within safe temperatures without having to worry abot overheating or damage.
Limiting CPU Wattage with ThrottleStop
To limit the CPU wattage through ThrottleStop, first open the application and then go to the FIVR tab. Once there, you can adjust the CPU Core and CPU Cache power limits to whatever wattage you’d like. Make sure to clear the Disable Power Limit Control box so ThrottleStop can send this power limit information to the CPU. You should be able to lower tese down to 45W or less. Finally, click ‘Apply’ and then restart your PC for the changes to take effect.
The Effects of Undervolting on CPU Performance
Undervolting your CPU can be done safely, but it is possible to damage it if the settings are not chosen correctly. The risk of damage increases as the voltage is lowered, so it’s important to be careful and make sure you know what you’re doing. If the voltage is set too low, your CPU may experience instability, crashes, and reduced performance. The most common issues are blue screens of death (BSODs) and freezes. If you’re unsure abot what setting to use, it’s best to consult an experienced technician or online guide for advice on how to properly undervolt your CPU.
Disadvantages of Undervolting
Undervolting is a process used to reduce the amount of power supplied to a component, such as a GPU, by reducing the voltage. While undervolting can bring about performance benefits, it also has some disadvantages that should be taken into account.
Firstly, it is possible to apply incorrect settings, which can lead to instability or poor performance. In addition, undervolting may not produce the same level of performance improvement with all graphics cards and CPU models. This means that you may end up spending time tweaking settings without much benefit in terms of performance gains.
Furthermore, undervolting can increase wear and tear on components if done excessively. This could potentially reduce the lifespan of your components. It is therefore important to be aware of how much voltage you are reducing and to ensure that your components are still running within the optimal range for their specifications.
Finally, undervolting does not always make a system more efficient; in some cases, it may actually consume more power than usual due to lower efficiency at lower voltages. This means that you may not be able to achieve the desired energy savings from undervolting your components.
The Safety of Disabling CPU Throttling
Disabling CPU throttling is not safe as it can lead to your computer being damaged from overheating. Thermal throttling is an unmanageable hardware feature and cannot be disabled, however you can disable power throttling policy in your OS. This will stop your CPU from being throttled back when it reaches a certain temperature. If the temperature continues to rise, then the CPU may be shut off completely by the OS power plan, so we recommend monitoring temperatures while disabling power throttling policy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, BD PROCHOT is a feature designed to protect your CPU from overheating. It automatically underclocks the CPU when temperatures reach a cetain threshold, ensuring that your processor remains safe from damage. Additionally, you can use Throttlestop to manually undervolt your CPU if your PC supports it. This will help reduce power consumption and improve the performance of your system. All in all, BD PROCHOT and Throttlestop are useful tools for keeping your CPU running at optimal temperatures and performance levels.
