The House of Burgesses, established in 1619 CE, holds a significant place in American history as the first elected legislative body in colonial Virginia. This assembly of representatives played a crucial role in shaping the foundations of representative government in America, paving the way for future democratic institutions.
The primary purpose of the House of Burgesses was to pass laws and maintain order in the Jamestown Colony and its surrounding settlements. It served as a forum for the early politicians of America, known as burgesses, to discuss and address the needs and concerns of the burgeoning colony.
One of the key reasons why the House of Burgesses holds immense importance lies in its role as a precursor to the American Revolution. In 1765, when the British Parliament imposed the infamous Stamp Act on the American colonies, the House of Burgesses took a stand against this unjust taxation policy. This act of defiance marked one of the earliest events that ultimately led to the Revolutionary War.
Moreover, the House of Burgesses fostered a sense of unity and collaboration among the colonial representatives. These elected officials gathered to deliberate on matters of governance, ensuring that the interests and voices of the people were heard and represented. This early form of representative government was a crucial stepping stone towards the establishment of democratic principles in America.
The significance of the House of Burgesses extends beyond its immediate impact on colonial Virginia. The conventions held by the House, which were essentially meetings without the presence of the governor and Council, played a vital role in shaping the future of American governance. These conventions set the stage for the First Continental Congress, a gathering of colonial representatives from across the thirteen colonies, which further solidified the path towards independence.
In addition, the House of Burgesses played a pivotal role in the revolution within Virginia itself. As tensions with British rule escalated, the House took bold actions, such as creating an army to defend the rights and liberties of the people. In June 1776, the House adopted a new constitution for the independent Commonwealth of Virginia, further cementing the foundations of self-governance.
The House of Burgesses holds immense historical significance as the first elected legislative body in colonial Virginia. Its establishment marked the beginning of representative government in America, setting the stage for future democratic institutions. Its resistance against unjust taxation policies and its role in the events leading up to the American Revolution solidify its place in the annals of American history. The House of Burgesses serves as a testament to the early efforts to establish a government of the people, by the people, and for the people.
What Was The Purpose Of The House Of Burgesses?
The House of Burgesses, established in 1619 CE, served as the first representative government in North America. It was created with the intention of fulfilling several important purposes within the Jamestown Colony of Virginia and its surrounding settlements. The main objectives of the House of Burgesses were to pass laws, maintain order, and ensure effective governance in the English colonies.
The primary purpose of the House of Burgesses was to pass laws. As a representative body, it allowed the colonists to have a say in the legislation that governed their daily lives. The members of the House of Burgesses were elected by the male landowners in each settlement, providing a means for the colonists to have a voice in the decision-making process. By passing laws, the House of Burgesses aimed to establish a framework for regulating various aspects of colonial life, including trade, commerce, land ownership, and social order.
Another significant purpose of the House of Burgesses was to maintain order within the colonies. It acted as a governing body, responsible for creating and enforcing regulations that promoted peace and stability. By establishing laws and regulations, the House of Burgesses aimed to ensure that societal norms were upheld, disputes were settled, and justice was served. This helped to maintain a sense of order and security for the colonists, contributing to the overall well-being of the settlements.
Furthermore, the House of Burgesses played a crucial role in providing effective governance. It served as a platform for the colonists to voice their concerns, address grievances, and propose solutions to the challenges faced by the colonies. Through open discussions and debates, the House of Burgesses aimed to foster a sense of unity among the colonists and promote the general welfare of the settlements.
The House of Burgesses had several purposes. It aimed to pass laws, maintain order, and provide effective governance for the English colonies in North America. By allowing the colonists to participate in the decision-making process, the House of Burgesses served as a milestone in the development of representative government in the New World.
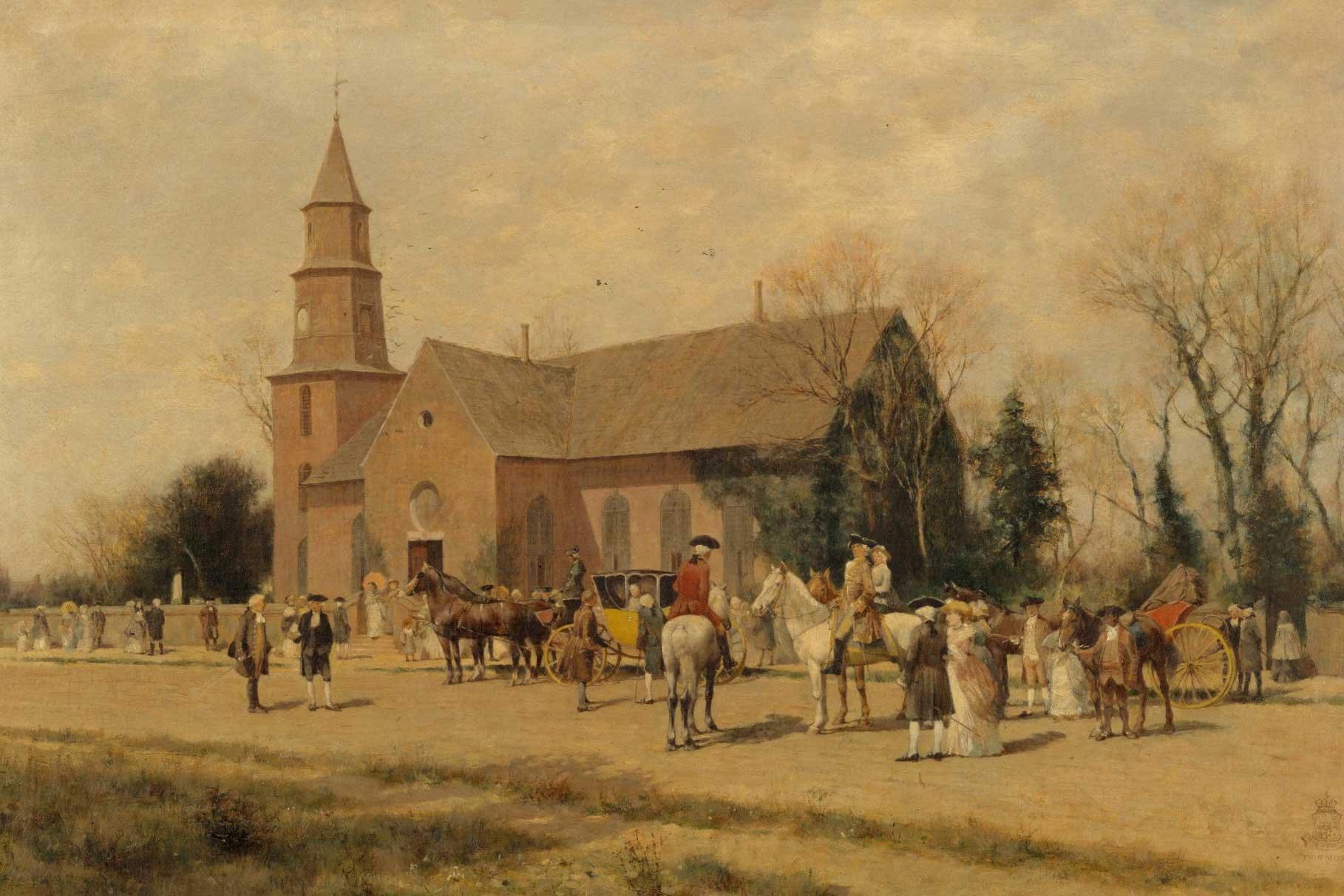
Why Was The House Of Burgesses Significant?
The House of Burgesses, established in 1619, was a significant milestone in American history. Here are some reasons why it was considered important:
1. First elected law-making body: The House of Burgesses was the first elected legislative assembly in the American colonies. Its creation marked the beginning of representative government in America, laying the foundation for democratic principles that would later shape the nation.
2. Colonial self-government: The House of Burgesses provided colonists with a platform to voice their concerns and make decisions on local matters. It allowed for greater self-governance and autonomy in the colony, granting the settlers a degree of control over their own affairs.
3. Legal framework: The establishment of the House of Burgesses introduced a legal framework through which laws and regulations could be enacted and enforced. It provided a structured means to address issues, resolve disputes, and promote order within the colony.
4. Limited self-rule: While the House of Burgesses operated under the authority of the British Crown, it offered a measure of self-rule to the colonists. This allowed them to develop and implement laws that were more tailored to their specific needs and circumstances, rather than being subjected to distant and potentially disconnected decision-making.
5. Precedent for future representative bodies: The House of Burgesses set a precedent for the creation of similar legislative bodies in other colonies. It served as a model for subsequent assemblies, such as the Provincial Congresses and the Continental Congress, which played crucial roles in the American Revolution and the establishment of the United States.
The House of Burgesses played a pivotal role in shaping the development of representative government in America. Its establishment marked a significant step towards self-governance, providing a legislative framework that would serve as a foundation for future democratic institutions in the country.
What Did The House Of Burgesses Influence?
The House of Burgesses had a significant influence on the political landscape and events in colonial Virginia. Here are some key ways in which the House of Burgesses impacted the course of history:
1. Representative government: The House of Burgesses was the first elected legislative body in the American colonies. Its establishment in 1619 marked an important milestone in the development of representative government in Virginia and served as a model for future colonial assemblies.
2. Colonial self-governance: The House of Burgesses provided a platform for colonists to voice their concerns, debate issues, and make decisions on matters pertaining to local governance. It allowed the colonists to have a say in their own affairs, laying the foundation for self-governance and fostering a sense of political empowerment.
3. Resistance to British rule: As tensions between the American colonies and Britain escalated, the House of Burgesses played a role in resisting British policies and asserting colonial rights. It passed resolutions and petitions, such as the Virginia Resolves in 1765, which protested against the Stamp Act and asserted the principle of “no taxation without representation.”
4. Revolutionary sentiments: The House of Burgesses became a hotbed of revolutionary sentiment in the years leading up to the American Revolution. It was a forum where ideas of independence and resistance to British authority were discussed and propagated. Many influential figures, such as Patrick Henry and Thomas Jefferson, used the platform of the House of Burgesses to advocate for revolutionary actions.
5. Conventions and the path to independence: The House of Burgesses played a pivotal role in convening conventions that laid the groundwork for the American Revolution in Virginia. These conventions, such as the Virginia Convention of 1774 and the Virginia Convention of 1775, brought together colonial representatives to discuss grievances, coordinate resistance efforts, and assert colonial rights. They paved the way for the formation of the First Continental Congress and ultimately led to the adoption of a new constitution for the independent Commonwealth of Virginia in 1776.
The House of Burgesses influenced the development of representative government, fostered colonial self-governance, fueled resistance to British rule, propagated revolutionary sentiments, and played an instrumental role in the path to independence in Virginia.
What Are 3 Facts About The House Of Burgesses?
1. The House of Burgesses was established in 1619 and was the first elected legislative body in colonial Virginia. It served as the precursor to the modern-day Virginia General Assembly.
– The House consisted of representatives, known as burgesses, who were elected by the male property owners in each county. This system of representative government played a crucial role in shaping the democratic principles of the United States.
– One of the significant achievements of the House of Burgesses was its opposition to the Stamp Act of 1765. This act imposed taxes on various paper goods and documents, which greatly angered the colonists. The House passed a series of resolutions denouncing the act and asserting the rights of the colonists to govern themselves, setting the stage for future acts of resistance against British rule.
– The House of Burgesses also played a role in the development of local laws and regulations. It had the power to pass legislation, levy taxes, and oversee the administration of justice. The House was responsible for addressing issues such as trade, agriculture, and public welfare, making it an essential institution in colonial Virginia.
The House of Burgesses was an influential political body in colonial America, setting the foundation for representative government and playing a pivotal role in the events leading up to the American Revolution.

Conclusion
The House of Burgesses holds great significance in the history of America as it was the first elected legislative body in colonial Virginia. Its establishment in 1619 marked the beginning of representative government in North America, setting a precedent for future democratic institutions. The House of Burgesses played a crucial role in passing laws and maintaining order in the Jamestown Colony and other settlements in Virginia.
Moreover, the House of Burgesses served as a platform for early American politicians, known as burgesses, to voice their concerns and advocate for the rights and liberties of the colonists. Their opposition to the oppressive Stamp Act was a pivotal event that contributed to the eventual outbreak of the Revolutionary War.
Additionally, the House of Burgesses paved the way for larger political assemblies, such as the First Continental Congress, which united the American colonies in their struggle against British rule. It also played a significant role in the Virginia Revolution, establishing an army and adopting a new constitution for the independent Commonwealth of Virginia.
The House of Burgesses played a crucial role in shaping the political landscape of America, laying the foundation for democratic governance and serving as a catalyst for the revolutionary ideals that would ultimately lead to the birth of a new nation. Its establishment and actions hold immense historical importance, making the House of Burgesses a key milestone in the journey towards American independence and the formation of a democratic society.
