The scharfes s, also known as the ß or sharp s, is a unique letter in the German alphabet. It is a ligature of the letters s and z, and is used to represent the voiceless alveolar fricative sound that occurs after a long vowel or diphthong.
While the use of the ß has been simplified in recent years, it is still widely used and required in German orthography. The letter is used after a long vowel or diphthong, indicating that the preceding vowel should be pronounced for a longer duration before transitioning to the s sound represented by the ß.
It is important to note that the scharfes s should not be confused with the lowercase Greek beta (β). While both characters may appear similar at frst glance, they represent different sounds and have different uses in language.
In addition to its linguistic significance, the scharfes s is also notable for its unique appearance. Its shape is a combination of the lowercase letters s and z, with a longer vertical line extending from the top of the letter to the bottom. This distinctive shape has made the ß a recognizable symbol of the German language.
Despite its importance in German orthography, the use of the scharfes s remains a topic of debate and controversy. Some argue that the letter should be phased out entirely, while others advocate for its continued use and preservation as a unique aspect of German language and culture.
Regardless of one’s opinions on the matter, the scharfes s remains an important and distinct element of the German language. Its use and significance continue to be studied and debated by linguists, writers, and language enthusiasts alike.
Is Scharfes S Still Used?
The ß, also known as the “scharfes S” or “sharp S” is stil used in the German language. Although the use of the letter has been simplified and reduced in recent years, it is still required in certain cases. The ß is used to represent a voiceless alveolar fricative sound after a long vowel or diphthong. When the vowel is short, the letter combination “ss” is used instead. It is important to note that the use of the ß varies depending on the country or region, with it being more common in Germany than in Switzerland, for example. Nevertheless, it remains an essential part of the German alphabet and orthography.
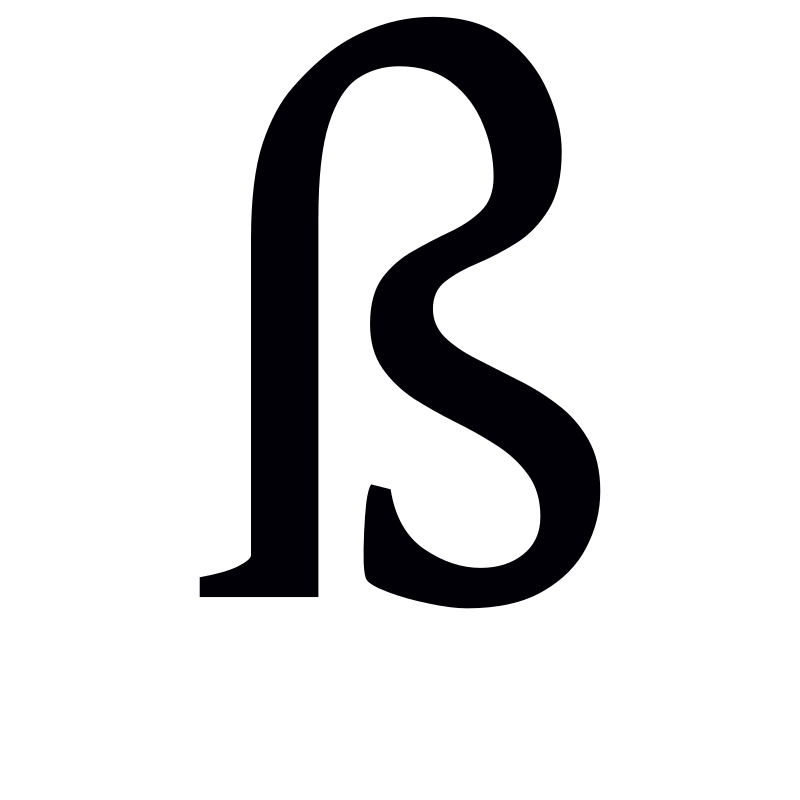
Is ß The Same As ß?
ß is not the same as β. The German special character, the Eszett (uppercase ẞ; lowercase ß), is a letter used in the German language to represent the “ss” sound. On the other hand, the lowercase Greek beta (β) is a letter used in the Greek alphabet and is commonly used in mathematics and science to represent various concepts, such as the second variable in a mathematical equation or the beta cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. It is important to not confuse the two characters as they have different meanings and functions in their respective languages and fields of study.
What Is ß Called In English?
The German letter ß, which is a ligature of the letters “s” and “s”, is commonly referred to in English as the “sharp s”. It is used exclusively in German language and is pronounced as a double “s” sound. It is important to note that while the “sharp s” may resemble a “B” in appearance, it is not equivalent to the English letter “B” in sound or meaning.
Is ß ß Or SZ?
The character “ß” is a letter of the German alphabet, called “Eszett” or “scharfes S”. It is a ligature of the letters “s” and “z” and it represents a unique sound in German pronunciation. Therefore, “ß” is neither “ß” nor “SZ”, but rater its own distinct character. It was officially recognized as a separate letter in the German alphabet in 2017, but it has been in use for centuries. In some cases, when “ß” is not available (for example, when typing on a keyboard that does not have this character), it can be replaced by “ss”. However, it is important to note that “ss” does not represent the exact same sound as “ß” and should not be used interchangeably in written German.
Conclusion
The scharfes s, also kown as the sharp s or ß, is a unique letter in the German language that represents the voiceless alveolar fricative sound after a long vowel or diphthong. While it may seem complicated, it is simply a ligature of the letters s and s. It is important to distinguish it from the lowercase Greek letter beta (β), which is commonly used in scientific research. Although there have been reforms in German orthography, the scharfes s remains an important and required letter in the language. As a writer, it is crucial to understand its proper usage to ensure clear and accurate communication in written German.
