The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer system that connects all the hardware components, including the CPU, memory, and storage devices. It is the backbone of the computer system, providing the necessary communication and power between all the components.
One of the essential components of a motherboard is the SATA ports. SATA or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment is a standard interface used to connect mass storage devices like hard drives and optical drives to the motherboard. SATA ports on a motherboard are used to connect SATA devices to the motherboard.
The number of SATA ports on a motherboard varies depending on the size and type of the motherboard. Most modern motherboards come with at least four SATA ports, but some high-end models can have up to 13 SATA ports.
SATA ports on a motherboard are usually located together in a cluster aong the edge of the board. They can also be stacked, depending on the motherboard’s layout. In some cases, they may be located diagonally across the motherboard from the other I/O connectors like USB, Ethernet, and audio connectors.
Each SATA port on the motherboard has its own individual bandwidth, so using different ports for different devices won’t impact the speed of the devices. It is important to note that the maximum number of SATA ports supported by a motherboard is determined during the manufacturing process. Therefore, it is crucial to check the specifications of the motherboard before purchasing it.
SATA ports on a motherboard support different SATA standards, including SATA I, SATA II, and SATA III. The SATA standard determines the maximum speed of data transfer. SATA I supports a maximum transfer rate of 1.5 Gbps, SATA II supports a maximum transfer rate of 3 Gbps, and SATA III supports a maximum transfer rate of 6 Gbps. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that the SATA devices you are using are compatible with the SATA standard supported by your motherboard.
SATA ports on a motherboard are essential for connecting mass storage devices to the motherboard. The number of SATA ports and the SATA standard supported by a motherboard vary depending on the motherboard’s type and size. It is crucial to check the motherboard’s specifications before purchasing it, and using the correct SATA standard for your devices can significantly impact their performance.
What Are SATA Ports On A Motherboard For?
SATA ports on a motherboard are used for connecting mass storage devices, such as hard drives and optical drives, to the motherboard. These ports enable high-speed data transfer btween the storage devices and the motherboard, allowing for faster access and retrieval of data. The SATA ports use a serial communication protocol, which allows for faster and more efficient data transfer compared to the older parallel communication protocol used by older storage devices. SATA ports typically support hot-swapping, which means that the storage devices can be added or removed from the system while it is still running. Some motherboards may have multiple SATA ports, allowing for the connection of multiple storage devices. SATA ports are essential components of modern motherboards that enable efficient and reliable communication between the storage devices and the computer system.
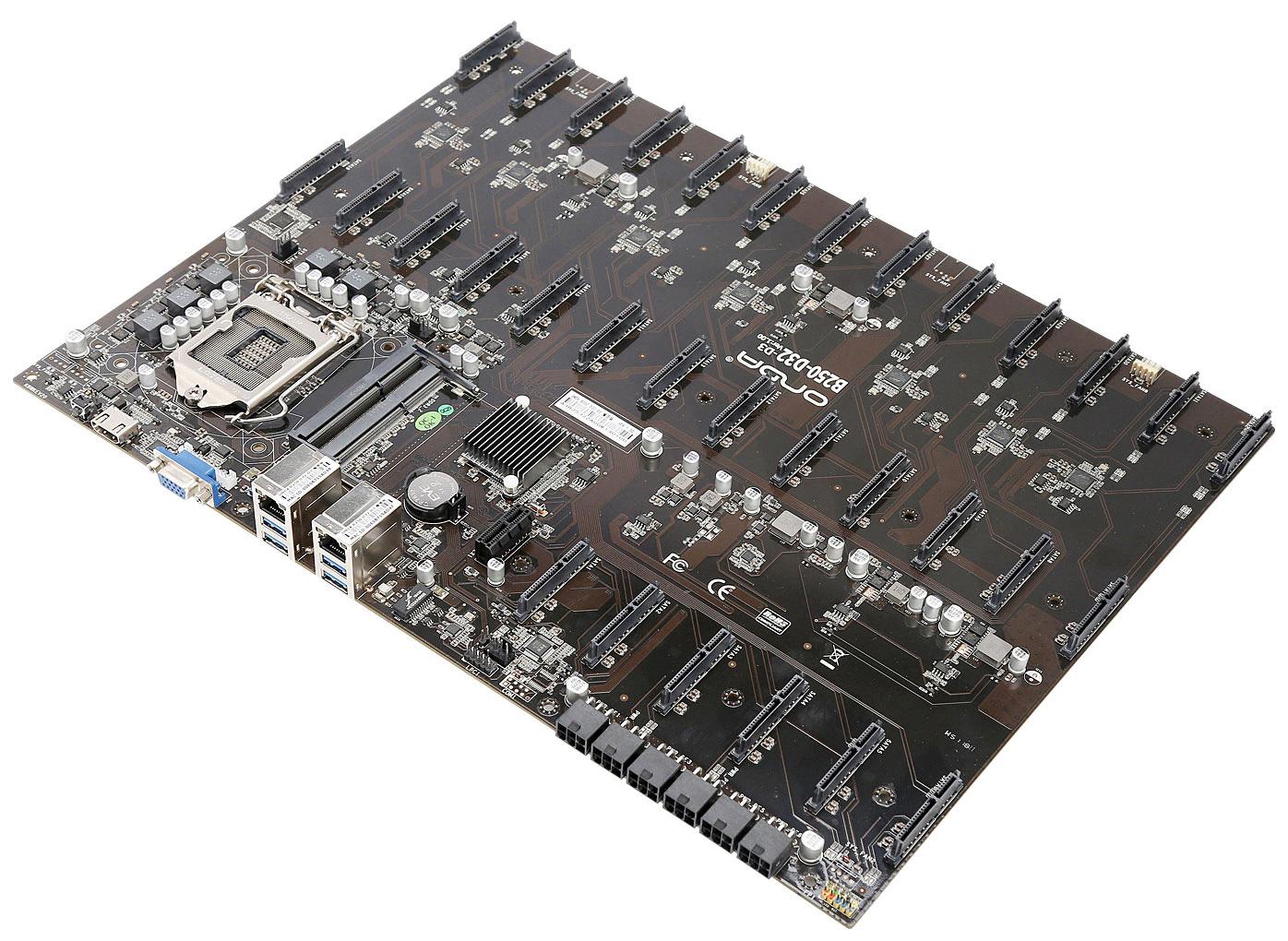
Where Are The SATA Ports On My Motherboard?
The SATA ports on a motherboard are generally located along the edge of the motherboard, behind the PCI/PCIe slots. They are typically clustered together in a row and may be stacked depending on the number of ports available. Alternatively, they may be located diagonally across the motherboard from the keyboard and other I/O connectors. It is important to note that the exact location of the SATA ports may vary depending on the specific motherboard model.
How Many SATA Ports Are On A Motherboard?
Motherboards are the primary circuit board of a computer, and they have numerous connectors and ports for connecting various components. One of the important connectors on a motherboard is Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) ports. SATA ports are used to connect storage devices like hard drives, solid-state drives, and DVD drives to the motherboard.
The number of SATA ports on a motherboard depends on the type and size of the motherboard. Most motherboards come with 4-8 SATA ports, which are sufficient for regular usage. However, some motherboards designed for high-end systems come with more SATA ports to support multiple storage devices.
To povide flexibility to users, motherboard manufacturers have started to provide a higher number of SATA ports. The highest number of SATA ports seen on a standard motherboard is 13, which is quite rare. A motherboard with 13 SATA ports is designed for advanced users who require large storage arrays or high-speed data transfer rates.
The number of SATA ports on a motherboard varies based on the motherboard’s type and size, with most motherboards typically having 4-8 SATA ports. However, some high-end motherboards can have up to 13 SATA ports, offering users greater flexibility in storage options.
Do Motherboards Have SATA Ports?
Motherboards have SATA ports. SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is a standard interface used to connect storage devices such as hard drives, solid-state drives, and optical drives to a computer’s motherboard. Most modern motherboards come with several SATA ports, which allow you to connect multiple storage devices to your computer. The number of SATA ports on a motherboard can vary depending on the motherboard model and manufacturer, but typically range from four to eiht ports. Some high-end motherboards may even offer more than eight SATA ports. It’s important to note that the maximum number of SATA ports a motherboard can support is determined by the motherboard’s chipset and other hardware specifications.
Conclusion
The motherboard is the backbone of a computer system, connecting all the vital components such as CPU, RAM, graphics card, and storage devices together. It determines the type and number of components that can be installed, as well as their compatibility and performance. It comes in various sizes and form factors, each with its unique features and limitations. It is essential to choose a motherboard that matches your needs and budget, keeping in mind factors such as socket type, chipset, expansion slots, and other features. With the rapid advancement of technology, motherboards are constantly evolving, providing faster speeds, improved connectivity, and beter functionality. Understanding the basics of a motherboard can help you make an informed decision while building or upgrading your computer system.
