Carbohydrates are one of the most essential biomolecules that are found in living organisms. They are known for their vital roles in energy production, cell signaling, and structural support. Carbohydrates are classified based on the number of monosaccharide units present in them. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates and they cnnot be further hydrolyzed into smaller units.
Monosaccharides can exist in two different forms, open-chain and cyclic. In the open-chain form, the monosaccharide exists as a straight chain, while in the cyclic form, the monosaccharide exists in a ring structure. Monosaccharides that contain six carbon atoms can exist in two different cyclic forms, pyranose, and furanose. The difference between pyranose and furanose is in the number of atoms in the ring structure. Pyranose has a six-membered ring consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, while furanose has a five-membered ring consisting of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom.
Pyranose is the most common form of cyclic monosaccharides. This is due to the fact that the six-membered ring is completely strain-free, making it more stable than the five-membered ring of furanose. Pyranose is also more common because it is the predominant form of glucose, which is the most abundant monosaccharide in nature.
Furanose, on the other hand, is less stable than pyranose due to the ring strain caused by the five-membered ring. This makes furanose less common among aldohexoses, which are monosaccharides that contain six carbon atoms and an aldehyde functional group. However, furanose is more common among pentoses, which are monosaccharides that contain five carbon atoms. Ribose, a pentose, exists mainly in the furanose form.
Fructose, a ketohexose, is another monosaccharide that can exist in both pyranose and furanose forms. Fructose is unique in that it exists in a 67% pyranose and 33% furanose ratio in solution. This is due to the fact that fructose has a ketone functional group, which can react with the hydroxyl group on the fifth carbon atom to form a furanose ring.
Pyranose and furanose are two different forms of cyclic monosaccharides. Pyranose is more stable and more common than furanose due to the six-membered ring being strain-free. However, furanose is more common among pentoses and fructose due to the presence of a ketone functional group. The presence of both pyranose and furanose forms in different monosaccharides contributes to the diverse functions that carbohydrates play in living organisms.
Why Is Pyranose More Stable Than Furanose?
The pyranose form of aldohexoses is more stable than the furanose form due to several factors. Firstly, the pyranose structure is a six-membered ring, which is completely strain-free and has a lower energy state compared to the five-membered ring in furanose. The five-membered ring of furanose has ring strain, which cases a destabilizing effect on the molecule. Additionally, the pyranose structure has a more optimal bond angle and bond length, which results in a more stable molecule. Furthermore, the pyranose form is more prevalent in nature, and enzymes that catalyze reactions involving aldohexoses typically recognize and bind to the pyranose form more readily. these factors contribute to the increased stability and prevalence of the pyranose form over the furanose form in aldohexoses.
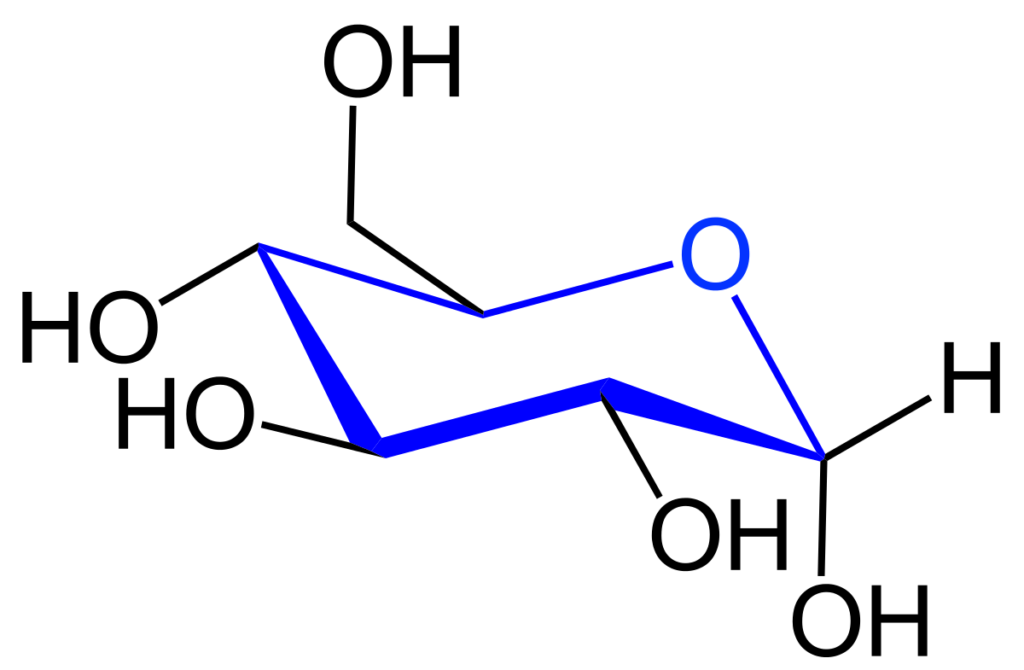
Is Glucose A Furanose Or Pyranose?
Glucose is predominantly found in the pyranose form in solution. Pyranose is a six-membered cyclic hemiacetal ring, whereas furanose is a five-membered cyclic hemiacetal ring. In the pyranose form, glucose contains an oxygen atom in the ring structure that links to one of the carbon atoms of the sugar, forming a six-membered ring. On the oter hand, the furanose form of glucose contains a five-membered ring with the oxygen atom linking to two carbon atoms of the sugar. It is important to note that although glucose can exist in both furanose and pyranose forms, the pyranose form is more stable and commonly found in solution.
Is Pyranose A 6 Membered Ring?
Pyranose is a type of saccharide that has a six-membered ring structure consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. This six-membered ring structure is also known as a pyran ring, which is where the name “pyranose” comes from. The six-membered ring structure is essential to the properties and behavior of pyranose sugars, which are commonly found in natural sources such as fruits, vegetables, and grains. The six-membered ring structure is also responsible for the stability and rigidity of pyranose sugars, which allows them to function as important energy sources in biological systems.
Conclusion
Pyranose and furanose are two different forms of cyclic structures that monosaccharides can adopt. Pyranose is a six-membered ring consisting of five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, which is more stable than the furanose form due to its lack of ring strain. On the other hand, furanose is a five-membered ring containing four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, which has some ring strain and is less stable than the pyranose form. While both forms can be found in some monosaccharides, the pyranose form is more common and prevalent in nature. Understanding the differences and properties of pyranose and furanose structures is essential for studying the chemistry and biochemistry of thse important biomolecules.
