Plasia is a medical term with an important meaning. It refers to the process of growth and cellular multiplication, which involves an increase in the number of cells in an organ or tissue. This phenomenon can be indicative of both positive and negative developments in a person’s health.
In some cases, plasia is seen as a sign of vitality and vigor. For example, it may indicate that an organ or tissue is growing at its proper rate and that the body is functioning optimally. Plasia can also be beneficial in the healing process after surgery or illness; increased cell production can help regenerate damaged areas more quickly.
On the other hand, plasia may also signify something more serious. It could suggest that some form of neoplasm has developed, either benign or malignant; this could be anything from a tumor to cancer. In such cases, it is essential for doctors to thoroughly investigate the cause of this increased cell production in order to determine what course of treatment would be most effective for their patient.
The study of plasia can provide scientists with valuable insight into how our bodies work and what might happen when things go wrong. The field requires extensive research and experimentation before any conclusions can be drawn about its significance and implications for our health.
Given its importance in understanding how our bodies function, it’s no surprise that plasia has been studied extensively by medical researchers over the years. In fact, many breakthroughs have been made as a result of their efforts – from better understanding how cancer develops to discovering new treatments for various illnesses.
What Does Plasia Mean In Medical?
Plasia is a medical term that decribes the process of growth and cellular multiplication. In particular, it refers to an increase in the number of cells in an organ or tissue. Plasia can be a sign of health and vitality, or it may indicate the presence of a disease or disorder.
Anaplasia vs Dysplasia
Is Plasia A Root Or Suffix?
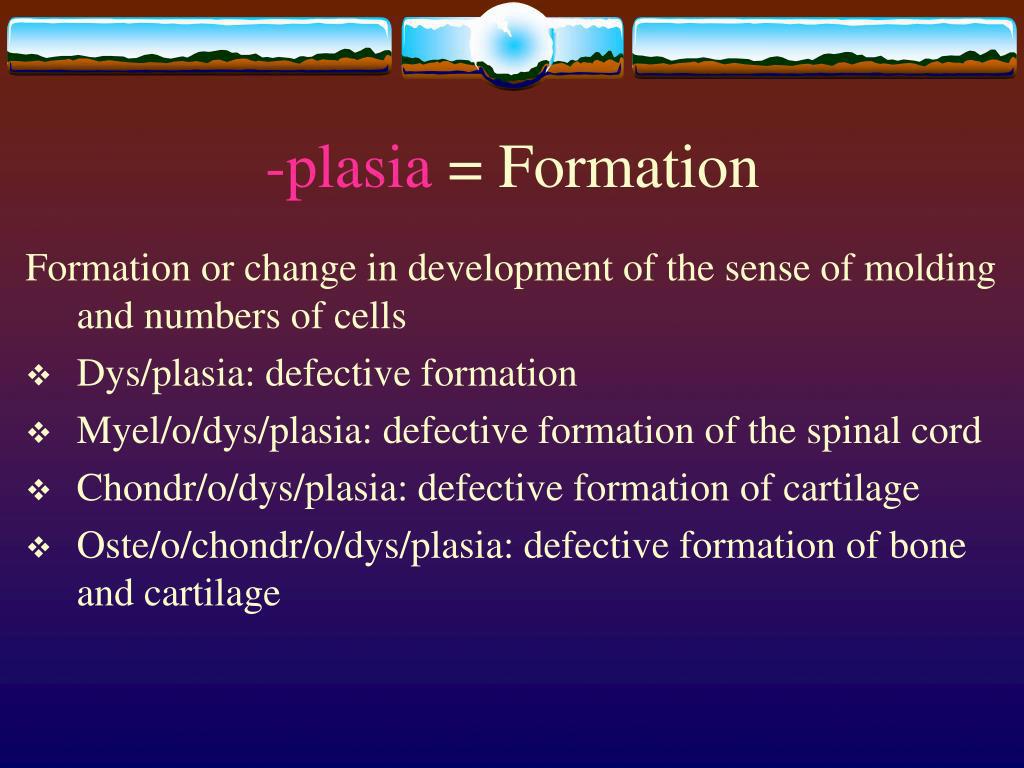
Plasia is a suffix meaning formation, growth, or proliferation.
What Does Anaplasia Mean In Medical Terms?
Anaplasia is a term used to describe cancer cells that divide rapidly and have litle or no resemblance to normal cells. This can be a sign that the cancer is becoming more aggressive.
What Does The Suffix Medical Term Mean?
The suffix of a medical term typically indicates the field of medicine that the term belongs to. For example, the suffix “-ectomy” typically denotes a surgical procedure, while the suffix “-itis” usually refers to an inflammatory condition. Alternatively, the suffix may simply make the word into a noun or adjective.
What Is The Medical Term For Referring To An Embryo?
The medical term for referring to an embryo is “embryo.” An embryo is an organism in the early stages of growth and differentiation, from fertilization to the beginning of the thrd month of pregnancy (in humans). After that point in time, an embryo is called a fetus.
What Does Hist O Mean?
Histo- is a combining form meaning “tissue.” It is oten used in medical terms, especially in anatomy and pathology. The form histo- comes from Greek histós, meaning “web (of a loom)” or “tissue.”
What Does PNEA Mean In Medical Terms?
PNEA stands for “psychogenic non-epileptic attacks.” This term is used to describe episodes that look like seizures, but are not caused by epilepsy. The cause of these attacks is usually emotional or psychological, such as stress, anxiety, or depression.
What Does Rrhage Mean In Medical Terms?
The suffix -rrhage means bursting forth. Hemorrhage is the escape of blood from tissue.
What Is Dysplasia And Anaplasia?
Dysplasia is a change in cell or tissue phenotype. This means that the cells in the tissue look diferent than they should. Anaplasia is a loss of structural differentiation within a cell or group of cells. This means that the cells lose their normal shape and function.
Do Benign Tumors Have Anaplasia?
It can depend on the type of benign tumor in question. However, in general, benign tumors do not have anaplasia. Anaplasia refers to a loss of differentiation in cells, meaning that they no longer look or behave like normal cells in that tissue or organ. This change can sometimes occur in benign tumors, but it is not common. If anaplasia does develop in a benign tumor, it may be an early sign that the tumor has becme malignant.
Are Neoplasms Always Malignant?
A neoplasm is a mass or lump that can be benign (not cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign neoplasms may grow large but do not spread into, or invade, nearby tissues or other parts of the body. Malignant neoplasms can spread into, or invade, nearby tissues. They can also spread to other parts of the body thrugh the blood and lymph systems.
What Is A Prefix And Suffix In Medical Terminology?
Prefixes are placed at the beginning of a word to modify or change its meaning. The prefix “pre” means “before.” This may idicate a location, number, or time. For example, the prefix “sub” means “below.” A suffix is the ending part of a word that modifies the meaning of the word. The suffix “-ectomy” means “to cut out.”
What Is The Medical Suffix For Pertaining To?
The medical suffix for pertaining to is “ary.” This suffix is attached to root words to indicate that something pertains to a certain area or function. For example, the word “cardiovascular” means “pertaining to the heart and blood vessels.”
What Are Common Medical Suffixes?
Medical suffixes are words that are added to the end of a root word to create a new word that has a specific meaning pertaining to medicine. Some common medical suffixes include -ectomy (the removal of a body part), -dynia (pain), and -oma (a tumor or mass). By adding these suffixes to root words, doctors can create new terms that describe specific medical conditions or procedures.
