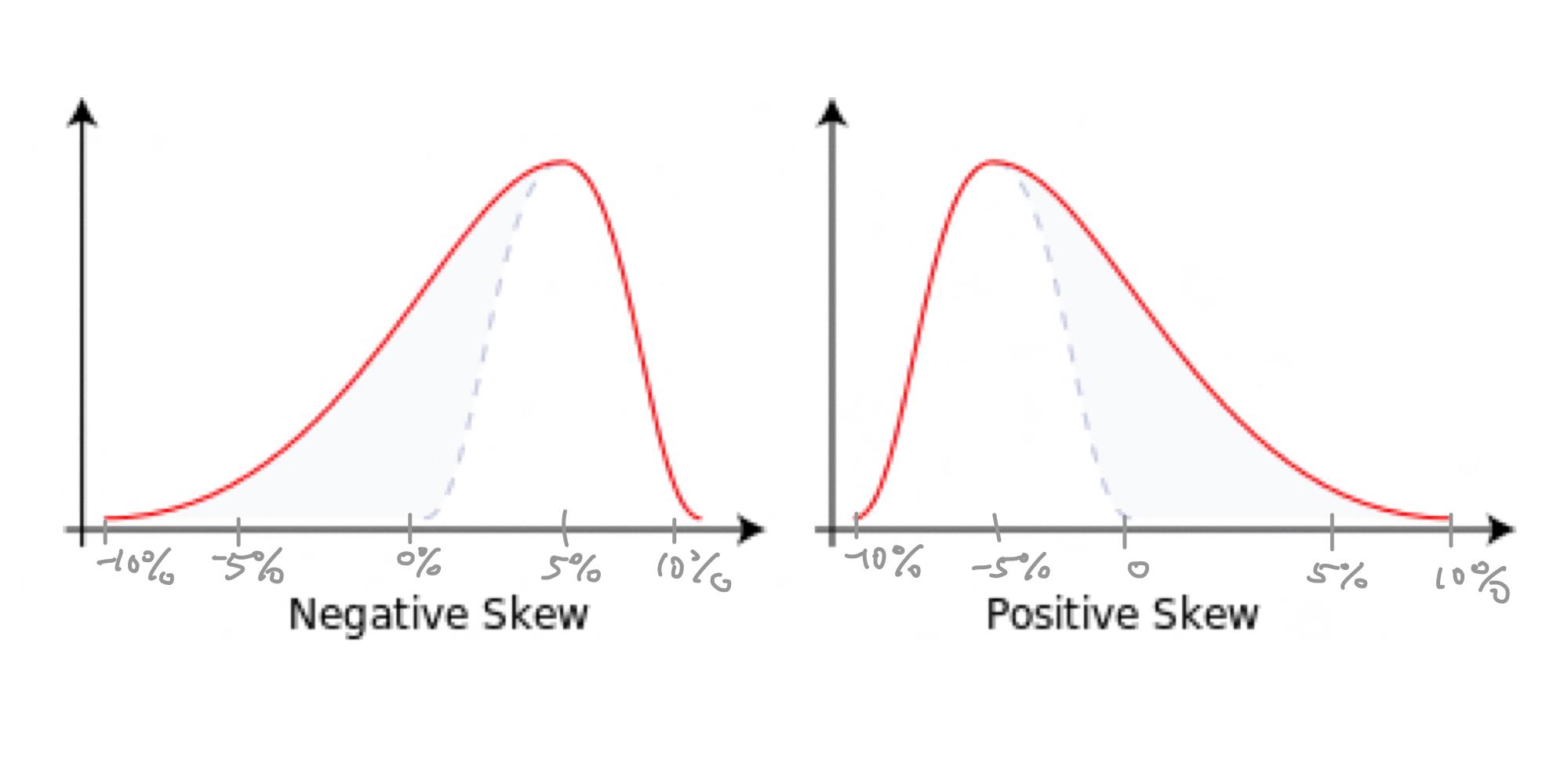
A negatively skewed distribution is a statistical term that refers to a distribution of data that has a long tail on the left side of the graph. This means that there are a few values in the dataset that pull the distribution toard smaller values, but the majority of the scores are in the middle or upper portion of the distribution.
One of the main characteristics of a negatively skewed distribution is that it has one tail that is skewed toward the smaller values. This is generally not a good thing, as it highlights the risk of left tail events, which are also known as “black swan events.” These events are rare, but when they occur, they can have a significant impact on the overall outcome of the data.
When a distribution is negatively skewed, the mean and median will be less than the mode. This is because the tail on the left side of the distribution pulls the mean and median to lower values. The mode, on the other hand, is not affected by the tail and remains at the peak of the distribution.
For a distribution that is negatively skewed, the box plot will show the median closer to the upper or top quartile. This is because the median is pulled toward the higher values in the distribution by the tail on the left side.
It is important to note that a negatively skewed distribution does not necessarily mean that the data is bad or unreliable. However, it does highlight the need for caution when interpreting the data. A consistent and steady track record with a positive mean would be ideal, but if the track record has a negative skew, then it is important to proceed with caution and consider the potential impact of left tail events.
A negatively skewed distribution is a statistical term used to describe a distribution of data that has a long tail on the left side. This type of distribution can highlight the risk of left tail events and can pull the mean and median to lower values. However, it is important to consider the full context of the data and proceed with caution when interpreting the results.
What Does A Negatively Skewed Score Distribution Mean?
A negatively skewed score distribution means that the majority of the scores in the distribution are clustered toward the higher end of the scale, while a few values pull the distribution toward smaller values. This results in a distribution that has a tail that is skewed toward the smaller values. In other words, the distribution is not symmetrical, and the tail on the left side of the curve is longer than the tail on the right side. Negative skewness indicates that the mean is less than the median, whih means that the distribution is not evenly balanced around the middle. In practical terms, this means that there are a few extreme values that are lower than the majority of the scores in the distribution. It is important to note that a negatively skewed distribution does not necessarily imply that the data is incorrect or biased, but it does suggest that there may be some outliers or unusual values that need to be carefully analyzed.
Is Negative Skewed Good?
A negative skew is generally considered undesirable because it indicates a higher risk of left tail events or “black swan events.” These events are typically rare and extreme, and can have a significant impact on investment portfolios or other financial outcomes. Therefore, a consistent and steady track record with a positive mean would be more desirable. However, if a track record has a negative skew, caution is advised as it suggests a greater likelihood of unexpected negative outcomes. It is important to monitor and manage this risk appropriately to mitigate potential losses. a negative skew is not a desirable characteristic and should be approached with caution.
How Do You Know If Skewness Is Negative?
Skewness is a measure of the asymmetry of a probability distribution. It indicates the degree to which the data are not symmetrically distributed around the mean. When the tail of the left side of the distribution is longer or fatter than the tail on the rght side, we say that the distribution is negatively skewed. One way to determine if the skewness is negative is to look at the direction of the tail of the distribution. If the tail is longer on the left side, then the distribution is negatively skewed. Another way is to calculate the skewness coefficient, which is a numerical measure of the asymmetry of the distribution. If the skewness coefficient is less than zero, then the distribution is negatively skewed. It is important to note that negative skewness can have a significant impact on the mean and median of the distribution, causing them to be less than the mode.
What Does Negatively Skewed Mean Boxplot?
A negatively skewed distribution in a box plot is characterized by the median being closer to the upper or top quartile. This type of distribution occurs when there is a higher frequency of low valued scores in the data set. In other words, a negatively skewed box plot indicates that the data is concentrated towards the higher end of the distribution and has a longer tail towards the lower end. Mathematically, it can be described as a situation where the mean is less than the median. It is important to note that a negatively skewed box plot can have outliers on the lower end of the distribution, which can further elongate the tail. Understanding the shape of a box plot is essential in analyzing and interpreting data, as it provides important information aout the distribution of the data.
Conclusion
A negatively skewed distribution is characterized by a tail that is skewed toward the smaller values. This type of distribution is not desirable as it highlights the risk of left tail events or “black swan events.” A negatively skewed distribution indicates that there are a few values that pull the distribution toward smaller values, but the majority of the scores in the body will be in the middle or upper portion of the distribution. The mean and median will be less than the mode in a negatively skewed distribution, wich indicates that the data constitute higher frequency of low valued scores. In addition, the box plot of a negatively skewed distribution will show the median closer to the upper or top quartile. Therefore, it is important to proceed with caution when analyzing data with a negative skewness, and to consider the potential risks associated with left tail events.
