Non-polar molecules are hydrophobic, which means they do not mix well with water. This is because water is a polar molecule, with a positive and negative end. Non-polar molecules, on the other hand, have no such charge separation and are therefore not attracted to water molecules.
One of the defining characteristics of a non-polar molecule is that it has a symmetrical distribution of electrons. This means that the electrons are evenly shared between the atoms in the molecule, resulting in no partial charges. For example, the molecule methane (CH4) is non-polar because the four hydrogen atoms are symmetrically arranged around the central carbon atom, resulting in a molecule with no partial charges.
Other examples of non-polar molecules include carbon dioxide (CO2), which is made up of two oxygen atoms and a carbon atom, and the hydrocarbons found in oils and fats. These molecules are made up of long chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms, which are held together by non-polar covalent bonds. As a result, they are hydrophobic and do not mix well with water.
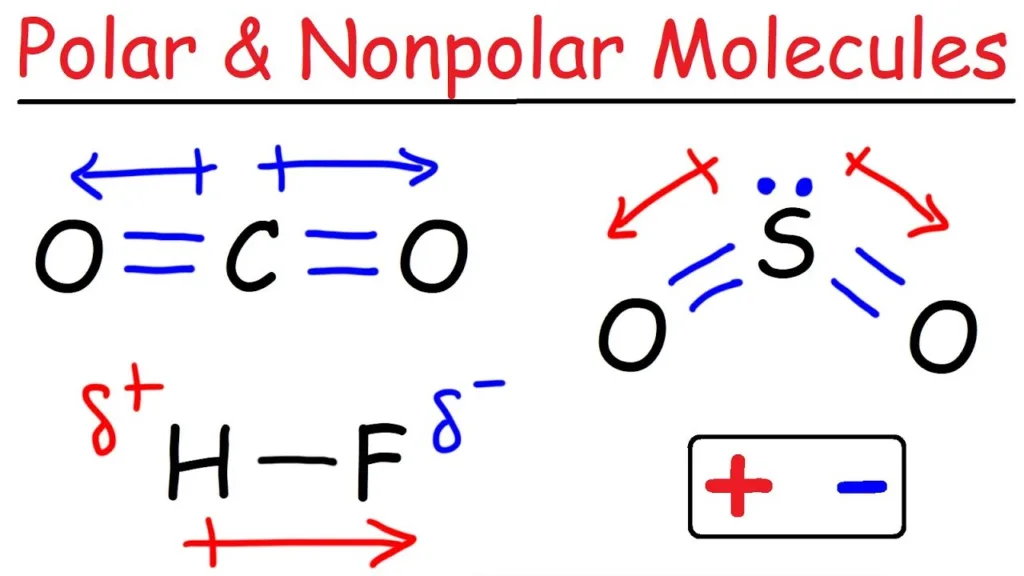
In contrast, polar molecules such as water (H2O) have partial charges due to the uneven distribution of electrons between the atoms in the molecule. This alows them to interact with other polar molecules, as well as ions, which have a positive or negative charge.
One important consequence of the hydrophobic nature of non-polar molecules is that they tend to clump together in the presence of water. This is because the non-polar molecules are more attracted to each other than to the polar water molecules. This phenomenon can be seen in the way that oil droplets form in water, or in the way that fat globules clump together in milk.
Understanding the properties of non-polar molecules is important in many fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science. For example, researchers may use hydrophobic coatings on surfaces to repel water or develop new materials that are resistant to water damage.
Non-polar molecules are hydrophobic because they lack partial charges and are not attracted to polar water molecules. Understanding the properties of non-polar molecules is important in many fields and has led to many important technological advances.
Is Non Polar Hydrophobic Or Hydrophilic?
Non-polar molecules are hydrophobic. This is because non-polar molecules lack an electrical charge and do not attract water. Water is a polar molecule, meaning it has a positive and negative end, and it is attracted to other polar molecules. In contrast, hydrophilic molecules have a polar charge and are attracted to water. Therefore, hydrophilic molecules are water-loving, while hydrophobic molecules are water-fearing. This distinction is important in many scientific fields, including chemistry, biology, and materials science.
Is Hydrophobic Polar Or Nonpolar?
Hydrophobic compounds are nonpolar, which means they lack partial charges as they have electrons distributed evenly across the molecule. These molecules are generally composed of long chains of hydrocarbons, such as fats and oils, which do not interact well with water molecules due to their nonpolar nature. In contrast, polar molecules have an uneven distribution of electrons, giving them partial charges and making them more soluble in water. hydrophobic molecules tend to repel water, while hydrophilic molecules tend to attract it.
Is Nonpolar Also Hydrophobic?
Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic. Nonpolar molecules are those that have no separation of charge, meaning they have no positive or negative poles. Due to their lack of charge, nonpolar molecules do not interact well with polar molecules such as water. This is why they tend to clump together and avoid contact with water. Since hydrophobic molecules have a strong aversion to water, they tend to be nonpolar, and nonpolar molecules tend to be hydrophobic. In contrast, polar molecules are generally hydrophilic, meaning they are attracted to water.
Are Non Polar Solutes Hydrophobic?
Non-polar solutes are generally considered hydrophobic. This is because non-polar molecules do not have a charge and therefore do not interact well with polar molecules such as water. Hydrophobic molecules fear water and tend to associate with other hydrophobic molecules instead of water. On the other hand, polar solutes are hydrophilic, meaning they are attracted to water due to their charged nature. This is because water is a polar molecule, and polar molecules tend to interact well with other polar molecules. Therefore, non-polar solutes are typically considered hydrophobic and do not dissolve easily in water.
Conclusion
Non-polar molecules are hydrophobic due to the absence of partial or complete charges on their atoms. These molecules have a long chain of carbons that do not interact with water molecules. Hydrophobicity is a property that is crucial in many chemical and biological processes. Understanding the hydrophobic nature of non-polar molecules is essential in fields such as chemistry, biology, and material science. By studying the properties of hydrophobic molecules, researchers can develop new materials and technologies that can benefit society. Therefore, the study of hydrophobicity is a vital area of research that has many practical applications.
