Glutamate and gluten are two different substances that can often be confused due to their similar names. Glutamate is a flavour enhancer used in many manufactured foods, while gluten is a protein complex found in wheat and other cereal grains.
Despite being derived from wheat, monosodium glutamate (MSG) is gluten-free. During processing, the wheat protein is completely hydrolysed or broken down, wich means that it can be safely consumed by people with coeliac disease.
However, it is important to note that glutamine peptides, which are often derived from wheat, should be avoided by gluten-free athletes. This form of the supplement contains gluten and can be harmful to people with coeliac disease.
It is also important to understand the difference between glutamine and gluten. Glutamine is an amino acid that is found in gluten in large amounts, but the two are not the same despite their similar names. Gluten proteins appear to be prolamins due to the significant amount of glutamine and proline amino acid residues present in their primary structures.
While glutamate may be derived from wheat, it is gluten-free and safe for consumption by people with coeliac disease. However, it is important to exercise caution when consuming glutamine peptides and to understand the difference between glutamine and gluten. As always, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about your dietary needs.
Is Glutamate Safe for People with Celiac Disease?
Glutamate, also known as monosodium glutamate (MSG), is a flavor enhancer that is commonly found in many manufactured foods. People with celiac disease may be concerned about consuming glutamate as it can be made from wheat. However, it is important to note that MSG is gluten-free.
During the manufacturing process of MSG, the wheat protein is completely hydrolyzed or broken down. This means that the gluten protein is no longer present and can be consumed by people with celiac disease.
It is important to note that wile glutamate is safe for people with celiac disease, some individuals may experience sensitivity or allergic reactions to MSG. Symptoms of a reaction can include headaches, flushing, sweating, and chest pain.
If you have celiac disease and are concerned about consuming glutamate, it is recommended to speak with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice. Additionally, it is important to read food labels carefully to ensure that the products you are consuming are gluten-free and safe for your dietary needs.
Glutamate is safe for people with celiac disease as it is gluten-free due to the hydrolysis process during manufacturing. However, some individuals may experience sensitivity or allergic reactions to MSG, and it is important to speak with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Can Glutamine Be Taken by Those Who Are Gluten Intolerant?
Glutamine is a popular supplement among athletes and fitness enthusiasts due to its potential benefits for muscle growth, recovery, and immune function. However, if you are gluten intolerant, you might wonder if it’s safe to take glutamine supplements.
Glutamine is an amino acid that is naturally present in the body and in many foods, including wheat and other gluten-containing grains. However, most glutamine supplements are derived from sources other than wheat, such as corn or beets.
That being said, some glutamine supplements may contain glutamine peptides, which are short chains of amino acids linked together. Glutamine peptides are often derived from wheat, which means that they may contain gluten. Therefore, if you are gluten intolerant or have celiac disease, you shold avoid glutamine supplements that contain glutamine peptides.
To ensure that you are taking a gluten-free glutamine supplement, you should look for products that are labeled as “gluten-free” or “certified gluten-free.” You can also check the ingredients list for any potential sources of gluten, such as wheat, barley, or rye.
If you are gluten intolerant, you can still take glutamine supplements as long as they are gluten-free and do not contain glutamine peptides derived from wheat. It’s important to read product labels carefully and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
The Difference Between Glutamine and Gluten
Glutamine and gluten are two distinct entities, despite sharing similar names. Gluten is a protein complex found in wheat and other cereal grains, while glutamine is an amino acid.
Gluten is composed of two main protein types, gliadin and glutenin, and is responsible for the elasticity of dough and the texture of baked products. It is also a common ingredient in many processed foods, such as bread, pasta, and cereals.
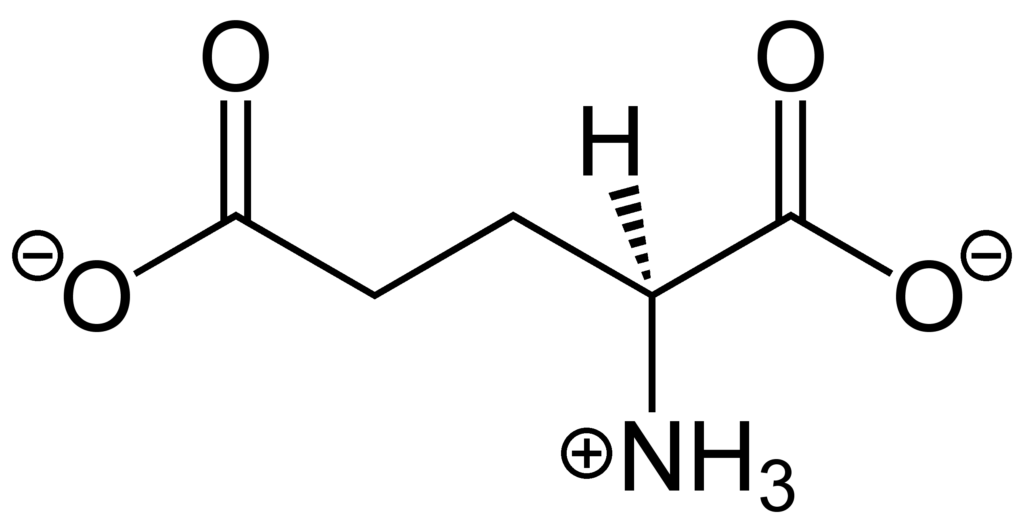
On the other hand, glutamine is one of the 20 amino acids that make up proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid, wich means that the body can produce it on its own. Glutamine is essential for the proper functioning of the immune system, the digestive system, and the brain.
While gluten contains high amounts of glutamine, the two are not interchangeable. Gluten is a complex protein made up of various amino acids, including glutamine. Therefore, consuming gluten-containing foods does not necessarily provide the body with a sufficient amount of glutamine.
Gluten and glutamine are two distinct entities that should not be confused with each other. While gluten is a protein complex found in wheat and other cereal grains, glutamine is an amino acid that is essential for various bodily functions.
Is Glutamine a Component of Gluten?
Gluten is a complex mixture of proteins that are found in the seeds of certain cereal grains, including wheat, barley, and rye. These proteins are known to be prolamins, a type of storage protein that is rich in the amino acids glutamine and proline.
Glutamine is an important amino acid that is involved in varous metabolic processes in the body. It is also a precursor for the synthesis of other amino acids and neurotransmitters. In gluten proteins, glutamine residues contribute to the compact and stable structure of the protein, as well as its unique properties such as its elasticity and ability to form a network.
Proline is another important amino acid that is present in high amounts in gluten proteins. It contributes to the strength and stability of the protein structure by forming rigid ring structures that help to maintain the protein’s shape.
The high content of glutamine and proline in gluten proteins is what makes them unique and contributes to their functional properties. However, it is important to note that not all proteins found in gluten-containing grains are prolamins, and not all prolamins are gluten proteins.
Conclusion
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) is gluten-free as it is derived from wheat whee the protein is completely broken down during processing. However, glutamine peptides, which are often derived from wheat, should be avoided by individuals with coeliac disease or gluten intolerance. It is important to note that while glutamine is an amino acid found in gluten, it does not contain gluten itself. As such, individuals who are gluten-free do not need to avoid foods containing glutamine. it is important to read food labels carefully and speak with a healthcare professional to ensure a safe and healthy diet for those with gluten sensitivities.
