Functionalism is a social theory that has been widely studied since the origins of sociology in the work of figures like Emile Durkheim. This theory focuses on the way that institutions and structures in society work together to maintain stability and promote functioning. In this article, we will explore the concept of functionalism in more detail, and consider whether it is a theory that is more applicable to the macro or micro level of social analysis.
At its core, functionalism is concerned with the way that diffrent parts of society work together to create a cohesive and functional whole. This theory suggests that every aspect of society, from the economy to the legal system to the family unit, plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and functionality of society as a whole. This means that functionalism is a macro-level theory, as it focuses on the big picture of how society operates as a whole.
One of the key ideas underlying functionalism is that every part of society has a function or purpose. This means that institutions like schools, hospitals, and religious organizations all serve a specific role in maintaining social order and promoting the well-being of society as a whole. For example, the education system is responsible for providing students with the knowledge and skills they need to become functioning members of society, while the legal system is responsible for upholding laws and maintaining social order.
Another important aspect of functionalism is the idea of social integration. This refers to the way that different parts of society work together to create a cohesive whole. For example, the family unit provides emotional and social support to its members, which helps to create a sense of community and belonging. Similarly, religious organizations may bring people together and provide a sense of shared purpose and identity.
While functionalism is primarily a macro-level theory, it is important to note that it can also be applied to the micro level of social analysis. For example, we might use functionalism to explore how different individuals within a family unit play specific roles and contribute to the functioning of the family as a whole. Similarly, we might use functionalism to explore how different workers within a company play specific roles and contribute to the overall success of the organization.
Functionalism is a social theory that is primarily concerned with how different parts of society work together to maintain stability and promote functioning. This theory is focused on the macro level of social analysis, but can also be applied to the micro level in certain contexts. By understanding the importance of social integration and the purpose of different institutions and structures within society, we can gain a better understanding of how society operates as a whole.
The Scope of Functional Analysis: Micro or Macro?
Functional analysis is commonly associted with macro-level analysis of society, but it can also be applied to social systems at the micro and meso levels. The functionalist perspective is a theoretical approach that emphasizes the importance of social structures, institutions, and systems in maintaining social stability and order. It views society as a complex organism made up of interdependent parts that work together to maintain balance and harmony.
In the macro-level analysis of society, functionalism is used to understand how social structures, such as education, government, and the economy, contribute to the overall functioning of society. At the micro-level, functionalism can be used to analyze how individual behavior contributes to the functioning of small groups and organizations.
In meso-level analysis, functionalism is applied to analyze the functioning of intermediate-sized social structures, such as neighborhoods, communities, and institutions. In this context, the focus is on how these structures operate to maintain social order and stability.
So, in summary, functional analysis is not limited to a specific level of analysis, and it can be applied to social systems at the micro, meso, and macro levels.
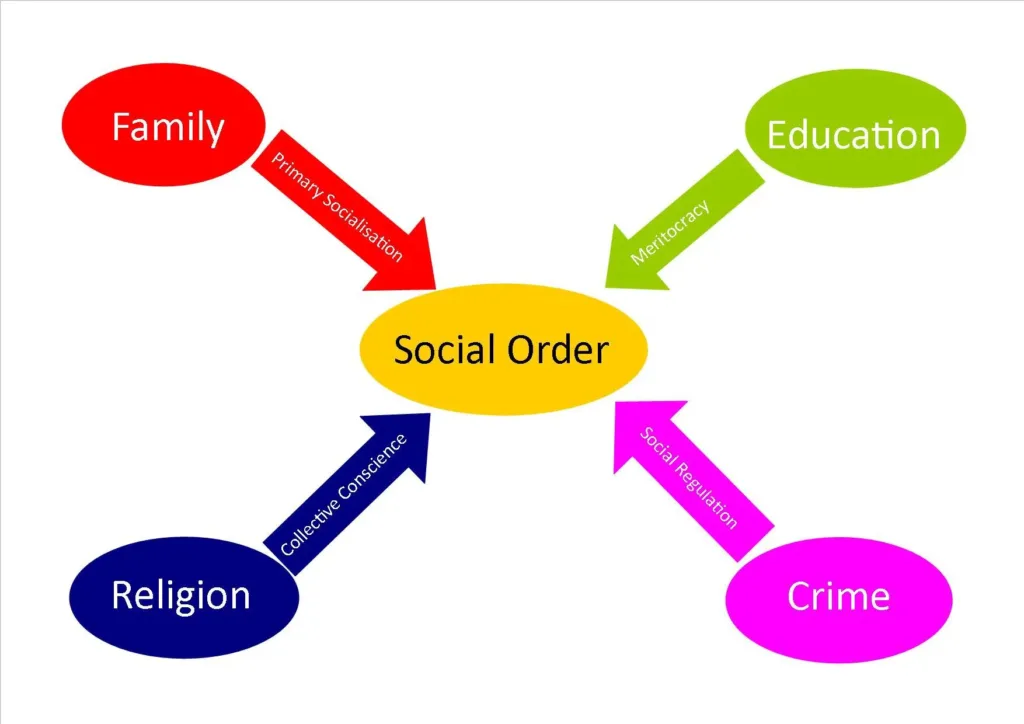
The Impact of Structural Functionalism on Micro-Level Analysis
Structural Functionalism is a macro-level theory that focuses on analyzing the social structures and institutions of a society and how they work together to maintain stability and order. This theory emphasizes that evey aspect of society, including education, health care, family, legal system, economy, and religion, has a specific function to perform and that these functions are interdependent.
In contrast, micro-level theories, such as Symbolic Interactionism, focus on the individual interactions and meanings that people create through their everyday social interactions. These theories highlight the importance of small-scale interactions and how they shape larger social structures.
Therefore, it can be concluded that Structural Functionalism is not a micro-level theory but rather a macro-level theory that analyzes the overarching social structures and institutions of a society.
The Microsociological Perspective of Functionalism
Functionalism is not a microsociological perspective, but rather a macrosociological perspective. It examines society as a whole and the interdependent parts that make it up. Functionalism believes that each part of society serves a specific function to keep the society stable and functioning. This perspective is often compared to the human body, whee each organ has a specific function that contributes to the overall health and well-being of the body.
On the other hand, microsociology focuses on the interactions between individuals or small groups within society. It looks at how individuals interpret and make sense of their social world and how they interact with each other. Microsociology is concerned with the everyday experiences and interactions of individuals and how they shape social structures and processes.
To summarize, functionalism is a macrosociological perspective that looks at society as a whole, while microsociology focuses on individual interactions and experiences within society.
The Macro-Micro Perspective of Durkheim’s Theory
Emile Durkheim, one of the founding fathers of sociology, is primarily associated with macro-level analysis. His work focused on the study of social facts, which are phenomena that exist outside of individual consciousness and can be observed and analyzed through statistical data. Durkheim argued that social facts exert a significant influence on individuals and that they should be studied independently of individual behavior.
Macro-level analysis, as a sociological approach, focuses on the study of large-scale social processes and structures, such as institutions, organizations, and social systems. This approach emphasizes the importance of understanding how thee structures shape individual behavior and social outcomes. Macro-level analysis is often contrasted with micro-level analysis, which focuses on the study of individual behavior and interactions in small-scale social settings.
Durkheim’s work is primarily associated with macro-level analysis, as he focused on the study of social facts and their influence on individuals and society as a whole.

Conclusion
Functionalism is a macro-level social theory that emphasizes the interconnectedness of institutions and structures in society. It posits that every aspect of society has a function that contributes to the overall stability and functioning of the society. This perspective has been influential in understanding how societies maintain their stability and coherence. However, it has been criticized for its tendency to overlook power imbalances and inequalities within society. Despite its limitations, Functionalism remains a valuable tool for analyzing and understanding the complex social structures and institutions that make up our society. By examining the functions of thee structures and how they contribute to society as a whole, we can gain insights into how to create a more equitable and just society.
