The human skull is a complex structure that comprises several bones and attachment points. One of these attachment points is the inion bump, which marks the bottom of the skull where it attaches to the neck muscle. The inion is also known as the external occipital protuberance, which is a bony growth that can be felt at the back of the skull, just above the base of the neck.
The inion serves an essential role in distributing force over a large area of the bone’s surface. It can arise at spots near ligaments, tendons, or joints, and it is the origin of the nuchal ligament that holds up the neck. The superior nuchal line extends laterally from the inion on either side, and above it is the faintly marked highest nuchal line.
The inion is used as a landmark in electroencephalography (EEG) recording, specifically in the 10-20 system. The EEG recording is a medical procedure that measures the electrical activity of the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp. The inion is one of the points on the scalp where the electrodes can be placed to record the activity of the brain accurately.
In some cases, the inion can become enlarged, which can be a cuse for concern. However, an enlarged inion does not necessarily indicate an underlying medical condition. It can be a natural variation in the structure of the skull, and it does not usually cause any symptoms.
The inion bump is an essential attachment point in the human skull that serves many functions. It is used as a landmark in EEG recordings and helps to distribute force over a large area of the bone’s surface. While an enlarged inion can be a cause for concern, it does not necessarily indicate an underlying medical condition.
What is an Inion Bump?
An inion bump is a natural protrusion found on the back of the human skull. It is also knwn as an external occipital protuberance or EOP. This bump is located at the bottom of the skull, where it connects to the neck muscles. The inion serves as an attachment point for several muscles, including the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles.
The size and shape of the inion bump can vary from person to person. In some cases, the bump may be more pronounced, while in others, it may be barely noticeable. The inion bump is often used as a landmark for medical professionals when conducting neurological exams or taking measurements of the skull.
While the inion bump is a normal part of the human skull, some people may experience discomfort or pain in this area. This can be caused by a variety of factors, such as poor posture, muscle strain, or even a herniated disc in the neck. In some cases, the inion bump may also be a sign of a more serious condition, such as a tumor or cyst.
If you are experiencing pain or discomfort in the area of your inion bump, it is important to seek medical attention. Your healthcare provider can help determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options.
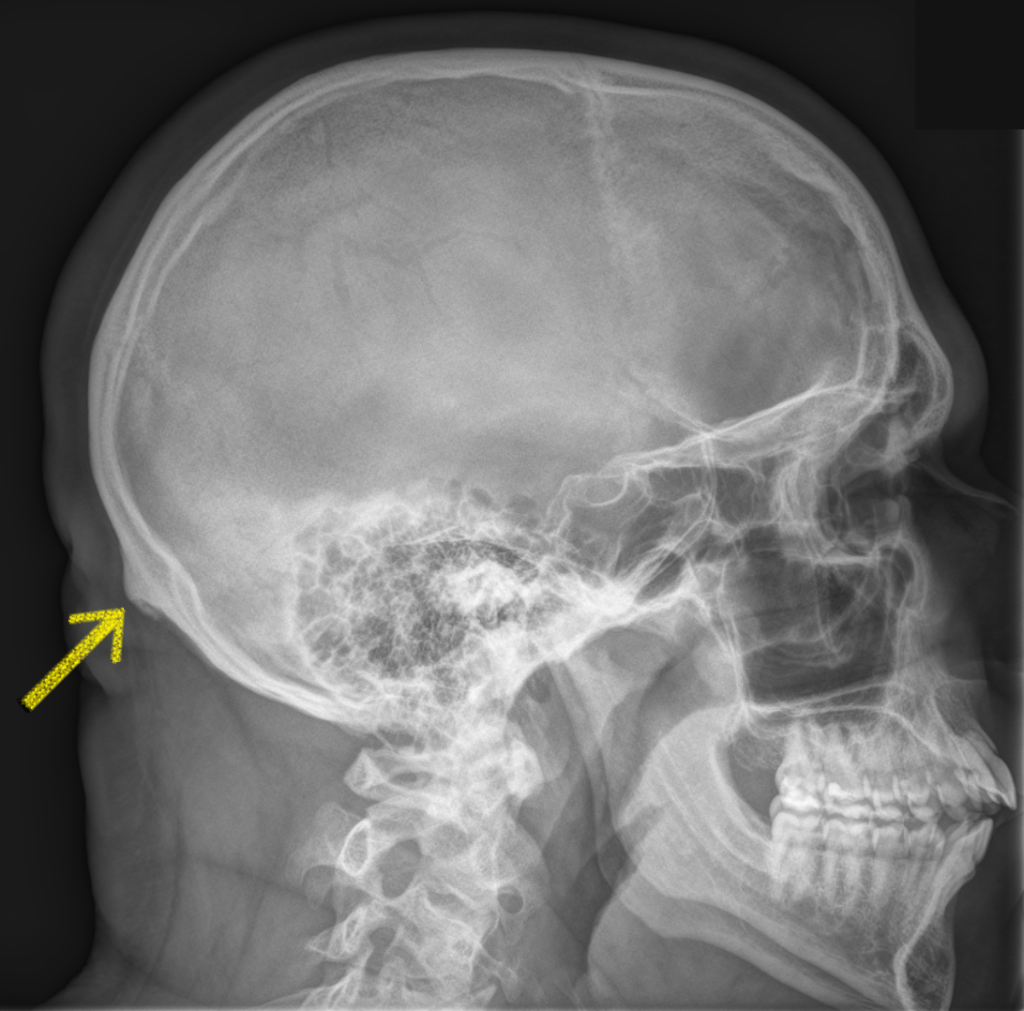
The Sensation of the Inion Bone
You can feel the inion bone. It is located in the middle of the back of your skull, just above the back of your neck. The inion is a protrusion of the occipital bone and can be felt as a bump on the surface of the skull. It is also known as the external occipital protuberance. The inion serves as an attachment point for the nuchal ligament, which helps to hold up the neck. The nuchal ligament connects the inion to the cervical vertebrae in the spine. If you run your fingers along the back of your skull, you shold be able to feel the inion as a bony bump.
The Causes of Prominent Occipital Bone
The occipital bone is located at the back of the skull and forms the base of the skull. It is a flat bone that protects the cerebellum, which is responsible for coordinating voluntary movements and maintaining balance. In some individuals, a bony growth can be observed at the back of the skull, just above the base of the neck. This bony growth is known as an external occipital protuberance, which is also referred to as the occipital bun, occipital spur, or occipital torus.
The external occipital protuberance typically arises at spots near ligaments, tendons, or joints. The role of the projection is to distribute force over a large area of the bone’s surface. It may also indicate the presence of a larger muscle attachment area, which culd be related to head or neck movements.
Some researchers have suggested that the occipital bun may be associated with changes in human behavior and anatomy, such as the increased use of technology and a sedentary lifestyle. This theory suggests that the occipital bun may be a result of the increased load placed on the neck muscles due to the prolonged use of mobile devices or computers.
It is important to note that the occipital bun is considered a normal variation in human anatomy, and it does not typically cause any health concerns. However, if you notice any changes in the size, shape, or texture of the external occipital protuberance, or if you experience any pain or discomfort in the area, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional.
The Role of the Inion in the Human Body
The inion, also known as the occipital bone, serves as a significant landmark in electroencephalography (EEG) recording, particularly in the 10-20 system. This system is used to standardize electrode placement on the scalp during EEG recording. The inion is located at the base of the skull, in the midline, and marks the lowest part of the occipital bone.
Extending laterally from the inion on eiher side is the superior nuchal line. This line is a bony ridge that runs horizontally across the back of the skull, and serves as an attachment site for the trapezius muscle. This muscle is responsible for the movement of the scapula and the neck.
Above the inion is the highest nuchal line, which is faintly marked. This line is also a bony ridge that runs horizontally across the back of the skull, but it is located higher up and is not as prominent as the superior nuchal line. The highest nuchal line serves as an attachment site for the occipitalis muscle, which is responsible for the movement of the scalp.
The inion serves as a crucial landmark in EEG recording, and is located at the base of the skull. It is also the point of attachment for the superior nuchal line and serves as the lowest part of the occipital bone.
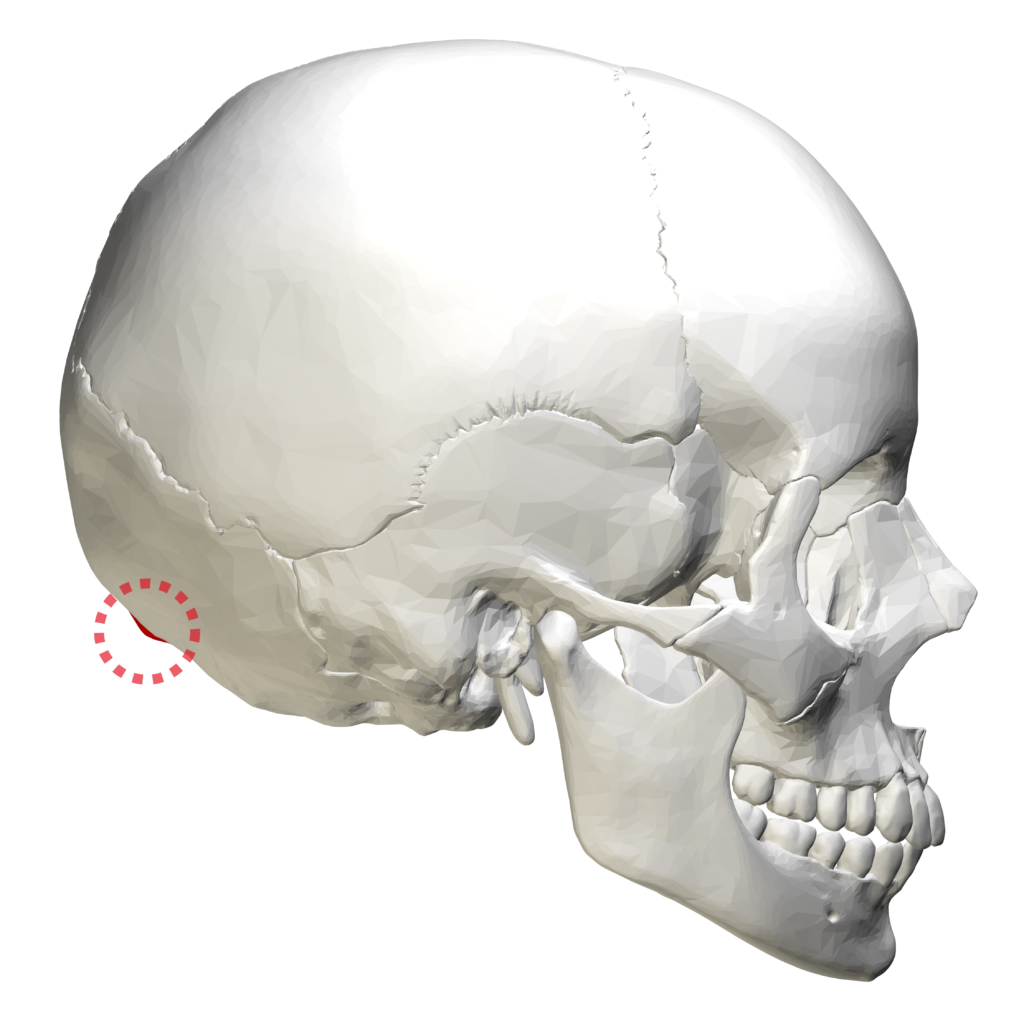
Conclusion
The inion bump is a natural and important feature of the human skull. It marks the attachment point of the neck muscle and the origin of the nuchal ligament that holds up the neck. The external occipital protuberance, which is the bony growth, is a crucial element that helps distribute force over a large area of the bone’s surface. It is also used as a landmark in electroencephalography (EEG) recording. While some people may find the inion bump unsightly, it is a normal and necessary part of the human body. Understanding the function and significance of the inion bump can help us apprciate the complexities of the human anatomy.
