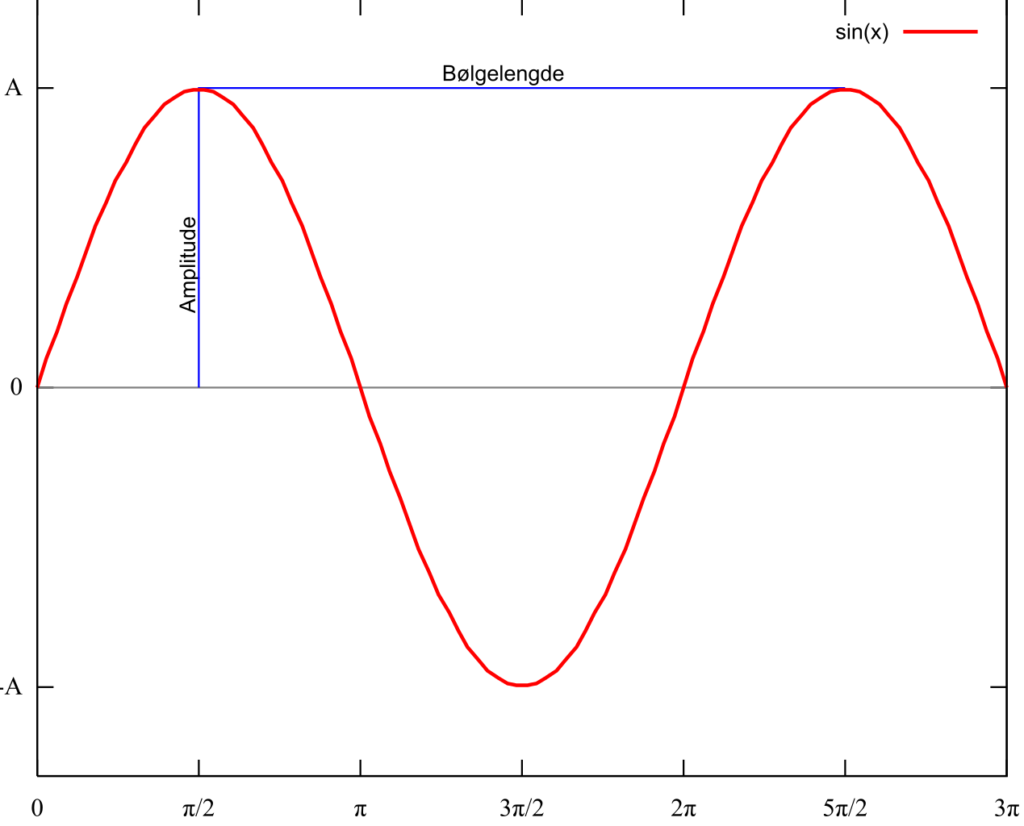
Amplitude is a term used to describe the magnitude or size of a wave. It is a measure of the maximum displacement of a wave from its rest or equilibrium position. The amplitude of a wave can be measured in various units such as meters, millimeters, or even micrometers. The energy of a wave is directly proportional to its amplitude, which means that increasing the amplitude of a wave will increase its energy.
Increasing the amplitude of a wave means that you are increasing the maximum displacement or distance that a wave travels from its rest position. This can be achieved in various ways, depending on the type of wave you are dealing with. For example, in the case of a sound wave, increasing the amplitude would mean increasing the loudness or volume of the sound.
Increasing the amplitude of a wave also means increasing the intensity of the wave. Intensity is a measure of the amount of energy that a wave carries per unit area. Therefore, increasing the amplitude of a wave will increase its intensity, which can have various effects depending on the type of wave.
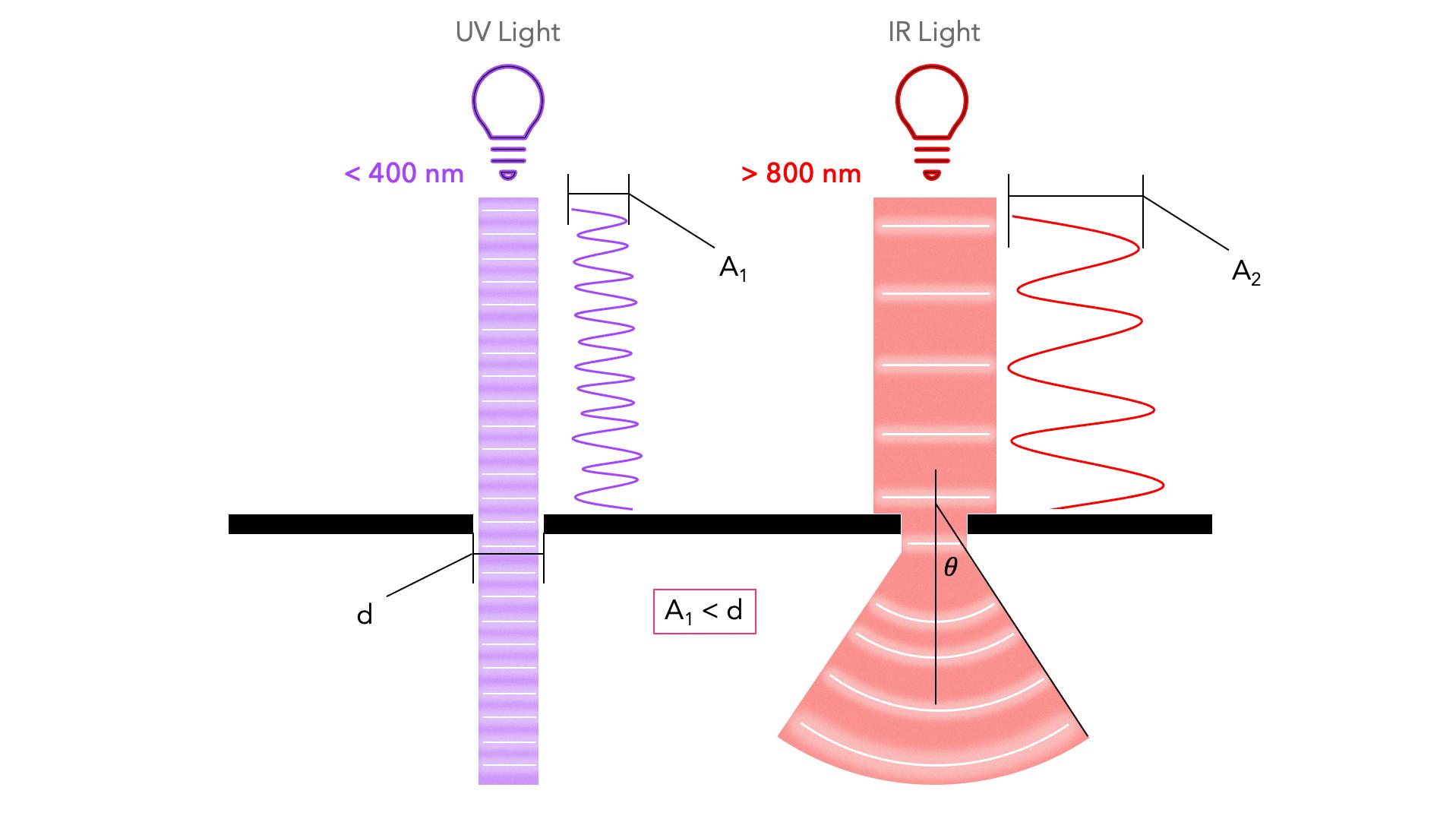
In the case of electromagnetic waves, such as light or radio waves, increasing the amplitude means increasing the brightness or strength of the wave. This can have various effects on the human body, depending on the wavelength and frequency of the wave.
In the case of mechanical waves, such as water waves, increasing the amplitude means increasing the height of the wave. This can have various effects on the environment, such as causing erosion or flooding.
Increasing the amplitude of a wave means increasing its energy, intensity, and strength. This can have various effects depending on the type of wave and the environment it is in. Whether you are dealing with sound waves, electromagnetic waves, or mechanical waves, understanding the effects of increasing the amplitude is crucial in many scientific and practical applications.
The Meaning of Increasing Amplitude
Increasing the amplitude of a wave refers to increasing the maximum displacement of the particles in the medium trough which the wave is traveling. This means that the wave will have a greater height or depth, depending on whether it is a transverse or longitudinal wave. The amplitude of a wave is measured from the equilibrium position to the crest or trough of the wave.
In practical terms, increasing the amplitude of a wave can result in a higher volume in sound waves or a more intense light in electromagnetic waves. However, it is important to note that increasing the amplitude of a wave does not necessarily mean an increase in frequency. In fact, the frequency of a wave remains constant as the amplitude increases.
It is also important to understand that increasing the amplitude of a wave results in an increase in energy. This is because the particles in the medium are being displaced to a greater extent, which requires more energy to accomplish. As a result, waves with higher amplitudes can be more destructive or powerful, as seen in ocean waves or earthquakes.
Increasing the amplitude of a wave means increasing its maximum displacement from the equilibrium position, resulting in a larger wave with more energy.
Source: expii.com
The Relationship Between Amplitude and Frequency
Increasing amplitude does not increase frequency. In fact, amplitude and frequency are inversely proportional to each other. This means that as the frequency of a wave increases, its amplitude decreases, and vice versa.
To understand this concept better, let’s firt define amplitude and frequency. Amplitude is the maximum displacement of a wave from its equilibrium position. It determines the loudness or brightness of the wave. Frequency, on the other hand, is the number of cycles of a wave that occur in a given time period. It determines the pitch or color of the wave.
When a wave has a high frequency, it means that it completes many cycles in a short amount of time. This rapid oscillation requires less energy to maintain its motion, resulting in a smaller amplitude. Conversely, a wave with a low frequency completes fewer cycles in the same amount of time. This slower oscillation requires more energy to maintain its motion, resulting in a larger amplitude.
To summarize, increasing amplitude does not increase frequency. Instead, the two are inversely proportional to each other. As frequency increases, amplitude decreases, and as frequency decreases, amplitude increases.
The Relationship Between Amplitude and Volume
Increasing the amplitude of a sound wave does increase its volume or loudness. The amplitude of a sound wave refers to the maximum displacement of air particles from their resting position. When the amplitude of a sound wave increases, the air particles are displaced more, creating a greater disturbance in the air. This disturbance results in a louder sound. Conversely, decreasing the amplitude of a sound wave results in a softer sound.
It is important to note that amplitude is not the only factor that affects the volume of a sound. The distance between the sound source and the listener, as well as any obstructions or reflections in the environment, can also affect the perceived volume of a sound.
To summarize, increasing the amplitude of a sound wave does increase its volume or loudness. However, othr factors can also affect the perceived volume of a sound.
Factors Contributing to Increased Amplitude
The amplitude of a wave refers to the maximum displacement of a particle in the medium from its equilibrium position. Various factors can cause an increase in amplitude, including the force applied to the medium, the frequency of the wave, and the elasticity of the medium.
When a force is applied to a medium, it causes the particles to vibrate, and this vibration leads to the propagation of a wave. The greater the force applied, the greater the amplitude of the resulting wave. This relationship between force and amplitude is known as Hooke’s law, wich states that the displacement of a spring (or in this case, the particles in the medium) is directly proportional to the force applied.
Another factor that can cause an increase in amplitude is the frequency of the wave. As the frequency increases, the wave’s energy increases, and this energy is transferred to the particles in the medium, causing them to vibrate with a greater amplitude.
The elasticity of the medium can also affect the amplitude of a wave. A more elastic medium will allow a greater amplitude pulse to travel through it; the same force causes a greater amplitude. This is because the elasticity of the medium determines how easily the particles can be displaced from their equilibrium position, and a more elastic medium will be easier to displace, resulting in a larger amplitude wave.
The amplitude of a wave can be increased by applying a greater force to the medium, increasing the frequency of the wave, or using a more elastic medium.
Conclusion
Amplitude is a fundamental property of waves that plays a crucial role in determining thir energy, loudness, and volume. It is directly related to the amount of energy a wave carries, with higher amplitudes indicating higher energy levels. Additionally, the amplitude and frequency of a wave are inversely proportional, meaning that as the frequency increases, the amplitude decreases, and vice versa. By understanding the relationship between amplitude and frequency, we can better understand and manipulate waves for various applications in fields such as acoustics, optics, and communication. Ultimately, the study of amplitude is essential to our understanding of the physical world and our ability to harness its energy for practical purposes.
