Tidal Bulges are a fascinating phenomenon that occurs due to the gravitational pull of the moon on the Earth’s water bodies. The moon’s gravitational force creates two bulges of water on opposite sides of the Earth. These bulges are responsible for the tides that we experience in our oceans, seas, and even some large lakes.
The first tidal bulge is created on the side of the Earth facing the moon. This is due to the moon’s gravitational pull on the water bodies on that side of the planet. The gravitational force pulls the water towards the moon, creating a bulge of water.
The secod tidal bulge is created on the opposite side of the Earth, away from the moon. This bulge is not due to the moon’s gravitational pull, but rather due to inertia. As the Earth rotates, the water on the surface wants to continue moving in a straight line. However, the Earth’s gravity pulls the water towards its center, creating a second bulge on the opposite side of the Earth.
The combination of these two bulges creates the tides that we experience. There are generally three types of tides: diurnal, semi-diurnal, and mixed. A diurnal tide has one high and one low tide each day. A semi-diurnal tide has two high and two low tides each day of equal heights. a mixed tide has two high and two low tides each day of different heights.
Tidal bulges are an incredible phenomenon that is responsible for the tides that we experience in our planet’s water bodies. The moon’s gravitational force creates one bulge, while inertia creates the other. The combination of these two bulges results in the different types of tides that we experience. Understanding this process is crucial for predicting tides and planning activities such as fishing, boating, and beach-going.
Number of Tidal Bulges on Earth
Tidal bulges are caused by the gravitational force of the moon and the sun on the Earth’s oceans. On Earth, two tidal bulges are formed, one on the side of Earth facing the moon and the other on the opposite side. The gravitational pull of the moon creates a bulge on the near side of the Earth, while the centrifugal force caused by the Earth’s rotation creates another bulge on the far side of the Earth. This results in two tidal bulges on the Earth, which move as the Earth rotates, causing the tides to rise and fall twce a day. It is important to note that the height of the tidal bulges varies based on a variety of factors, including the alignment of the sun, moon, and Earth, and the topography of the ocean floor.
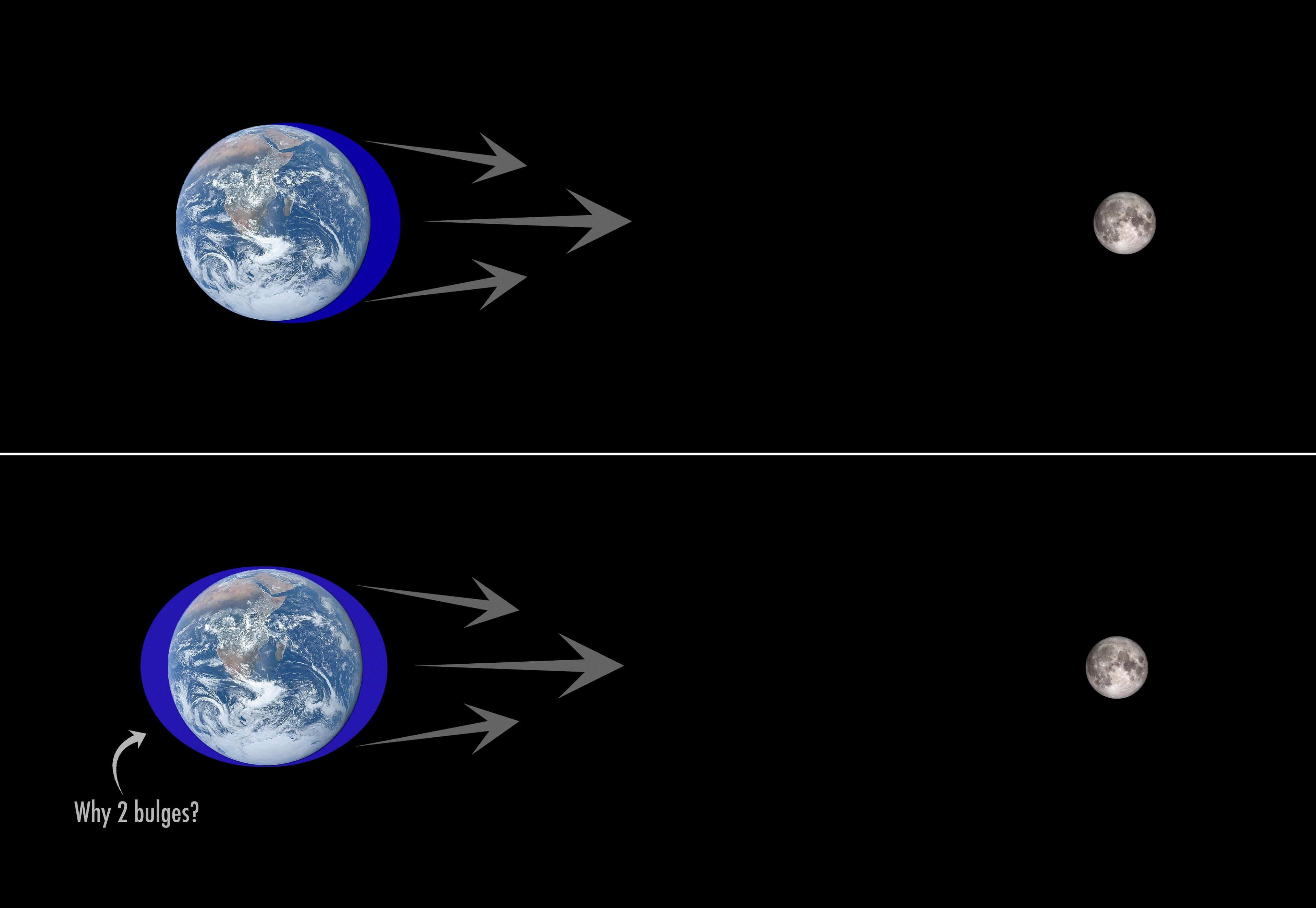
Source: reddit.com
Types of Tides
Tides refer to the periodic rise and fall of sea levels caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun on Earth’s oceans. There are four main types of tides: diurnal tide, semi-diurnal tide, mixed tide, and meteorological tide.
1. Diurnal tide: Diurnal tide is a type of tide that has only one high tide and one low tide within a 24-hour period. This means that the sea level rises and falls once a day. Diurnal tides are typically found in coastal areas near the equator.
2. Semi-diurnal tide: Semi-diurnal tide is a type of tide that has two high tides and two low tides within a 24-hour period. The two high tides are usually of equal height, and the same is true for the two low tides. Semi-diurnal tides are commonly found on the Atlantic coast of the United States.
3. Mixed tide: Mixed tide is a type of tide that has two high tides and two low tides within a 24-hour period, but the height of each tide can be different. This means that sometimes the high tide can be higher or lower than the other high tide, and the same is true for low tides. Mixed tides are usually found in coastal areas near the Pacific Ocean.
4. Meteorological tide: Meteorological tide is a type of tide that is caused by weather patterns such as high winds or low atmospheric pressure. These tides are not caused by the gravitational pull of the moon or the sun, but they can stll cause significant changes in sea level. Meteorological tides are often seen during storms and hurricanes.
The four main types of tides are diurnal tide, semi-diurnal tide, mixed tide, and meteorological tide. Each type of tide has its unique characteristics and can affect coastal areas in different ways. Understanding the different types of tides is essential for coastal communities to prepare for and mitigate the impact of tides on their daily lives.
The Two Tidal Bulges
Tides are the rhythmic rise and fall of ocean waters. They are caused by the gravitational attraction of the moon and the sun acting on the Earth’s waters. The two tidal bulges are the two elevated areas of water on the Earth’s surface that are created by the gravitational force of the moon.
One tidal bulge is created on the “near” side of the Earth, the side facing the moon. The gravitational force of the moon pulls the ocean’s waters toward it, creating this bulge. This is known as the “direct tide.”
On the other hand, the second tidal bulge is created on the “far” side of the Earth, the side opposite the moon. Here, inertia dominates and the ocean waters tend to remain in place while the Earth is pulled away, creating a second bulge. This is known as the “indirect tide.”
It is important to note that these tidal bulges are not static, but rather they move around the Earth as the moon orbits the planet. This results in a constant rise and fall of the ocean waters, wich we experience as tides.
The two tidal bulges are the elevated areas of water on the Earth’s surface created by the gravitational force of the moon. One is created on the near side of the Earth, and the other on the far side, resulting in the rhythmic rise and fall of ocean waters known as tides.
Types of Tides
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun on the Earth’s oceans. There are three primary types of tides: diurnal, semi-diurnal, and mixed.
Diurnal tides are characterized by one high and low tide each day. They are most common in regions closer to the equator, such as the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea.
Semi-diurnal tides have two high and low tides each day, with roughly the same height. These tides occur in many parts of the world, including the east coast of North America and the west coast of Africa.
Mixed tides have two high and low tides each day, but the heights of the tides are different. These tides are most common in the Pacific Ocean, particularly along the west coast of North America.
It is important to note that the type of tide in a particular location can vary depending on factors such as the shape of the coastline, the depth of the water, and the position of the moon and sun. Understanding the different types of tides can help with activities such as boating, fishing, and beachcombing.

Conclusion
Tidal bulges are a fascinating phenomenon that occurs due to the gravitational pull of the moon on the Earth’s oceans. This creates two bulges of water on opposite sides of the planet, resulting in the different types of tides we observe. Understanding tidal bulges is important for predicting and managing the effects of tides on coastal areas, shipping, and fishing industries. As we continue to study the forces of nature, we gain a greater appreciation for the complexity and beauty of our planet.
