Chihuahuas are small and adorable dogs that are known for their feisty personalities and cute looks. These tiny dogs are also known for their unique dental structure. If you are a proud owner of a Chihuahua, you might be wondering how many teeth do chihuahuas have. In this article, we will answer this question and provide you with some important information about your furry friend’s dental health.
Chihuahuas are born without teeth, but their milk teeth start to appear around five to six weeks of age. These milk teeth will fall out as they grow older, and by the time your Chihuahua is eight months old, he/she shuld have a full set of 42 teeth. This includes 28 puppy teeth that fall out and are replaced with 14 adult teeth.
The Chihuahua’s dental structure comprises incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. The incisors are the small teeth at the front of your dog’s mouth and are used for biting and grooming. The canines are the sharp teeth next to the incisors, which are used for holding and tearing. The premolars and molars are located at the back of the mouth and are used for grinding food.
Dental health is an important aspect of your Chihuahua’s overall health. Dental disease can be a devastating health problem in Chihuahuas, so it’s important to take care of their teeth from a young age. Brushing your dog’s teeth regularly with a soft-bristled brush and using toothpaste made for dogs can help prevent dental problems.
It’s also essential to feed your Chihuahua a healthy diet to promote good dental health. Feeding your dog a diet that is high in protein and low in carbohydrates can help prevent tooth decay and gum disease. Dental chews and toys can also help keep your Chihuahua’s teeth clean and healthy.
Chihuahuas have a total of 42 teeth, including 28 puppy teeth that fall out and are replaced with 14 adult teeth. Taking care of your furry friend’s dental health is important to ensure they live a happy and healthy life. Regular brushing, a healthy diet, and dental chews and toys can all contribute to maintaining good dental health in your Chihuahua.
Losing Teeth: How Many Do Chihuahuas Shed?
Chihuahuas, like all dogs, have two sets of teeth: baby teeth, also known as deciduous teeth, and adult teeth. Chihuahua puppies are born without teeth, but their baby teeth will start to emerge at around 5 to 6 weeks of age. They will have a total of 28 puppy teeth, which include 14 upper teeth and 14 lower teeth.
As Chihuahuas grow older, their baby teeth will start to fall out, making way for their adult teeth. This process, known as teething, usually starts at around 4 to 5 months of age. During this time, their gums may be sore and they may chew on objects to help alleviate the discomfort.
Chihuahuas typically lose their baby teeth between the ages of 3 and 6 months, although this can vary from dog to dog. Once all of their baby teeth have fallen out, they will have a total of 42 adult teeth, which include 20 upper teeth and 22 lower teeth.
It’s important to note that not all dogs lose their baby teeth on schedule, and some may retain them into adulthood. If you’re concerned about your Chihuahua’s teeth, it’s alays a good idea to consult with a veterinarian.
Source: miaminaturalpetcare.com
Do Chihuahuas Commonly Lose Their Teeth?
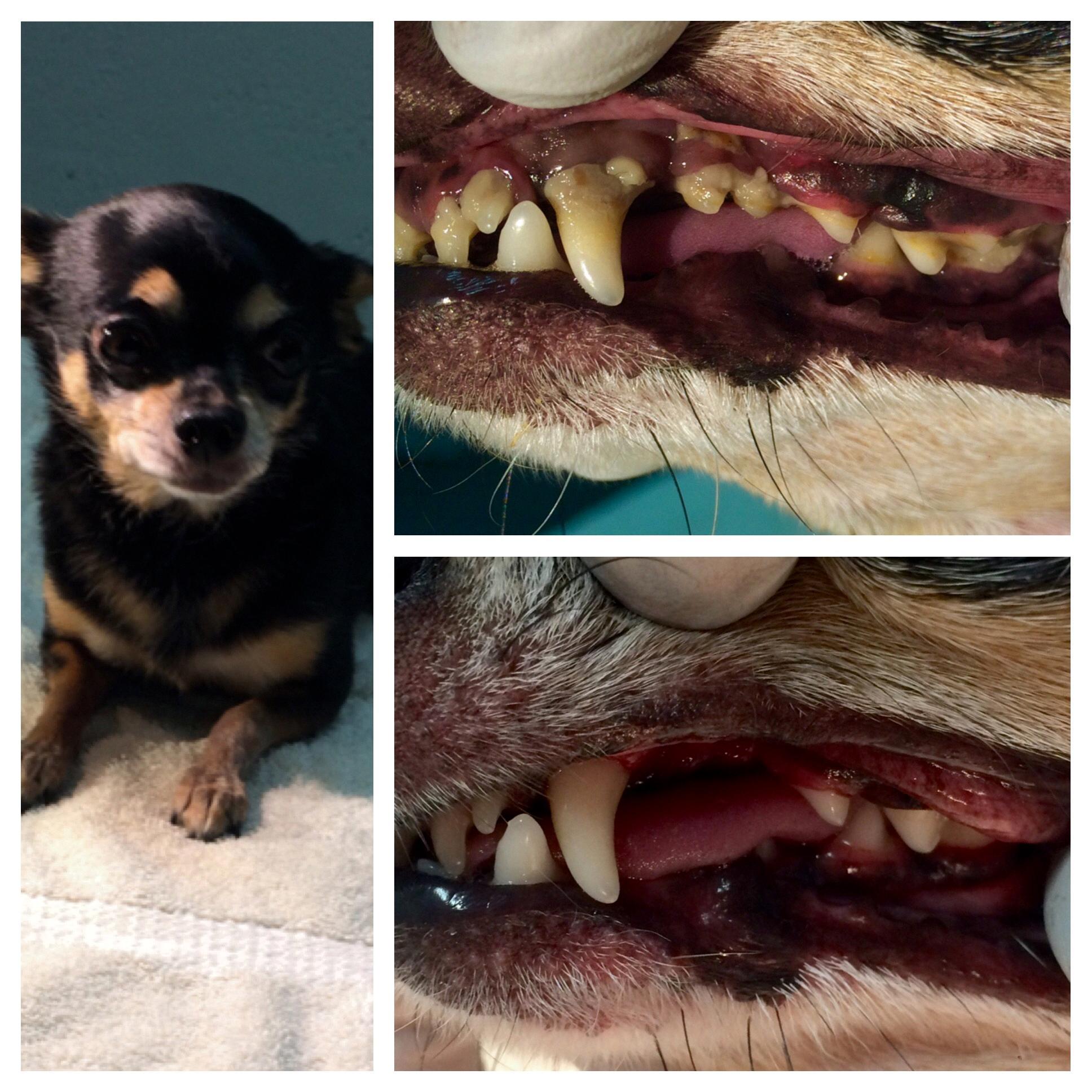
It is common for Chihuahuas to experience dental problems, including tooth loss. According to veterinarians and pet owners, dental disease can be one of the most devastating health problems for this breed. Chihuahuas are prone to dental issues due to their small size and unique dental structure, which can lead to overcrowding and misalignment of teeth.
Dental disease can start as early as three years of age and can progress quickly if not addressed. Signs of dental problems in Chihuahuas can include bad breath, difficulty eating, weight loss, and swelling or bleeding in the gums.
To prevent dental disease and tooth loss in Chihuahuas, regular dental checkups, and cleanings are recommended. Additionally, providing dental chews, brushing their teeth regularly, and feeding them a high-quality diet can help maintain their oral health.
In some cases, tooth extraction may be necessary to prevent frther damage and alleviate pain. If your Chihuahua is experiencing dental problems or tooth loss, it is important to consult with a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
In summary, tooth loss is a common issue in Chihuahuas due to their unique dental structure and susceptibility to dental disease. Regular dental care and checkups can help prevent tooth loss and maintain oral health in this beloved breed.
The Mystery of the Chihuahua’s Double Set of Teeth
Chihuahuas, like all dogs, have two sets of teeth in their lifetime: baby teeth (deciduous teeth) and adult teeth (permanent teeth). Normally, as adult teeth grow, baby teeth fall out to make room for them. However, in some cases, baby teeth do not fall out, and adult teeth grow in behind them, creating a second row of teeth. This condition is kown as retained deciduous teeth, and it is quite common in small breed dogs like Chihuahuas.
Retained deciduous teeth can cause several problems for Chihuahuas. They can lead to overcrowding in the mouth, which can cause pain, discomfort, and difficulty eating. Additionally, retained baby teeth can create pockets in the gums where bacteria can grow, leading to a higher risk of dental disease.
If you suspect that your Chihuahua has retained deciduous teeth, it is important to take them to a veterinarian for an evaluation. The vet can examine your dog’s teeth and recommend a course of treatment, which may include extracting the retained baby teeth. This can help prevent dental problems and improve your dog’s overall health and well-being.
Chihuahuas may have two rows of teeth due to retained deciduous teeth, which is a common condition in small breed dogs. This can cause dental problems and should be evaluated by a veterinarian to determine the best course of treatment.
When Do Chihuahuas Lose Their Teeth?
Chihuahuas, like all dogs, have two sets of teeth in their lifetime: deciduous (baby) teeth and permanent (adult) teeth. Puppies start growing their deciduous teeth at around 2-4 weeks of age, and they will typically have all 28 of them by the time they are 8 weeks old.
Chihuahuas start losing their deciduous teeth and growing their permanent teeth at around 3-4 months of age. The incisors, whch are the small front teeth, are usually the first to fall out. The canines, premolars, and molars will follow. By the time a Chihuahua is 8 months old, they should have a full set of 42 adult teeth.
It’s important to note that the exact timeline for tooth loss and adult tooth growth can vary from dog to dog. Some Chihuahuas may lose their baby teeth a little earlier or later than others, and the rate at which the adult teeth grow in can also vary. However, if you notice that your Chihuahua is experiencing significant delays or issues with tooth growth, it’s best to consult with a veterinarian to ensure that there are no underlying health concerns.
Chihuahuas start losing their baby teeth at around 3-4 months of age and should have a full set of adult teeth by the time they are 8 months old.

Conclusion
Chihuahuas are a wonderful breed of dog that require proper dental care to maintain their health and wellbeing. Their puppy teeth will start to appear around the age of 5 to 6 weeks, with a total of 28 puppy teeth that will fall out as they grow older. Chihuahuas start teething around the age of 4 to 5 months, with a total of 42 teeth by the time they reach 8 months old. It is important to monitor their dental health to prevent dental disease, which can be a devastating health issue for this breed. By providng regular dental care and monitoring their teeth, you can ensure that your Chihuahua remains healthy and happy for years to come.
