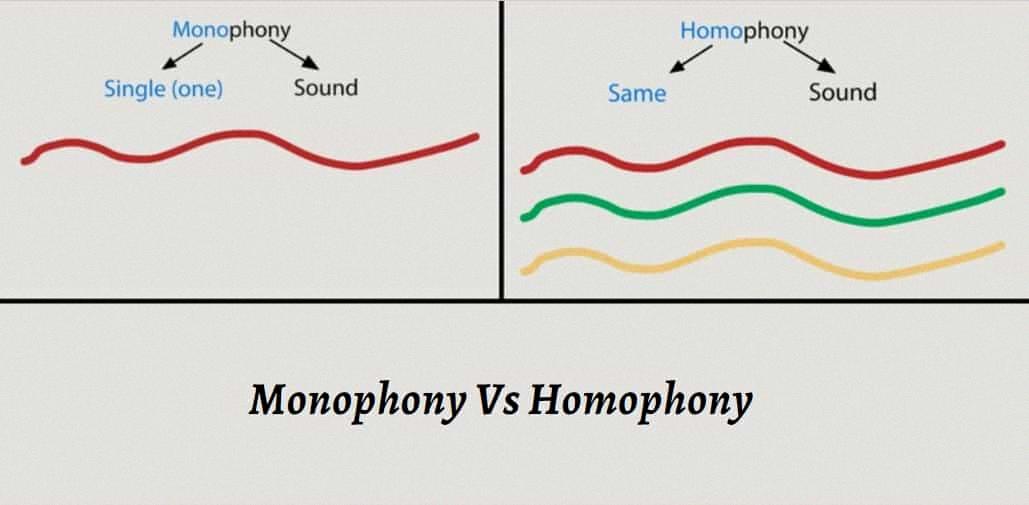
Homophony is a musical texture that features one main melody supported by accompanying sounds or chordal accompaniment. This texture is commonly found in various music genres, including rock, pop, and classical music.
In homophonic music, the melody is the dominant element, and the othr instruments or voices support it by playing harmonies or chords. This creates a rich and layered sound that is pleasing to the ear.
One of the essential features of homophonic music is the use of harmony. Harmony refers to the combination of different notes played simultaneously to create a pleasing sound. The harmonies used in homophonic music can be simple or complex, depending on the style and genre of the music.
Homophonic music is often contrasted with polyphonic music, which features multiple independent melodies played simultaneously. While polyphonic music can be more complex and intricate, homophonic music is often more accessible and easier to listen to.
Examples of homophonic music can be found in all sorts of music genres, from classical pieces like Beethoven’s “Moonlight Sonata” to modern pop songs like Adele’s “Someone Like You.”
Homophony is a musical texture featuring one main melody supported by accompanying sounds or chordal accompaniment. It is a common feature in various music genres and creates a rich and layered sound that is pleasing to the ear.
Understanding Homophony in Music
Homophony is a musical texture that is characterized by a single melody that is supported by an accompanying chordal or harmonic structure. In simple terms, it is a musical texture in whch all the voices or parts move together in harmony to support the melodic line. In homophonic music, there is a clear distinction between the melody and the accompaniment, which provides a harmonic foundation for the melody.
Homophony is often used in popular music, folk music, and hymns, as it allows for a clear and straightforward presentation of the melody with a supporting harmony. This musical texture is also commonly used in classical music, particularly in the Baroque period, where it was used extensively in the works of composers such as Johann Sebastian Bach.
One of the hallmarks of homophonic music is the use of chords, which are played or sung in a rhythmical pattern that supports the melody. The chords may be played by instruments such as a piano or guitar, or sung by a choir or vocal ensemble. The melody may be sung by a soloist or a group of singers, and the harmony may be provided by other singers or instruments.
Homophony is a musical texture that is characterized by a single melody that is supported by an accompanying chordal or harmonic structure. It is a popular texture in many different musical genres and is often used to create a clear and straightforward presentation of the melody with a supporting harmony.

The Definition of Homophony Sound
Homophony refers to a musical texture where multiple instruments or voices play the same melody simultaneously, with one of them being the dominant element. In this type of music, the accompanying parts usually consist of chords or harmonies that support the melody, rather than having a distinct melody of their own.
Homophonic music can be found in varios genres and styles, such as classical music, pop, rock, and folk. One of the most common examples of homophonic music is a choir singing a hymn or a popular song, where all the voices sing the same melody but in different harmonies.
The term homophonic is derived from the Greek words homos, meaning “same,” and phone, meaning “sound.” In other words, homophonic music is characterized by a single sound or melody being played by multiple instruments or voices at the same time.
Some examples of homophonic music include popular songs like “Yesterday” by The Beatles, “Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen, and “I Will Always Love You” by Whitney Houston.
Homophonic music is a type of musical texture where multiple instruments or voices play the same melody simultaneously, with one of them being the dominant element. This type of music can be found in various genres and styles and is characterized by a single sound or melody being played by multiple instruments or voices at the same time.
The Characteristics of Homophonic Texture
Homophonic texture is a musical texture that is characterized by multiple voices or instruments playing different notes simultaneously, but all harmonizing with and supporting the same melody. In other words, it involves a single melody that is supported by a harmonic accompaniment. This type of texture is commonly found in popular music, where a singer or instrumentalist performs a melody while being accompanied by a band or other instruments. The accompaniment may differ in terms of harmony, rhythm, or texture, but it always supports and enhances the melody. Homophonic texture is often contrasted with polyphonic texture, whih involves multiple melodies that are played or sung simultaneously and independently. It is important to note that homophonic texture does not necessarily mean that all the parts are playing or singing the same rhythm or notes, but rather that they are all supporting the same melody. homophonic texture is a common and important musical texture that can be found in many different genres of music.
Identifying Homophony
Homophony is a musical texture characterized by multiple voices moving together harmonically at the same pace. To identify homophony, one should listen for a clear melody accompanied by harmonies that support the melody. The harmonies should move in the same rhythm as the melody, creating a pleasant and consistent sound. Homophonic music often sounds symmetrical and balanced due to the harmonies being structured around the melody. A common exaple of homophonic music is a hymn or choral work, in which the melody is sung by the choir, and the accompaniment is played by the organ or other instruments. It is worth noting that homophonic music may have occasional moments of polyphony, but the overall texture should be homophonic. To determine if a piece of music is homophonic or not, it is essential to listen to the relationship between the melody and harmony and how they move together throughout the piece.
Exploring the Music Texture of Homophony
Homophony is a type of musical texture that is based primarily on chords. In homophonic music, multiple instruments or voices play different parts that are harmonically related and move togeher in a similar rhythm, creating a unified sound. This is in contrast to polyphony, which involves multiple, independent melodies playing simultaneously. Homophony is commonly used in many genres of music, including pop, rock, and classical, and can be found in both vocal and instrumental music. It is an important aspect of music theory and composition, and understanding the differences between homophony and polyphony is essential for analyzing and appreciating different types of music.

What is Homophonic in Simple Terms?
Homophonic refers to a musical texture where a single melody is played or sung by one or more instruments or voices at the same time. In other words, all parts or voices are in harmony and move together rhythmically to create a single musical line. This contrasts with polyphonic music, where two or more independent melodies are played or sung simultaneously. Homophonic music can be found in various genres such as classical, pop, jazz, and folk music. Examples of homophonic music include a singer accompanied by a piano, a guitar strumming chords whle a singer sings a melody, or a choir singing the same lyrics in unison with varying harmonies. The homophonic texture is often used to create a clear and simple sound, making it a popular choice for many musical compositions.
Examples of Homophony
Homophony is a musical texture wherein multiple voices or instruments play different notes, but in a way that creates harmony and a sense of unity. In other words, homophony is a type of music where different parts move together in a harmonious manner, with one part typically being the melody or the main focus, while the others provide accompaniment.
An example of homophony could be a singer accompanied by a guitar. The guitar player might be picking or strumming chords that harmonize with the melody that the singer is singing. Another example could be a jazz combo comprising a bass, a piano, and a drum set providing the “rhythm” background for a trumpet improvising a solo.
In homophonic music, the different parts are not necessarily equal in importance, and they can be distinguished from each other based on ther function, range, and texture. However, they all work together to create a unified and pleasing sound.
Other examples of homophony include a single bagpipes or accordion player playing a melody with drones or chords. In these cases, the melody is usually the main focus, while the drones or chords provide a harmonic backdrop.
Homophony is a common type of musical texture that can be found in various genres of music, including classical, jazz, folk, and pop. It is characterized by the harmonious interplay of different parts, and it can create a rich and dynamic sound that is pleasing to the ear.
The Meaning of Homophony in Semantics
Homophony is a linguistic term used in semantics to describe a phenomenon where two or more words are pronounced the same but have different meanings. This means that homophonic words have the same sound but different spellings and meanings. For example, the words “flower” and “flour” are homophones becase they sound the same but have different meanings. Similarly, the words “write” and “right” are also homophones.
There are many examples of homophones in the English language. Some of the most common examples include “their,” “there,” and “they’re,” “to,” “too,” and “two,” and “bare” and “bear.” It is important to note that homophones can cause confusion in both spoken and written language, which is why it’s essential to understand their meanings and use them correctly.
Homophony is a linguistic term that refers to words that have the same sound but different meanings. It is important to be aware of homophones and use them correctly to avoid confusion in communication.
Characteristics of Homophony in Music
Homophony is a type of musical texture that is characterized by the presence of multiple notes or voices sounding simultaneously, but with a clear melodic line beig played in the foreground. In this texture, the supporting harmonies or accompaniment are typically less complex and serve to reinforce the melodic line, often consisting of chords or block-like structures.
Some of the key characteristics of homophonic music include a clear sense of melody and harmony, with the melody often being carried by a single instrument or voice. The accompaniment serves to support the melody and provide a harmonic foundation, but it is generally less prominent and intricate than the melody itself.
Homophonic music can take many forms, ranging from simple folk songs to complex orchestral works. It can also be found in a variety of musical genres, including classical, pop, and jazz.
The defining characteristic of homophonic music is the presence of a clear melodic line supported by a simpler harmonic accompaniment. This texture can provide a sense of clarity and coherence to musical compositions, making it a popular choice for many composers and performers.

Types of Homophony
Homophony is a musical texture where multiple parts or voices play different notes, but all the parts move at the same rhythm. In other words, all the voices or instruments have the same harmonic rhythm. This type of texture is quite common in music, and there are two main types of homophony: melody-and-accompaniment, and chorale-type (homorhythmic) homophony.
Melody-and-accompaniment homophony is when one voice or instrument plays a melody, wile the other voices or instruments play accompanying chords or rhythms. This type of homophony is often used in popular music, where the lead singer sings the melody, while the band plays chords and rhythms to support the melody. It’s also common in classical music, where the soloist plays the melody, and the orchestra plays the accompaniment.
On the other hand, chorale-type or homorhythmic homophony is when all the voices or instruments play the same rhythm and harmony, creating a harmonious and unified sound. This type of homophony is often used in choral music, where all the singers sing the same melody and lyrics, but in different vocal ranges. It’s also common in orchestral music, where all the instruments play the same rhythm and harmony, creating a powerful and majestic sound.
To summarize, the two main types of homophony are melody-and-accompaniment and chorale-type (homorhythmic) homophony. While melody-and-accompaniment homophony is often used in popular and classical music, chorale-type homophony is common in choral and orchestral music.
Is Homophony a Form of Polyphony?
Homophony can be considered a sub-type of polyphony, as both refer to the texture of music. Polyphony is a broader term that encompasses any musical texture that is not monophonic. It refers to the simultaneous sounding of two or more independent melodic lines. Homophony, on the other hand, is a type of polyphony where all voices or instruments perform a melody together, with one voice or instrument dominating the oters in terms of rhythm and harmony. In other words, homophony involves multiple voices or instruments playing the same or similar melody at the same time, but with some variation in the accompaniment. Therefore, while homophony is a type of polyphony, it is not the only type, and there are other forms of polyphony that do not involve homophonic textures.
What is Monophonic?
Monophonic, in music, is a term that refers to a single line of melody without any accompanying harmony or othr musical parts. It is a musical texture that features only one musical layer, the melody, and is typically performed by a single instrument or voice. Monophonic music can be found in various musical traditions worldwide, including ancient Greek music, Gregorian chant, and many forms of traditional folk music. Monophonic music is often used in religious or ceremonial contexts, as it can create a sense of simplicity and purity, and can be easily sung or played by large groups of people. In contrast to polyphonic music, which features multiple independent melodies played or sung simultaneously, monophonic music is focused solely on the melody and its variations.
Exploring the Characteristics of Homorhythmic Texture
Homorhythmic texture is a term used in music to describe a specific type of texture in which all parts or voices sing or play the same rhythm at the same time. This means that there is a similarity of rhythm in all parts, resulting in a very uniform and harmonious sound.
Homorhythm is commonly used in simple hymns or chorale settings, were the focus is on creating a unified and harmonious sound. It is also a condition of homophony, which refers to a type of texture in which all voices sing or play different notes but move together rhythmically to create a harmonious blend.
In homorhythmic texture, the music is typically structured around a single melody or harmonic progression, with all voices moving in unison to create a cohesive and powerful sound. This type of texture can be used in a variety of musical genres and styles, from classical music to choral and vocal arrangements, and even in contemporary pop and rock music.
Homorhythmic texture is an essential element of music that creates a sense of unity and harmony among different parts or voices. It is a valuable tool for composers and arrangers who want to create a strong and cohesive musical statement, and it is a fundamental concept for anyone interested in understanding the structure and texture of music.
Source: cmuse.org
Describing Monophonic Music
Monophonic is a term used in music to describe a type of musical texture that consists of a single melody line with no accompanying harmony or chords. This means that there is only one note being played or sung at any given time. It is the simplest form of musical texture and is often found in folk songs, traditional music, and early Western classical music.
In monophonic music, there is no harmony or counterpoint, whch are techniques used to create more complex textures in music. Instead, the focus is solely on the melody and the expression of the lyrics or message of the song. Monophonic music can be performed by a single singer or instrumentalist, or by a group of singers or instrumentalists performing the same melody together.
Examples of monophonic music include Gregorian chants, traditional folk songs, and some early Western classical music compositions. It is important to note that while monophonic music may seem simplistic, it can still convey deep emotion and meaning through the melody and lyrics.
Monophonic music is a type of musical texture that consists of a single melody line without harmony or counterpoint. It is often found in traditional and early Western classical music and can be performed by a single musician or a group of musicians.
Conclusion
Homophony is a musical texture that has one melody as the dominant element, with othr parts providing supporting sounds or chordal accompaniment. This texture is commonly used in popular music genres such as rock, pop, and hip-hop. Homophonic music allows for multiple instruments to play different notes but still revolve around the same melody, creating a unified sound.
Homophony differs from other musical textures, such as monophony and polyphony, because it emphasizes one melody over others. This texture has been used in music throughout history, from classical music to contemporary pop songs.
Homophony is an essential element in modern music, providing a harmonious and cohesive sound that is pleasing to the ears. Its simplicity and versatility make it a widely used texture, and it continues to be a popular choice for musicians and listeners alike.
