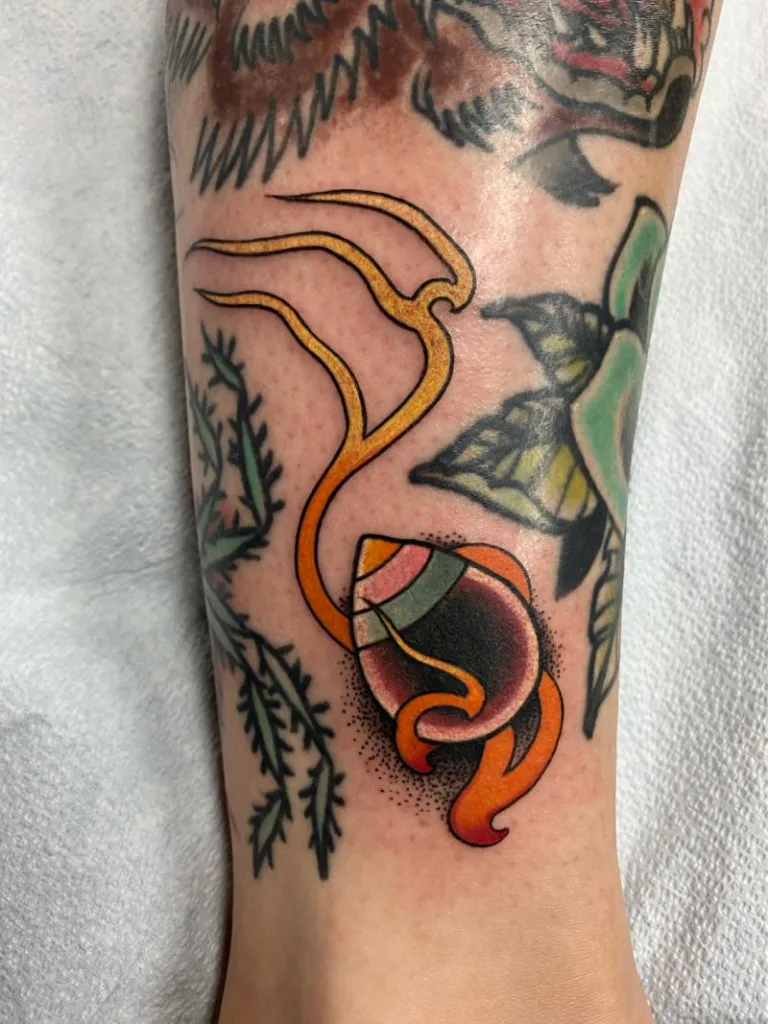
The hoju is a symbol that has strong ties to Buddhism and is considered to be a wish fulfilling jewel, bringing good health and prosperity to those who possess it. It is often depicted as an orb with a pointed top and is occasionally surrounded by flames, representing its power and significance.
In Buddhism, the hoju is a sacred object and is said to represent the three jewels of Buddhism; Buddha, Dharma, and Sangha. It is believed that possessing a hoju can bring spiritual enlightenment and help one to achieve their goals.
Aside from its religious significance, the hoju is also associated with a traditional household system knwn as the hoju system. This system existed prior to the amendment to the Civil Act in March 2005 and was a way of organizing households with a house head at its core. Under this system, only direct male descendants could inherit the position of the household head, and all family members were registered under the head’s record book.
However, with the amendment of the Civil Act, the hoju system was abolished, and every family member can now have their own individual record book. This new record book contains information on the person’s birth, death, marriage, adoption, as well as basic information on their spouse, parents, and children.
The hoju is a powerful symbol that holds significant meaning in Buddhism and traditional household systems. Its ability to bring good health and prosperity makes it a sought-after object, and its historical significance adds to its value. Whether for spiritual purposes or as a household item, the hoju is a symbol that continues to hold importance in various aspects of life.
The Meaning of a Hoju Tattoo
A hoju tattoo is a popular design among tattoo enthusiasts due to its cultural and spiritual significance. The hoju is a Japanese symbol that is believed to bring good health and fulfill wishes. It is often depicted as an orb with a pointed top and is sometimes surrounded by flames.
The hoju has strong ties to Buddhism and is considered to be a representation of the three jewels of Buddhism; Buddha, Dharma, and Sangha. A hoju tattoo can, therefore, be seen as a symbol of one’s devotion to the Buddhist faith and a reminder of the importance of these three jewels in one’s life.
Aside from its spiritual significance, the hoju tattoo can also be a symbol of good luck and prosperity. In Japanese culture, the hoju is associated with the mythical bird, the phoenix, which is said to bring good fortune and rebirth.
The design of a hoju tattoo can vary depending on the individual’s preference. Some may opt for a simple, minimalist design, whie others may choose a more elaborate design that incorporates other elements such as flowers, dragons, or kanji characters.
A hoju tattoo can hold various meanings for different individuals. However, at its core, it is a symbol of good health, good fortune, and spiritual devotion to the Buddhist faith.
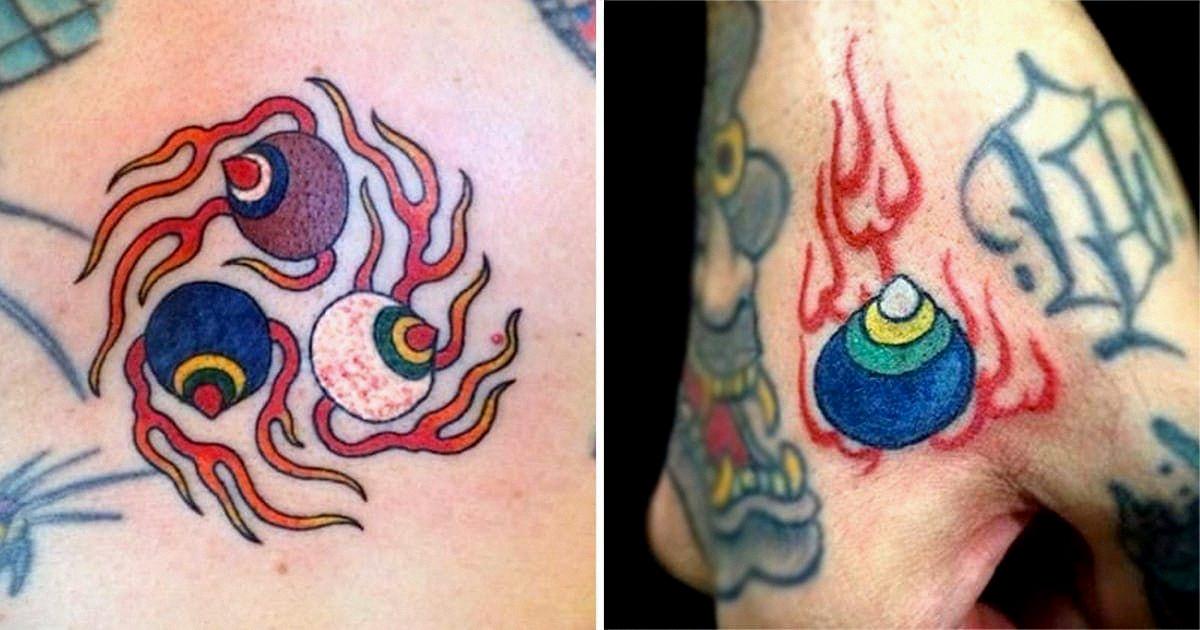
Source: pinterest.com
The Meaning of a Hōju
A Hōju, also known as Hōshu, is a term used in Buddhism to refer to a sacred object that is shaped like a sphere or a teardrop. The word “Ho” means treasure or jewel, wile “ju” means ball or sphere. This object is considered to be a symbol of enlightenment and is often used in Buddhist rituals and ceremonies.
The Hōju is a symbol of the Buddha’s teachings and represents the wisdom and compassion that he embodied. It is believed that when one is in possession of a Hōju or is in the presence of one, they are able to connect with the Buddha’s teachings and attain a sense of inner peace.
The Hōju is typically made of a variety of materials, including precious stones, metals, and wood. Some of the most common materials used to make Hōju include jade, crystal, gold, and silver. The shape of the Hōju may vary, but it is usually spherical or teardrop-shaped.
The Hōju is often displayed on altars or in sacred spaces, where it is believed to radiate positive energy and help to purify the environment. It is also used in Buddhist meditation practices, where it is held or visualized to aid in concentration and focus.
The Hōju is a sacred object that holds great significance in Buddhist culture. It is a symbol of wisdom, compassion, and enlightenment, and is revered by Buddhists around the world.
The Hoju System: An Overview
The Hoju system was a traditional household system that existed in South Korea. Under this system, the household had the house head, also known as the Hoju, at its core. Only direct male descendants were eligible to inherit the position of the household head, and they served as successive household heads.
The Hoju system was in place until March 2005, when the Civil Act was amended by Act No. 7427. This amendment abolished the Hoju system, and the succession of household headship was no longer restricted to direct male descendants.
Before the amendment, the Hoju system was deeply rooted in Korean culture and tradition. It was believed that the Hoju system helped to maintain the family lineage and preserve the family’s assets. The system also provided a clear hierarchy within the household, with the Hoju being the ultimate decision-maker.
However, the Hoju system was also criticized for being discriminatory towards women and non-direct male descendants. It was seen as a barrier to gender equality and social mobility.
The Hoju system was a traditional household system that existed in South Korea. It was based on the idea of a male-dominated family hierarchy, where only direct male descendants could inherit the position of the household head. Although the system was abolished in 2005, its legacy sill influences Korean society today.
Understanding the Korean Household Register
A Korean household register, also knon as a juminhyo, is an official document that serves as a record of a family’s genealogy and vital information. It is a legal requirement for all Korean citizens to be registered in the household register system, which is overseen by the local government authorities.
Each family will have their own household register, which contains information on each individual family member, including their full name, date of birth, gender, and relationship to the head of the household. The register also includes information on marriages, divorces, deaths, and adoptions that occur within the family.
The household register is an important document for a number of reasons. It serves as proof of identity and citizenship, and is required for a variety of legal and administrative purposes, such as applying for a passport or driver’s license, enrolling in school, or receiving government benefits.
In addition, the household register system provides valuable demographic data that is used for planning and policy-making purposes by the government. For example, it can be used to track population trends, identify areas of need for social services, and allocate resources for public infrastructure projects.
The Korean household register system is a vital component of the country’s administrative and legal framework, providing a comprehensive record of families and individuals that helps to ensure the smooth functioning of society.
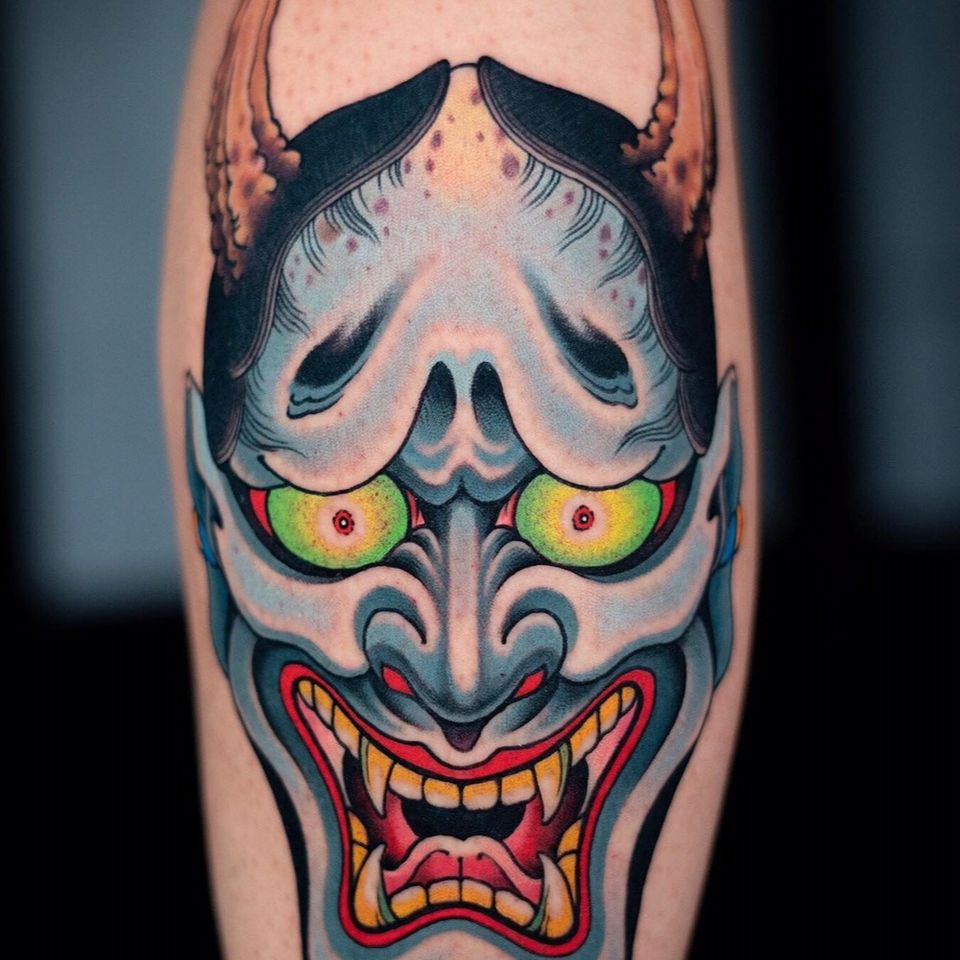
The Meaning Behind the Japanese Devil Tattoo
The Japanese devil tattoo is commonly referred to as the Hannya mask tattoo. This type of tattoo is inspired by the Hannya mask, a traditional Japanese mask that is often used in Noh theater performances. The Hannya mask is typically depicted as a demon or a female demon, and it is often used to represent the darker side of human nature.
The Hannya mask tattoo is a popular choice for many people who are looking to express thir darker side or to embrace their inner demons. This tattoo typically features a highly detailed and intricate design that showcases the demonic features of the Hannya mask. The tattoo can be created using a variety of different colors, but it is most commonly depicted using red ink.
The Hannya mask tattoo is often associated with the concept of pure evil and the idea of giving in to one’s dark side. In traditional Japanese storytelling, if a woman’s Hannya mask turns red, it is used to showcase that she has completely given in to her dark side, fully transitioning into a demonic entity.
The Hannya mask tattoo is a powerful and striking tattoo that is deeply rooted in Japanese culture and mythology. It is a popular choice for people who are looking to express their darker side or to embrace their inner demons, and it is often depicted using highly detailed and intricate designs that showcase the demonic features of the Hannya mask.

The Meaning of a Three Flying Birds Tattoo
A tattoo of three flying birds is a popular design that is often seen on many people. The meaning behind this tattoo is derived from the number three in numerology, which is believed to signify joy, happiness, and optimism. The symbolism of birds themselves also holds significant meaning in many cultures, representing freedom, family, and ease.
The three birds in the tattoo design are often depicted in flight, with their wings spread wide open, ready to soar. This image is a powerful symbol of hope, reminding the wearer to remain optimistic and to alwys strive for their dreams.
Additionally, the three birds in the tattoo design can also represent family values. Birds are known to be fiercely protective of their young, and the image of three birds in flight can be a representation of the strong bond between family members.
The three flying birds tattoo is a beautiful and powerful symbol of hope, joy, and family. It’s a reminder to stay positive and to never give up on your dreams.
Symbolic Meaning of Clouds in Japan
In Japan, clouds symbolize a variety of meanings and hold significant cultural value. Clouds are often associated with nature and the beauty of the natural world. They represent hope, as they can bring rain and nourishment to crops, bringing new life and growth.
However, clouds also represent impermanence and change, as they are constantly shifting and evolving. This is reflective of the Buddhist belief in the impermanence of all things.
In Japanese folklore, clouds are also seen as an omen, with certain types of clouds being associated with good or bad luck. For example, a cloud shaped like a crane is considered a good omen, while a cloud shaped like a demon is seen as a bad omen.
Clouds are also seen as a symbol of proximity to the gods, with the belief that the gods reside in the heavens above the clouds. This is reflected in Japanese mythology, where many gods and goddesses are associated with the sky and the clouds.
In addition, clouds are often used as a decorative pattern in Japanese art and design. The cloud motif, known as kumo, is commonly used as a signature or crest by Japanese carpenters.
Clouds hold significant cultural vale in Japan, representing hope, impermanence, omen, proximity to gods, change, and the beauty of nature.
Exploring the Meaning of Hozen in Buddhism
A hōzen, also known as a treasure ball or a wish-granting jewel, is a symbol in Buddhism that represents the power to grant wishes and reconnect people. It is oten depicted as a round ball with four or five circular layers, each representing a different element or direction. The hōzen is believed to have the power to purify negative energy and bring good fortune and blessings to those who possess it.
In Buddhist mythology, the hōzen is said to have been created by the dragon king and is often associated with the bodhisattva Avalokiteshvara, who is believed to hold a hōzen in each of his four hands. The hōzen is also commonly associated with the Buddhist deity Jambhala, who is often depicted holding a hōzen in one hand while sitting on a lotus flower.
In addition to its symbolism of wish-granting and reconnecting, the hōzen also represents the idea of abundance and prosperity. It is believed that by possessing a hōzen, one can attract wealth, good luck, and positive energy into their life.
The hōzen is a powerful symbol in Buddhism with deep spiritual significance. It represents the power to grant wishes, purify negative energy, and bring good fortune and blessings to those who possess it.
The Traditional Japanese Staff
The Japanese staff is commonly known as a bō, which translates to “staff” in English. It is a traditional weapon used in Japanese martial arts, prticularly in the art of bōjutsu. The bō is typically made of hardwood or bamboo and measures around 1.8 m (71 in) in length.
In addition to its use in martial arts, the bō has also been adapted for use in other areas such as entertainment and sports. The staff is often seen in traditional Japanese performances, including theater and dance. It is also used in various forms of martial arts competitions and demonstrations.
The bō has a long history in Japan, dating back to the feudal period when it was used as a weapon by samurai warriors. Its use eventually spread to the common people as a means of self-defense. Today, the bō remains an important part of Japanese culture and martial arts, with many practitioners continuing to study and develop their skills with the staff.
To summarize, the Japanese staff is known as a bō and is a traditional weapon used in Japanese martial arts, with a history dating back to the feudal period. It is also used in other areas such as entertainment and sports.
The Meaning of the Finger Cross in Korea
In Korea, the crossed thumb and forefinger gesture is commonly known as the “Finger Heart” or “Heart Sign”. It is a gesture that has gained popularity among Korean pop stars and their fans, and is often used to express affection and love.
The Finger Heart gesture involves crossing the thumb and forefinger to form a small heart shape, which is then held up to the chest or pointed towards somene as a sign of endearment. The gesture is especially popular among K-pop idols, who use it frequently during concerts, music videos, and social media posts.
The origin of the Finger Heart gesture is not entirely clear, but some suggest that it may have originated from the Japanese “yubikiri” gesture, which involves interlocking the little fingers to make a promise.
Regardless of its origins, the Finger Heart has become a cultural phenomenon in Korea and beyond, with fans of K-pop stars and Korean culture adopting the gesture as a way to show their support and love for their idols.
In addition to the Finger Heart, there are other hand gestures that are popular in Korean culture, such as the “V” sign, which involves holding up the index and middle finger in a V shape. This gesture is often used to indicate victory or peace, and is also commonly seen in K-pop culture.
The Finger Heart gesture has become a beloved symbol of affection and support in Korea, and is a testament to the power of pop culture to unite people across cultures and borders.
How Koreans Address Their Family Members
In Korean culture, family is highly valued and respected. The Korean language has specific terms for each family member, depending on teir relation to the speaker.
The father is called 아버지 (abeoji) and the more informal term for dad is 아빠 (appa). The mother is referred to as 엄마 (eomma).
Siblings are commonly referred to by their birth order. For example, the oldest brother is called 형 (hyeong) and the oldest sister is called 누나 (nuna). The younger brother is called 동생 (dongsaeng), while the younger sister is called 여동생 (yeodongsaeng).
Grandparents are also highly respected in Korean culture. The grandfather is called 할아버지 (halabeoji) and the grandmother is called 할머니 (halmeoni).
For extended family members, the nephew is called 조카 (joka) and the niece is called 조카딸 (jokattal). The cousin is called 사촌 (sachon). The grandson or grandchild is called 손자 (sonja), while the granddaughter is called 손녀 (sonnyeo).
Korean culture places great importance on family and has specific terms for each family member. Knowing how to address family members correctly is a sign of respect and is deeply ingrained in Korean culture.
The Origin of the Korean Name ‘Hoju’ for Australia
Australia is often referred to as Hoju in Korean. This term is derived from the Chinese characters 濠州, which can be roughly translated as “a state/province surrounded by water”. It is believed that this name was first used by Chinese traders who visited the region and later adopted by Korean traders and scholars.
The character 濠 (ho) is a phonetic approximation of the word “Australia”, while the character 州 (ju) means state or province. Together, they create the term Hoju, which is now commonly used to refer to Australia in Korea.
Interestingly, Hoju is not an official name for Australia, and the Australian government does not use this term in official communications with Korea. However, it is widely recognized and used by the Korean people. In fact, the Australian Embassy in Korea even uses “駐韓 濠州大使館” as their official name, which translates to “Embassy of Hoju in Korea”.
The use of Hoju as a name for Australia in Korean is a fascinating example of how language and culture can influence each other. Despite not being an official name, it has becme a widely accepted and recognized term in Korea.
Conclusion
Hoju is a fascinating concept in Asian culture that has strong ties to Buddhism and traditional household systems. The hoju is believed to be a wish fulfilling jewel and a bringer of good health. It is often depicted as an orb with a pointed top and is occasionally surrounded by flames.
In Buddhism, the hoju has significant importance as three hoju together represent the three jewels of Buddhism; Buddha, Dharma, and Sangha. The hoju is also associated with good fortune and is often used in Buddhist ceremonies and rituals.
The hoju system, whih was a traditional household system in Korea, was abolished in March 2005 by Act No. 7427. Under this system, the house head was at the core of the household, and only direct male descendants inherited the position to serve as successive household heads. However, with the new amendment to the Civil Act, every family member is registered under their own individual record book, which contains information on their birth, death, marriage, adoption, and basic information on their spouse, parents, and children.
The hoju is a symbol of good fortune, health, and prosperity in Asian culture, and it has significant ties to Buddhism and traditional household systems. Although the hoju system is no longer in place, its influence can still be seen in various aspects of Asian culture.
