Hydrogen bromide, also known as HBr, is a colorless gas that is highly soluble in water. It is a strong acid, meaning that it completely dissociates into H+ and Br- ions when placed in water. This results in a solution that is highly acidic, with a low pH value.
The strength of an acid is determined by its ability to donate protons, and HBr is a strong acid because it donates protons very easily. When dissolved in water, HBr molecules break apart into H+ and Br- ions, with the H+ ions being responsible for the acidic properties of the solution. This dissociation is nearly complete, meaning that a large amount of H+ ions are generated, resulting in a very acidic solution.
The acidity of a solution can be measured using the pH scale, which ranges from 0 to 14. A pH value of 7 indicates a neutral solution, while values below 7 indicate an acidic solution and values above 7 indicate a basic solution. The pH value of a solution containing HBr will be below 7, indcating that it is highly acidic.
HBr is classified as a binary acid, meaning that it is composed of only two elements – hydrogen and bromine. In binary acids, the strength of the acid is determined by the polarity of the H-X bond, where X is the halogen atom. Because bromine is larger than chlorine, the H-Br bond is longer and weaker than the H-Cl bond. This results in HBr being a stronger acid than HCl.
In addition to its use as a laboratory reagent, HBr is also used in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and other chemicals. It is also used in the semiconductor industry for etching silicon wafers.
HBr is a strong acid that completely dissociates into H+ and Br- ions when placed in water. This results in a solution that is highly acidic, with a low pH value. Its strength as an acid is due to the polarity of the H-Br bond, which is weaker than the H-Cl bond in HCl. HBr has a wide range of industrial applications and is an important reagent in many chemical reactions.
Strength of HBr as an Acid
Hydrogen bromide (HBr) is a binary acid, which means it consists of two elements, hydrogen and bromine. The strength of an acid refers to its ability to donate hydrogen ions (H+) in an aqueous solution. In the case of HBr, when it is dissolved in water, it ionizes completely, producing hydrogen ions and bromide ions (Br-). This complete ionization indicates that HBr is a strong acid.
A strong acid is defined as an acid that ionizes completely in water, producing H+ ions. This means that the concentration of H+ ions in a solution of a strong acid is high. On the oher hand, a weak acid is an acid that only partially ionizes in water, producing a small concentration of H+ ions.
The strength of an acid depends on its chemical structure and the polarity of its bonds. HBr has a highly polar bond between hydrogen and bromine, which results in a high degree of dissociation when it is dissolved in water. This dissociation produces a large concentration of H+ ions, making HBr a strong acid.
HBr is a strong acid due to its ability to ionize completely in water, producing a high concentration of H+ ions.
Source: chem.libretexts.org
The Strength of HBr as an Acid
Hydrogen bromide (HBr) is a strong acid due to its ability to completely dissociate into its ions when it is placed in water. Dissociation is the process in which an acid molecule breaks apart into its constituent ions. When HBr dissolves in water, it splits into hydrogen cations (H+) and bromide anions (Br-). This reaction is represented by the following equation:
HBr (aq) → H+ (aq) + Br- (aq)
This dissociation reaction is almost complete, meaning that nearly all HBr molecules break apart into H+ and Br- ions. This makes HBr a strong acid.
The strength of an acid is determined by its ability to donate hydrogen ions (H+) to a solution. Strong acids are those that completely dissociate in water and release a large amount of H+ ions. In contrast, weak acids only partially dissociate in water and release a small amount of H+ ions.
HBr is not the only strong acid. Other examples of strong acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), nitric acid (HNO3), and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). These acids all have a high degree of dissociation in water and produce a large amount of H+ ions.
In addition to being a strong acid, HBr is also a strong electrolyte. An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity when it dissolves in water. Because HBr dissociates almost completely in water, it produces a large number of ions, which makes it an effective conductor of electricity.
To summarize, HBr is a strong acid bcause it completely dissociates in water, releasing a large amount of H+ ions. This dissociation reaction makes HBr an effective conductor of electricity, which further demonstrates its strong acid properties.
Comparing the Strength of HBr and HCl Acids
When it comes to binary acids, such as hydrobromic acid (HBr) and hydrochloric acid (HCl), the strength of the acid is determined by the strength of the bond between the hydrogen (H) and halogen (Br or Cl) atoms. In this case, HBr is indeed a stronger acid than HCl.
This is due to the fact that bromine (Br) is a larger atom than chlorine (Cl), which means that the H-Br bond is longer than the H-Cl bond. A longer bond implies that there is a weaker attraction between the hydrogen and halogen atoms, making it easier for the hydrogen ion (H+) to dissociate from the molecule and form an acidic solution.
In addition to the bond length, there are othr factors that can influence the strength of an acid, such as the polarity of the molecule and the stability of the conjugate base. However, in the case of HBr and HCl, the bond length is the main factor that determines the relative strength of the acids.
To summarize, HBr is a stronger acid than HCl because the H-Br bond is longer and weaker than the H-Cl bond. This leads to a higher degree of dissociation of H+ ions in solution, resulting in a stronger acidic character for HBr.
The Type of Acid Present in HBr
Hydrobromic acid, also known as hydrogen bromide, is a strong acid that is commonly used in various industrial and laboratory applications. This acid is a binary acid, which means it is composed of only two elements – hydrogen and bromine. Its chemical formula is HBr, and it is a diatomic molecule, which means it exists as a molecule composed of two atoms of hydrogen and bromine.
Hydrobromic acid is highly soluble in water, and when it is dissolved in water, it dissociates into hydrogen ions (H+) and bromide ions (Br-). This makes it a strong acid, as it readily donates hydrogen ions in solution, making it highly acidic. In fact, hydrobromic acid is even stronger than hydrochloric acid, which is aother common binary acid.
Hydrobromic acid is commonly used in the production of various chemicals, including pharmaceuticals, dyes, and other organic compounds. It is also used in the production of semiconductors, as well as in the refining of metals like zinc and magnesium.
Hydrobromic acid is a highly important and versatile acid that is used extensively in various industries and laboratory settings. Its strong acidity makes it a valuable tool for many chemical reactions and processes.
Are Hydrogen Fluoride and Hydrogen Bromide Strong Acids?
When we talk about the strength of an acid, we refer to its ability to donate a proton (H+ ion) in an aqueous solution. The strength of an acid depends on its bond strength and the stability of the resulting conjugate base.
HF (hydrogen fluoride) and HBr (hydrogen bromide) are both binary acids, meaning they consist of only two elements, hydrogen and a halogen (fluorine and bromine, respectively). However, they have different bond strengths and therefore different acid strengths.
HF is a weak acid becase the bond between hydrogen and fluorine is relatively strong due to the small size of fluorine atoms and the overlap of their orbitals, which makes it difficult to break the bond and donate a proton. As a result, HF only partially dissociates in water, meaning that only a small fraction of HF molecules donate protons to form H+ ions and F- ions.
On the other hand, HBr is a strong acid because the bond between hydrogen and bromine is comparatively weaker than that of HF. This is because the size of bromine atoms is larger than fluorine atoms, and the overlap of orbitals between H and Br atoms is smaller. This weak bond strength makes it easier for HBr molecules to donate protons in water and form H+ ions and Br- ions, resulting in a complete dissociation of HBr in aqueous solutions.
HF is a weak acid, while HBr is a strong acid due to the difference in bond strength and the stability of their conjugate bases.
Strength of HBr as an Electrolyte
Hydrogen bromide, or HBr, is a strong electrolyte. This means that it completely dissociates into ions when dissolved in water, producing a large number of ions that can conduct electricity.
Strong electrolytes are substances that are highly soluble in water and dissociate completely into ions when dissolved. In the case of HBr, it dissociates into H+ and Br- ions, whch are highly mobile in water and can carry an electric charge.
It is important to note that not all acids are strong electrolytes. Some weak acids, such as acetic acid (HC2H3O2), do not dissociate completely in water and only produce a small number of ions. In contrast, strong acids like HBr dissociate completely and produce a high concentration of ions.
HBr is a strong electrolyte that dissociates completely into ions when dissolved in water, making it an effective conductor of electricity.
Is HBr an Acid, Base, or Neutral?
HBr is an acid. An acid is a type of compound that donates a proton (H+) to a solution. When an acid dissolves in water, it increases the concentration of H+ ions in the solution. This leads to a lower pH value, whih is a measure of how acidic a solution is.
HBr is a binary acid, which means it consists of two elements, hydrogen (H) and bromine (Br). When HBr dissolves in water, it releases H+ ions, which makes the solution acidic.
Acids can be strong or weak, depending on how readily they donate H+ ions. HBr is a strong acid, which means it readily donates H+ ions and has a low pH value.
HBr is an acid that releases H+ ions in a solution, leading to a lower pH value.
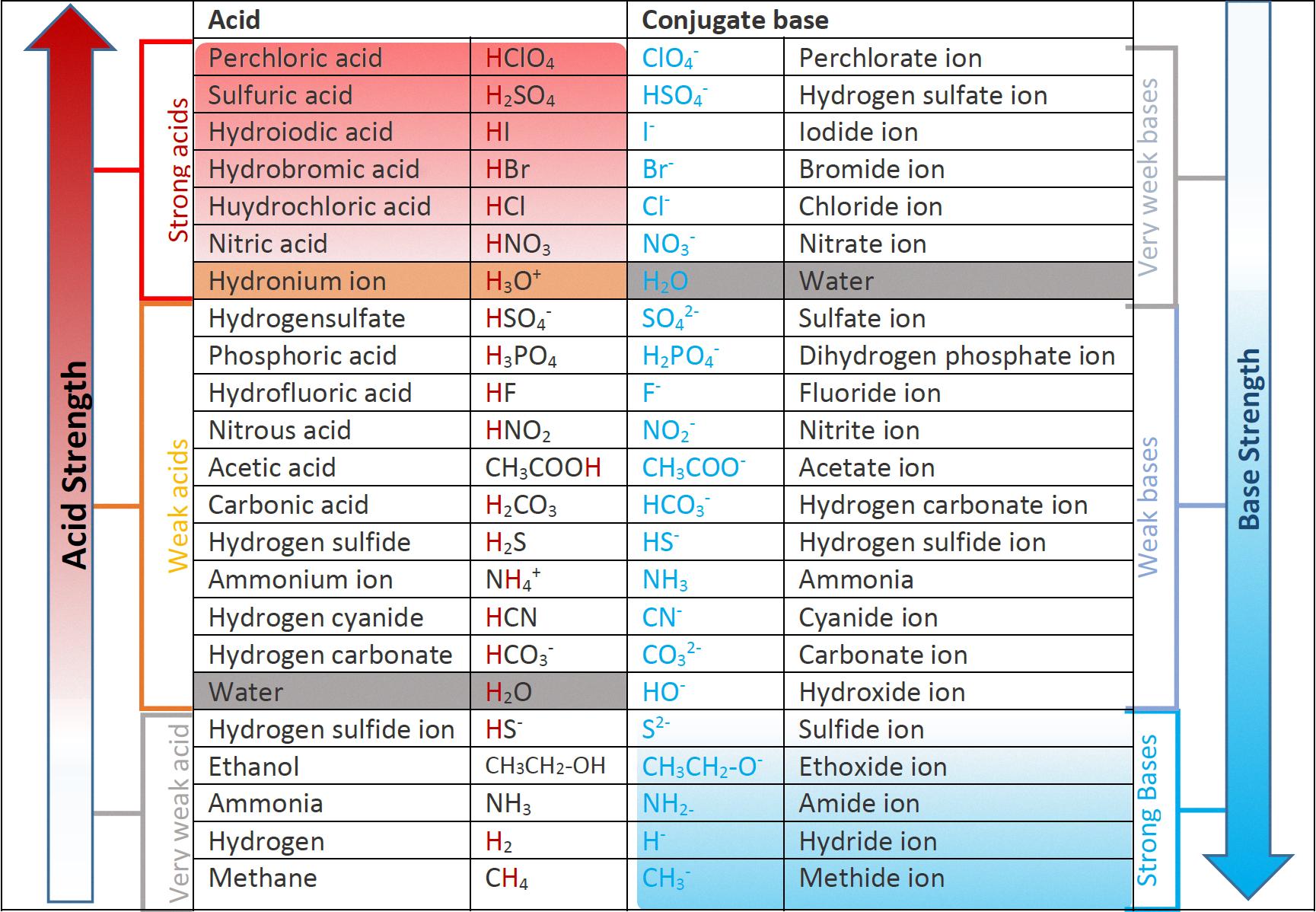
What Is a Strong Acid?
Strong acids are a group of acids that can completely dissociate in water, making them highly reactive and capable of donating protons to other molecules. These acids are oftn used in various industrial processes, laboratory experiments, and chemical reactions. Of the many acids that exist, only seven are classified as strong acids due to their high dissociation constant. These seven acids are chloric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydrochloric acid, hydroiodic acid, nitric acid, perchloric acid, and sulfuric acid.
Chloric acid is a strong acid with the chemical formula HClO3. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and is used in the production of many chemicals, such as chlorine dioxide and perchlorates.
Hydrobromic acid, with the chemical formula HBr, is a strong acid that is commonly used in organic synthesis and as a reagent in various chemical reactions.
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, has the chemical formula HCl. It is a highly corrosive and versatile acid that is used in many industrial processes, such as pickling and metal cleaning.
Hydroiodic acid, with the chemical formula HI, is a strong acid that is commonly used in the production of various chemicals, such as iodides and hydriodic acid.
Nitric acid, with the chemical formula HNO3, is a strong acid that is used in the production of fertilizers, explosives, and dyes. It is also used in the etching of metals and glass.
Perchloric acid, with the chemical formula HClO4, is a strong acid that is used in the production of various chemicals, such as perchlorates and chlorates. It is also used in laboratory experiments and as a reagent in chemical reactions.
Sulfuric acid, with the chemical formula H2SO4, is a strong acid that is widely used in many industrial processes, such as the production of fertilizers, detergents, and dyes. It is also used in the manufacturing of batteries and as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.
The seven main strong acids are chloric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydrochloric acid, hydroiodic acid, nitric acid, perchloric acid, and sulfuric acid. These acids have a high dissociation constant and are capable of completely dissociating in water, making them highly reactive and useful in various chemical reactions and industrial processes.
Which Acid is the Strongest?
When considering the strength of acids, it is important to understand that the strength is determined by their ability to donate hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. The more easily an acid can donate thse ions, the stronger it is.
In the case of HBr, HI, HF, and HCl, they are all strong acids, but the order of their strength varies. The strongest acid among these is HI, followed by HBr, HCl, and HF.
The reason for this order lies in the stability of their conjugate bases. When an acid donates a hydrogen ion, it forms a conjugate base. The stability of the conjugate base determines the strength of the acid. In the case of HI, its conjugate base is the most stable, followed by HBr, HCl, and HF.
Another factor that contributes to the strength of an acid is the polarity of the molecule. In this case, HF is the weakest acid due to the strong hydrogen-fluorine bond, which makes it difficult to donate hydrogen ions in a solution.
To summarize, the order of acid strength among HBr, HI, HF, and HCl is HI > HBr > HCl > HF. This is due to the stability of their conjugate bases and the polarity of their molecules.

Which Acid is Stronger: HBr or H2S?
When comparing the acid strength of HBr and H2S, we must first consider their respective pKa values. HBr has a pKa of -9, while H2S has a first pKa of 7. This indicates that HBr is a stronger acid than H2S.
The pKa value is a measure of the strength of an acid in solution. The lower the pKa value, the stronger the acid. It is important to note that H2S has two pKa values, with the second being 13.9. This means that H2S can donate two protons, making it a diprotic acid. However, even with its second pKa value, H2S is still not as strong as HBr.
To further understand why HBr is a stronger acid than H2S, we need to examine their chemical structures. HBr is composed of hydrogen and bromine, while H2S is composed of hydrogen and sulfur. The electronegativity of bromine is higher than sulfur, which means that the bond beteen hydrogen and bromine is more polarized than the bond between hydrogen and sulfur. This polarization makes it easier for HBr to donate a proton, making it a stronger acid than H2S.
HBr is a stronger acid than H2S due to its lower pKa value and the greater polarization of its hydrogen-bromine bond.
Conclusion
HBr is a strong acid that completely dissociates into H+ and Br- ions when placed in water. This means that it produces a large number of protons, making it a strong electrolyte. The H-Br bond is longer than the H-Cl bond, making it weaker and allowing HBr to be a stronger acid than HCl. Additionally, NH4Br is an acidic salt due to its derivation from a weak base (NH3) and a strong acid (HBr). Understanding the properties of HBr as a strong acid is important in chemistry and can be applied in various fields of study.
