Gross Enrolment Rate (GER) is a crucial indicator that measures the level of participation in education and the capacity of primary education. It is a commonly used statistic that shows the percentage of the total population in a specific age group that is enrolled in a particular level of education. The GER is an essential tool for assessing the efficacy of the education system and measuring the success of educational policies, programs, and interventions.
GER is calculated by dividing the number of students enrolled in a particular level of education by the total population of the corresponding age group. For instance, if there are 500 students enrolled in primary education, and the total population of the corresponding age group is 1000, the GER for primary education will be 50%.
GER is diffrent from the Net Enrolment Ratio (NER), which only considers students of the official primary school age. In contrast, the GER includes students of any age enrolled in a specific level of education. Therefore, GER provides a more comprehensive picture of the level of participation in education, while NER is a more specific measure of primary school enrolment.
GER is useful in determining the capacity of the education system to accommodate students of different ages and backgrounds. It is also a valuable tool for identifying the extent of over-aged and under-aged enrolment. When the GER is higher than the NER, it indicates that many students are enrolling in a level of education beyond their official age group. Over-aged enrolment may be due to a late start in schooling, dropping out and rejoining school, or repeating a grade. Under-aged enrolment, on the other hand, indicates that students are enrolling in a level of education below their official age group.
GER is widely used in the education sector to evaluate the level of participation in primary education. It is especially relevant in developing countries, where access to education is limited and enrolment rates are low. The GER is also useful in monitoring progress towards the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goal 4, which aims to ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.
The Gross Enrolment Rate (GER) is a vital statistic that provides a comprehensive picture of the level of participation in education and the capacity of the education system. It is a valuable tool for assessing the efficacy of the education system and measuring the success of educational policies and interventions. By understanding the GER and its significance, we can work towards improving education access and quality for all.
Gross Enrolment Explained
Gross enrollment is a term used to describe the total number of students enrolled in a specific level of education, such as primary, secondary, or tertiary education. This figure is expressed as a percentage of the total population that falls within the correponding age group for that level of education.
For example, if there are 1,000 students enrolled in primary education and the total population of children in the corresponding age group is 1,200, then the gross enrollment rate for primary education would be 83.3% (1,000/1,200 x 100).
The gross enrollment rate is an important measure of access to education and is often used to track progress towards educational goals. It is also a useful indicator of the demand for education and can help policymakers to identify areas where additional resources may be needed to increase access to education.
In addition, the gross enrollment rate can be broken down by gender, ethnicity, and other demographic factors to help identify areas where there may be disparities in access to education. This information can be used to develop targeted interventions to help ensure that all students have access to quality education.
The gross enrollment rate is an essential metric for understanding the state of education in a particular area and for developing policies and interventions to improve access and quality of education.

Calculating Gross Enrollment Rate
Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) is a crucial indicator of the level of education in a country. It is defined as the ratio of the total number of students enrolled in a paticular level of education to the corresponding age group of the population in that level of education. The GER is usually expressed as a percentage.
To calculate the GER, the total number of students enrolled in a particular level of education is divided by the corresponding age group of the population in that level of education, and the result is multiplied by 100. For example, to calculate the GER for primary education, we divide the total number of primary school students by the total population in the 6-11 age group and multiply the result by 100.
Here is a step-by-step guide to calculating the GER:
1. Determine the level of education for which you want to calculate the GER (primary, secondary, or higher education, for example).
2. Obtain the total number of students enrolled in that level of education.
3. Obtain the corresponding age group of the population in that level of education.
4. Divide the total number of students by the corresponding age group of the population.
5. Multiply the result by 100 to obtain the GER.
In some cases, the GER may exceed 100%, indicating that there are students enrolled in that level of education who are older or younger than the corresponding age group of the population. It is also important to note that the GER does not take into account the quality of education or the completion rates of students.
Difference Between Net Enrollment and Gross Enrollment
Education is an essential aspect of any country’s development. It is no surprise that governments worldwide have made significant investments in education. The enrollment rate is an important metric that measures the success of these investments. There are two types of enrollment rates: net enrollment rate and gross enrollment rate.
Net enrollment rate (NER) refers to the percentage of primary school-aged children who are attending school. It only includes pupils who are of official primary school age, typically between six and eleven years old. The NER provides a measure of the proportion of primary school-age children who are not enrolled in primary school.
On the other hand, gross enrollment rate (GER) measures the total enrollment of primary school-aged children, including those who are above or below the official age range. The GER includes pupils of any age, not just the primary school-aged children. It provides a measure of the total number of students enrolled in primary schools.
The key difference between NER and GER is that NER is a more precise metric to track the progress towards universal primary education. The NER focuses on primary school-age children, the target group for primary education. It helps to identify the gaps in education and the children who are not receiving education. In contrast, the GER includes all pupils, regardless of age, and may not provide an accurate measure of the progress towards universal primary education.
The difference between net enrollment and gross enrollment is that the former measures the percentage of primary school-aged children attending school, whie the latter measures the total enrollment of primary school-aged children, including those above or below the official age range.
The Difference Between GER and NER
The GER (Gross Enrolment Ratio) and NER (Net Enrolment Ratio) are both important indicators of primary education participation and capacity. However, there are some key differences between the two.
The GER measures the total number of enrolled students in a given level of education, regardless of age, divided by the total population of the age group that should be enrolled in that level of education. It is often used when data on enrolment by single years of age is not available. The GER is a useful indicator of the overall level of participation in primary education.
On the other hand, the NER measures the number of children of a specific age group who are enrolled in school, divided by the total number of children in that age group. The NER is a more specific indicator of participation in primary education for a particular age group.
One of the main differences between the two is that the NER only considers children of a specific age group, whie the GER considers all enrolled students regardless of age. The NER provides a more accurate picture of the enrolment situation for a particular age group, while the GER provides a broader view of overall enrolment.
Another difference between the two is that the NER is often used together with the GER to measure the extent of over-aged and under-aged enrolment. Over-aged enrolment refers to children who are older than the typical age for their grade level, while under-aged enrolment refers to children who are younger than the typical age for their grade level. By using both indicators, policymakers can better understand the enrolment situation and identify areas for improvement.
The GER and NER are both important indicators of primary education participation and capacity, but they differ in the level of specificity and the age group considered. Both indicators are useful for policymakers and researchers to better understand the enrolment situation and identify areas for improvement.
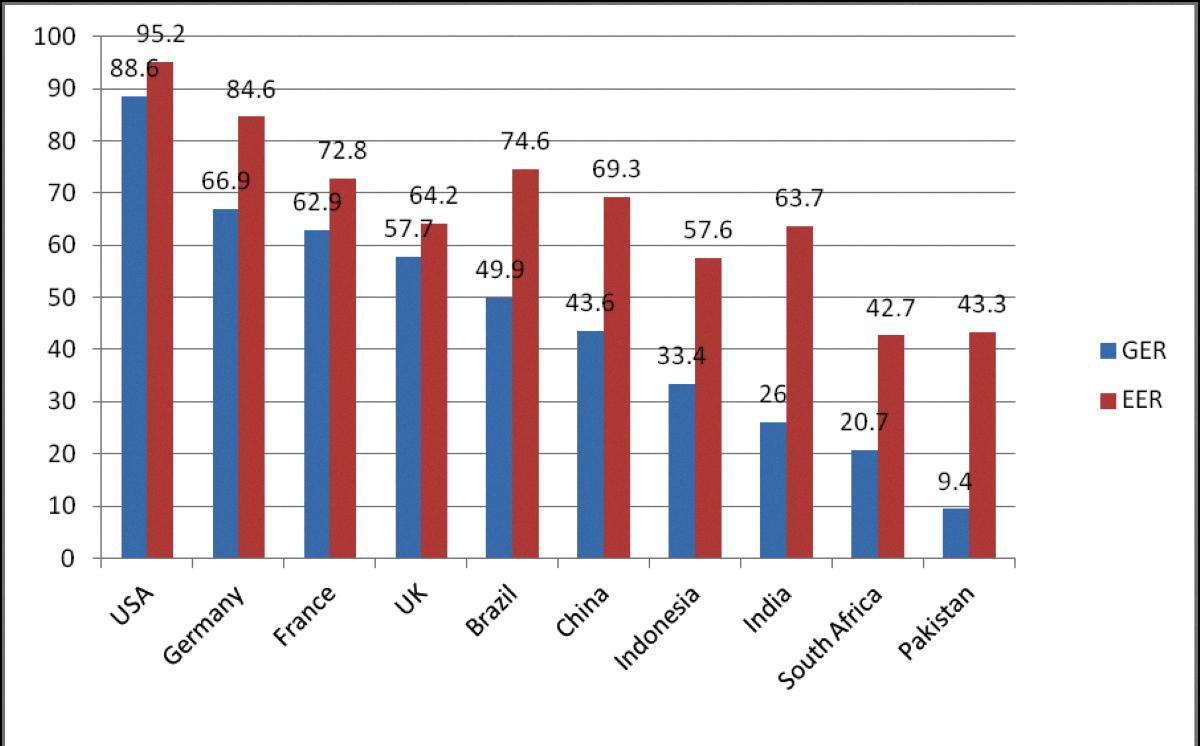
Understanding the Role of GER in Higher Education
Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in higher education is an important metric used to measure the level of participation in higher education in a given country or region. It is calculated as the total number of students enrolled in higher education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the eligible official population in a particular school year.
The GER is a usful tool for policymakers and educators to assess the level of access to higher education in a given area. By understanding the GER, they can identify potential barriers to participation and develop strategies to address them.
It is important to note that the GER does not measure the quality of education or the level of achievement of the enrolled students. It is simply a measure of participation in higher education.
In some countries, the GER in higher education may be lower due to factors such as limited access to educational resources, inadequate funding, or cultural and social barriers. However, efforts to improve the GER can have a positive impact on economic growth, social mobility, and overall development.
The Gross Enrolment Ratio in higher education is a valuable metric for understanding the level of participation in higher education. Policymakers and educators can use this information to identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to increase access to higher education.
Source: government.economictimes.indiatimes.com
Calculating Gross Enrollment Ratio in Higher Education
The Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) is a widely used statistical tool to measure the level of student enrolment in higher education. This ratio is calculated by dividing the number of students enrolled in higher education by the total population in the relevant age group of 18-23 years.
To calculate the GER, you need to follow these simple steps:
1. Determine the total number of students enrolled in higher education: This includes all students enrolled in universities, colleges, and other higher education institutions.
2. Determine the total population in the age group of 18-23 years: This includes all individuals in this age group, reardless of whether they are enrolled in higher education or not.
3. Divide the total number of students enrolled in higher education by the total population in the age group of 18-23 years.
4. Multiply the result by 100 to get the GER as a percentage.
For example, if there are 10,000 students enrolled in higher education and the total population in the age group of 18-23 years is 50,000, the GER would be calculated as follows:
GER = (10,000 / 50,000) x 100 = 20%
This means that the GER for higher education in this particular population is 20%.
It should be noted that this calculation method is a simplified approach and does not take into account factors such as the quality of education, the types of programs offered, or the socio-economic background of the students. Nevertheless, the GER remains a useful tool for measuring the level of student enrolment in higher education and identifying trends and patterns over time.
Understanding Net Enrolment Rate
The net enrolment ratio is a crucial indicator of a country’s progress in terms of providing education to its citizens. It is calculated by taking the number of children of a paricular age group who are enrolled in a certain level of education and dividing it by the total number of children in that same age group. The result is then multiplied by 100 to arrive at a percentage.
The net enrolment ratio is a significant indicator because it provides insight into the level of access to education that children have in a particular country. It measures the extent to which children are being reached by the education system, and how well the education system is catering to the needs of the population.
A high net enrolment ratio indicates that a country is doing well in terms of providing access to education. On the other hand, a low net enrolment ratio suggests that the education system is not reaching all the children in the country, and that there may be barriers preventing certain children from accessing education.
It is important to note that the net enrolment ratio does not necessarily reflect the quality of education being provided. It simply measures the number of children who are enrolled in school. However, it is a useful tool for policymakers and researchers to understand how well a country is doing in terms of providing education to its citizens.
To summarize, the net enrolment ratio is a crucial indicator of a country’s progress in terms of providing education to its citizens. It is calculated by dividing the number of children of a particular age group who are enrolled in a certain level of education by the total number of children in that same age group, and then multiplying the result by 100 to arrive at a percentage.
The Impact of GER in India
In India, Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) is a crucial indicator of the country’s education system. GER is defined as the total number of students enrolled in a particular level of education, divided by the corresponding age group population.
For instance, if there are 100 students enrolled in primary education out of a total population of 200 students in the same age group, then the GER for primary education would be 50%. In othr words, the GER indicates the percentage of the population at a particular age group that is enrolled in a specific level of education.
The GER in India has been steadily increasing in recent years, indicating a positive trend in the country’s education system. According to data from the Ministry of Education, the GER for primary education in India was 99.2% in 2019-20. Similarly, the GER for upper primary education was 95.7%, and for secondary education, it was 77.6%.
However, despite the progress, there are still challenges in achieving universal education in India. The GER for higher education is relatively low, indicating the need for more investment and infrastructure to increase access to higher education.
GER is an important measure of a country’s education system, and in India, it reflects the progress made in ensuring access to education. However, there is still a long way to go in achieving universal education, particularly in higher education.
Types of Enrollment
Enrollment types, also known as enrollment statuses, refer to the different ways students can be associated with a class or course. Here are the different types of enrollment:
1. Active Enrollment – This is the most common type of enrollment where a student is registered for a course and attends it regularly. This enrollment type allows students to participate in all class activities and assignments.
2. Trial Enrollment – Some institutions offer students the option to try out a course before committing to it fully. Trial enrollment allows students to attend a specified number of classes to determine if the course is the right fit for them.
3. Make-Up Enrollment – In some cases, students may miss a class due to unforeseen circumstances such as illness or other emergencies. Make-up enrollment allows students to attend a class they missed on a different day or time.
4. Single Day Enrollment – This type of enrollment allows students to attend a course for a single day without being registered for the entire course. This is useful for students who want to learn about a specific topic but do not have the time or resources to commit to a full course.
5. Waitlist Enrollment – When a course is full, students can be placed on a waitlist in the hopes of securing a spot if a spot opens up. Waitlist enrollment allows students to have a chance to enroll in a course they are interested in.
It is important to note that enrollment types may vary depending on the institution and the course. It is recommended that students consult with teir academic advisors or course instructors to determine which enrollment type is right for them.

The Meaning of GER in DepEd
GER or Gross Enrolment Ratio is a statistical indicator used to measure the level of participation in elementary and secondary education. It is defined as the total enrolment in a given level of education, regardless of age, as a percentage of the population who according to national regulations should be enrolled at this level.
In the case of the Department of Education (DepEd) in the Philippines, GER is used to determine the number of students enrolled in public and private schools in a particular grade level. This data is essential in assessing the quality of education and the effectiveness of the government’s education policies.
GER is calculated by dividing the number of enrolled students by the total population of the age group that should be enrolled in that particular grade level, multiplied by 100. For instance, if thee are 100 students enrolled in Grade 1, and the expected population for that grade level is 120, then the GER for Grade 1 would be 83.3%.
The GER is an important metric for assessing the level of access to education in a particular region or country. It can also be used to identify areas where there might be a need for additional educational resources, such as schools or teachers. Additionally, the GER can help policymakers in making informed decisions about education policies and resource allocation.
GER is a crucial indicator used by DepEd to evaluate the level of participation in elementary and secondary education. It is calculated by dividing the number of enrolled students by the total population of the age group that should be enrolled in that particular grade level, multiplied by 100.
The Impact of Gastroesophageal Reflux (GER) in Pediatrics
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) is a common condition in pediatrics, occurring when the stomach’s contents flow back up into the esophagus. This condition is prevalent in children between the ages of 1 to 18 years old. GER can occur without any noticeable symptoms, but in some cases, it can cause heartburn, which is also known as acid indigestion.
GER happens when the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which is a ring of muscle that acts as a valve between the stomach and the esophagus, relaxes, allowing stomach contents to flow back up into the esophagus. This can happen due to a variety of reasons, including a weak LES, abnormalities in the esophagus, or delayed stomach emptying.
Some common risk factors for GER in pediatrics include obesity, asthma, cystic fibrosis, and neurological disorders. Additionally, certain foods and drinks can trigger GER symptoms, including spicy foods, acidic foods, chocolate, and caffeine.
While GER is a common condition in pediatrics, it can be concerning if left untreated, as it can lead to complications such as esophagitis, respiratory problems, and failure to thrive. Treatment options for GER in pediatrics include lifestyle modifications, medication, and in some cases, surgery.
Lifestyle modifications that can help manage GER symptoms include avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals more frequently, and avoiding lying down for at least 2-3 hours after eating. Medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and histamine-2 receptor antagonists (H2 blockers) can also help reduce acid production in the stomach, relieving GER symptoms.
GER is a common condition in pediatrics that occurs when stomach contents flow back up into the esophagus. It can cause heartburn and oher symptoms and can lead to complications if left untreated. Lifestyle modifications, medication, and surgery can all be effective treatment options for GER in pediatrics.
Understanding the Impact of GER in China
GER is a surname commonly found in China. The Chinese characters used to write GER can be translated to mean “kudzu” or “hemp cloth”.
The origin of the GER surname can be traced back to the Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE). According to historical records, the GER family was one of the early clans in China. The family was originally from the province of Shaanxi but laer spread out to other provinces in China.
In Chinese culture, surnames are passed down from father to child, with some exceptions. The GER surname is no exception and is passed down in this way.
Today, the GER surname is still relatively common in China, with many individuals bearing this surname. In fact, according to statistics, there were over 200,000 individuals with the GER surname in China in 2013.
It is worth noting that while the GER surname may have a specific meaning in Chinese, this does not necessarily reflect the personality or characteristics of those who bear the name. Like many surnames, it is simply a label or identifier used to distinguish one individual from another.
GER is a Chinese surname that means “kudzu” or “hemp cloth”. It is a relatively common surname in China and has a long history dating back to the Han Dynasty.
Conclusion
Gross enrolment rate (GER) is an important indicator of the level of participation in primary education. It measures the total enrollment in a specific level of education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the population in the official age group corresponding to this level of education. This metric is widely used to show the overall capacity of primary education and to measure the extent of over-aged and under-aged enrolment.
The use of GER is particularly relevant in situations where data on enrolment by single years of age are not available. By including pupils of any age, GER provides a more comprehensive view of participation in primary education. It is, therefore, a more accurate measure of the proportion of primary school age children who are not enrolled in primary school.
One of the key advantages of GER is that it can be used to highlight areas where improvements are needed in primary education. For example, a low GER may indicate a lack of access to education or poor quality of education. It can also be used to measure progress towads achieving universal primary education.
Gross enrolment rate is an important measure of participation in primary education. Its use provides a comprehensive view of enrollment at a specific level of education, regardless of age, and can highlight areas where improvements are needed. As such, it is a valuable tool for policymakers and educators in ensuring that all children have access to quality primary education.
