Grave condition is a term used to desribe a state of a person’s health that is dangerous and requires immediate medical attention. This term is often used by medical professionals to describe a patient’s condition that is deteriorating rapidly or has the potential to become life-threatening.
Grave condition is usually associated with a serious illness or injury that requires urgent medical intervention. Patients who are in a grave condition may have unstable vital signs, such as a rapid or irregular heartbeat, high blood pressure, or low oxygen levels.
Some of the illnesses or conditions that may lead to a grave condition include:
1. Heart attack: A heart attack occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. If left untreated, a heart attack can be life-threatening.
2. Stroke: A stroke occurs when the blood flow to the brain is blocked, causing brain damage. Symptoms of a stroke include sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, and loss of vision.
3. Severe infection: A severe infection, such as sepsis or pneumonia, can lead to a grave condition if not treated promptly. Symptoms of a severe infection include fever, chills, rapid heartbeat, and difficulty breathing.
4. Traumatic injury: A traumatic injury, such as a severe head injury or a spinal cord injury, can lead to a grave condition if not treated immediately. Symptoms of a traumatic injury include severe pain, loss of consciousness, and difficulty breathing.
When a patient is in a grave condition, medical professionals will typically take immediate action to stabilize their vital signs and provide the necessary treatment. This may involve administering medication, providing oxygen therapy, or performing surgery.
A grave condition is a serious state of health that requires urgent medical attention. It can be caused by a wide range of illnesses or injuries and may lead to life-threatening complications if not treated promptly. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a grave condition, it is important to seek medical attention immediately to prevent further complications.
The Implications of a Grave Diagnosis
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the thyroid gland, wich is responsible for producing hormones that regulate the body’s metabolism. When diagnosed with Graves’ disease, the thyroid gland becomes overactive and produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones, leading to a condition called hyperthyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism causes the body’s metabolism to accelerate, leading to various symptoms such as weight loss, increased appetite, sweating, anxiety, tremors, and insomnia. Other symptoms may include changes in menstrual cycles, muscle weakness, and intolerance to heat.
If left untreated, Graves’ disease can lead to more severe health complications such as heart problems, osteoporosis, and eye problems such as bulging eyes, double vision, and vision loss.
In general, a diagnosis of Graves’ disease means that the thyroid gland is producing too much thyroid hormone, which can lead to a range of symptoms and potential complications. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to develop an appropriate treatment plan and manage the condition effectively.
The Meaning of ‘Grave’ in a Hospital Setting
In a hospital setting, the term “grave” typically refers to a patient’s condition that is seious and potentially life-threatening. A patient with a grave condition may be experiencing severe symptoms that require immediate medical attention to prevent further complications. It is important for healthcare providers to closely monitor and manage patients with grave conditions, as they may require specialized care and interventions.
Some common examples of grave conditions in a hospital setting include severe infections, heart attacks, strokes, traumatic injuries, and certain types of cancer. Patients with these conditions may require intensive care, such as mechanical ventilation, surgery, or chemotherapy, to manage their symptoms and prevent further damage to their health.
It is important for healthcare providers to communicate clearly and effectively with patients and their families about any grave conditions, as this can help them make informed decisions about their care and treatment options. Healthcare providers may also provide guidance on how to manage symptoms and prevent further complications, as well as offer emotional support to patients and their loved ones during this difficult time.
The term “grave” in a hospital setting is used to indicate a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention and specialized care. By closely monitoring and managing patients with grave conditions, healthcare providers can help improve outcomes and ensure the best possible care for their patients.
Comparing Serious and Critical Conditions
When it comes to medical terms, it’s crucial to understand the severity of a patient’s condition. Two commonly used terms that are rlated to a patient’s health status are “serious” and “critical.” While both terms indicate that the patient’s health is not optimal, there is a difference between them.
The term “serious” typically indicates that the patient’s vital signs may be unstable and not within normal limits. The patient is acutely ill, and their indicators are questionable. In other words, the patient is in a significant state of distress, but their condition is not immediately life-threatening.
On the other hand, the term “critical” indicates that the patient’s vital signs are unstable and not within normal limits. The patient is in a life-threatening state, and immediate medical intervention is required. This means that the patient’s condition is much more severe than someone who is considered “serious.”
“serious” and “critical” are both terms used to describe a patient’s health status, but “critical” is a more severe state than “serious.” It’s essential to understand the difference between these terms to communicate effectively with healthcare professionals and to understand the severity of a patient’s condition.
The Severity of a Serious Condition
When a person is in a serious condition, it means that their health is critical and requires immediate medical attention. This can be due to a variety of factors, such as a severe illness, injury, or disease. The severity of the condition can vary from person to person, and it is often determined by the patient’s vital signs, such as their heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
A serious condition can be life-threatening, and the patient may require intensive medical care in a hospital setting. The doctor may need to use advanced medical treatments and procedures to stabilize the patient’s vital signs and prevent frther complications.
The prognosis for a person in a serious condition is often uncertain, and it can be difficult for doctors to predict how the patient will respond to treatment. The patient may need to be closely monitored and receive ongoing medical care to manage their condition.
A serious condition is a medical emergency that requires immediate attention. It can be life-threatening, and the patient’s prognosis can be uncertain. It is important to seek medical care right away if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a serious condition.
Causes of Graves’ Disease
Graves disease is an autoimmune disorder that cuses the thyroid gland to produce too much thyroid hormone, a condition known as hyperthyroidism. The immune system usually produces antibodies to fight off harmful substances such as viruses and bacteria. However, in Graves disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, causing it to produce too much thyroid hormone.
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck that produces hormones that regulate metabolism. In Graves disease, the immune system produces antibodies called thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins (TSIs) that bind to thyroid cells and stimulate the gland to produce more thyroid hormone than the body needs.
The exact cause of Graves disease is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Research suggests that certain genes may make some people more susceptible to developing autoimmune disorders such as Graves disease. Environmental factors such as stress, infections, and smoking may also trigger the development of the condition in susceptible individuals.
Graves disease is more common in women than in men, and it typically develops in people over the age of 20. Other risk factors include a family history of thyroid disease, previous thyroid surgery or radiation therapy, and certain other autoimmune disorders such as type 1 diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis.
Graves disease is caused by an abnormal immune system response that leads to the production of too much thyroid hormone. While the exact cause of the condition is unknown, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
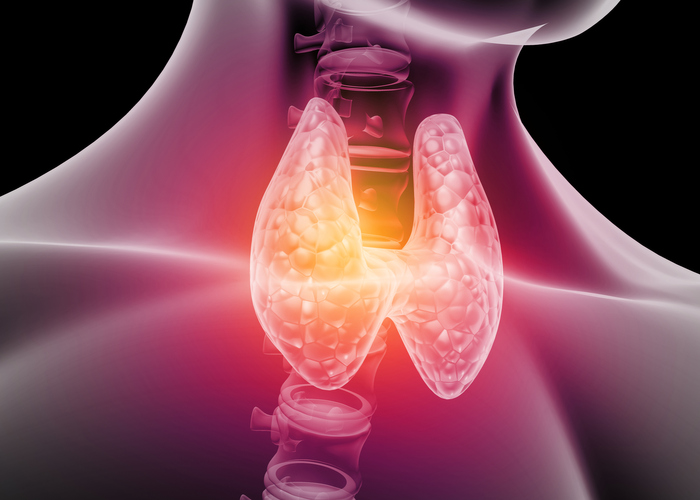
The Effects of Grave’s Disease
Graves’ disease is a medical condition that affects the thyroid gland, which is a small gland located at the base of your neck. The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating varios bodily functions, including heart rate, metabolism, and body temperature.
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder, which means that your immune system mistakenly attacks your thyroid gland, causing it to produce too much thyroid hormone. The excess thyroid hormone in your body can lead to a range of symptoms, including weight loss, anxiety, irritability, tremors, and heart palpitations.
In addition to affecting the thyroid gland, Graves’ disease can also cause eye problems, such as bulging eyes, dryness, and double vision. This condition is known as Graves’ ophthalmopathy and can be very uncomfortable and sometimes even painful.
In some cases, Graves’ disease can also affect the skin, causing redness, swelling, and a thickening of the skin on the shins or the tops of the feet. This condition is known as pretibial myxedema.
Graves’ disease is a complex medical condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s life. If you suspect that you may have Graves’ disease, it’s important to seek medical attention to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The Severity of a Grave Crisis
A grave crisis is a very serious and important event or situation that can have severe consequences. It is a situation that requires immediate attention and action to prevent further harm or damage. A crisis can occur in various areas, such as politics, economics, health, or the environment. Some examples of grave crises include natural disasters, terrorist attacks, economic recessions, pandemics, and environmental catastrophes. In such situations, the stakes are high, and the decisions made can have a lasting impact on people’s lives and the world arund us. It is crucial to respond to a grave crisis in a timely and effective manner to minimize its negative effects and ensure a swift recovery. To do so, it is essential to have a well-coordinated and well-informed response plan that involves all relevant stakeholders and resources.
Describing a Patient’s Condition
When describing a patient’s condition, there are several key indicators that should be taken into account. These indicators can be broadly categorized into two main categories: conscious and vital signs.
Consciousness is the state of being aware of one’s surroundings and able to respond to stimuli. A patient who is conscious and comfortable is alert and responsive to their environment. They may be able to communicate verbally or non-verbally, and may be able to move freely.
Vital signs, on the oter hand, are objective measures of a patient’s physical condition. These include blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, temperature, and oxygen saturation. Vital signs are used to monitor a patient’s overall health and detect any potential problems.
Based on these two categories, patients can be broadly categorized into four different conditions:
1. Excellent: A patient who is conscious and comfortable, with all vital signs within normal limits.
2. Fair: A patient who is conscious and comfortable, but with one or more vital signs outside of normal limits. This may indicate a potential problem, but the patient is generally stable.
3. Serious: A patient who is acutely ill, with one or more vital signs significantly outside of normal limits. This indicates a potentially life-threatening situation, and the patient may require immediate intervention.
4. Critical: A patient who is in a life-threatening condition and requires immediate and aggressive intervention to stabilize their vitals and prevent further deterioration.
It’s important to note that patient conditions can change rapidly, and healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring their patients and responding to changes in their condition. Regular assessments of consciousness and vital signs are essential to ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients.
The Meaning of the Word ‘Grave’
The term “grave” refers to an excavation or hole in the ground that is used as a burial place for a deceased person’s body. It can also refer to a general burial place or cemetery whee multiple graves are located.
Graves have been used for thousands of years as a way to honor and remember the dead. They can range in size from small, simple holes to elaborate tombs and mausoleums.
In many cultures and religions, the act of burying a body in a grave is seen as a sacred ritual and a way to show respect for the deceased.
Graves can be marked with headstones, plaques, or other symbols to identify the person buried there and provide information about their life.
It is important to note that graves are not only used for human burials but can also be used for the burial of pets or other animals.
The term “grave” refers to a specific location where a deceased person’s body is laid to rest, and it holds significant cultural and emotional meaning for many people.
The Meaning of Critical
The term “critical” is often used in medical contexts to describe a patient’s condition. While it can indicate a serious illness or injury, it does not necessarily mean that the patient is dying.
In medical terminology, “critical” is often used to describe a patient’s vital signs or overall condition. A patient who is in critical condition may have unstable or abnormal vital signs, such as a dangerously low or high blood pressure, heart rate or breathing rate. This can indicate a serious illness or injury that requires immediate medical attention.
However, it is important to note that a critical condition does not necessarily mean that the patient is dying. With proper medical care, many critical patients can recover and regain teir health.
That being said, a critical condition can also indicate major complications or medical emergencies that can lead to death if not treated promptly and appropriately. It is important for medical professionals to monitor critical patients closely and provide the necessary interventions to stabilize their vital signs and address any underlying medical issues.
While a critical condition can indicate a serious medical problem, it does not automatically mean that the patient is dying. It is a term used to describe a patient’s unstable vital signs or overall condition, and prompt medical intervention is crucial to ensure the best possible outcome.
Can Critical Condition be Reversed?
It is posible for someone to come back from critical condition. However, the road to recovery can be long and difficult for the survivors of critical illness. At the time of ICU discharge and even at the time of hospital discharge, survivors of critical illness experience real and profound impairments.
The impairments that survivors of critical illness may experience include physical, cognitive, and emotional difficulties. Physical impairments may include muscle weakness, fatigue, and difficulty breathing. Cognitive impairments may include memory loss, difficulty concentrating, and confusion. Emotional impairments may include anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
In time, many of these symptoms will improve, but survivors may need to undergo rehabilitation and management to help them recover fully. Rehabilitation may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Management may involve medication, psychological counseling, and support from family and friends.
It is important to note that the recovery process is different for each person and may depend on factors such as age, overall health, and the severity of their illness. However, with the right support and care, many survivors of critical illness are able to return to their normal activities and lead fulfilling lives.
Living with Critical Illness
When a person is in critical condition, it means that their health is in a precarious state and they require intensive medical care. In this situation, the patient’s vital organs may be faling or at risk of failing, and they may be experiencing severe pain or discomfort.
While it is possible to survive a critical condition, it is important to note that recovery can be a long and challenging process. Patients who have been in critical condition may experience a range of physical, cognitive, and emotional symptoms that can impact their ability to function independently.
Physical weakness is a common symptom experienced by patients who have survived critical illness. This can make it difficult for patients to carry out everyday tasks such as walking, dressing, or feeding themselves. In some cases, patients may require rehabilitation or physical therapy to regain their strength and mobility.
In addition to physical symptoms, patients who have survived critical illness may experience cognitive difficulties such as memory problems or difficulty concentrating. They may also experience emotional symptoms such as depression, anxiety, or PTSD.
It is important to note that recovery from critical illness is not a linear process and can vary significantly from person to person. Some patients may recover quickly and resume their normal activities within a few weeks, while others may require months or even years of rehabilitation and support.
While it is possible to survive critical illness, recovery can be a challenging process that may involve a range of physical, cognitive, and emotional symptoms. Patients who have survived critical illness may require ongoing medical care and support to help them regain their independence and quality of life.
Five Life-Threatening Conditions
There are various health conditions that can be life-threatening, and they require immediate medical attention. Here are five common life-threatening conditions:
1. Diabetes: This chronic condition occurs when the body cannot produce or properly use insulin, which is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. If left untreated, high blood sugar levels can damage organs and lead to life-threatening complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and blindness.
2. Severe allergies: Allergic reactions can range from mild to life-threatening, causing anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially fatal reaction. The most common triggers for severe allergies include foods like peanuts and shellfish, insect stings, and medications.
3. Epilepsy/seizure disorder: Seizures can be caused by various conditions, but epilepsy is a chronic disorder that can cause recurrent seizures. Seizures can be life-threatening, especially if they occur while a person is swimming, driving, or operating heavy machinery.
4. Severe asthma: Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the airways. Severe asthma attacks can be life-threatening and require emergency medical care. Symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing, chest tightness, and coughing.
5. Cardiac/heart conditions: Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. Various conditions, including coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, and heart failure, can increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, and sudden cardiac arrest. Symptoms can include chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, and fainting.
It’s important to note that tese are just a few examples of life-threatening conditions. If you or someone you know experiences any severe symptoms, seek medical help immediately.

Source: npr.org
Stages of Hospital Conditions
Hospitals are designed to provide medical care to individuals in need. Based on the severity of the patient’s condition, hospitals have different stages of care. These stages are commonly referred to as hospital conditions. There are three primary hospital conditions: good, fair, and serious.
Good hospital condition indicates the patient’s vital signs are stable and within normal limits. Patients in good condition may still be receiving medical treatment or may be recovering from a minor injury or illness. They are conscious and alert, and their indicators are favorable.
Fair hospital condition indicates that the patient’s vital signs may be stable, but not necessarily within normal limits. Patients in fair condition may be uncomfortable, and their indicators may not be as favorable as tose in good condition. However, they are still conscious and alert.
Serious hospital condition indicates that the patient’s vital signs may be unstable and not within normal limits. Patients in serious condition may be unconscious or unresponsive, and their indicators may not be favorable. They require immediate medical attention and may be in critical condition.
It is important to note that hospital conditions may vary depending on the hospital and the medical condition of the patient. However, these three conditions are commonly used across various healthcare facilities to describe the state of a patient’s health.
Hospital conditions are used to describe the severity of a patient’s medical condition. Good, fair, and serious are the three primary hospital conditions used to indicate the state of a patient’s health.
Length of Stay in ICU
Intensive Care Units (ICUs) are specially designed hospital wards that provide round-the-clock care for critically ill patients. Patients in ICU require close monitoring and specialized medical attention, and the length of time they spend in the unit can vary depending on a range of factors.
In general, the length of stay in the ICU depends on the severity of the patient’s condition and the underlying medical issues they are facing. For example, some patients may only need a few days in the ICU to recover from a surgery or injury, while ohers may require weeks or even months of care.
Factors that can affect the length of stay in the ICU include:
– The type and severity of the illness or injury
– The patient’s age and overall health
– The complexity of the medical care required
– The availability of resources and staffing in the ICU
It’s worth noting that while some patients may spend a long time in the ICU, this is not always the case. In many cases, patients are able to recover and be discharged from the ICU relatively quickly.
That being said, there are some cases where patients may need to stay in the ICU for an extended period of time. For example, patients with severe burns, traumatic brain injuries, or chronic illnesses may require ongoing care and monitoring in the ICU for weeks or even months.
The length of stay in the ICU can vary widely depending on a range of factors, and it’s not possible to give a definitive answer to the question of how long a patient can stay in the unit. However, ICU staff work closely with patients and their families to provide the best possible care and support throughout their stay in the unit.
Conclusion
A grave condition refers to a serious illness, disease, or injury that is dangerous and life-threatening. Patients with a grave condition require urgent medical attention, as their vital signs may be unstable and not within normal limits. This condition can be caused by vaious factors, including genetic predisposition, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Graves’ disease, for example, is a common cause of a grave condition, leading to hyperthyroidism and a rapid increase in metabolism. It is essential to seek medical help immediately if you suspect you or someone you know has a grave condition. Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve the chances of recovery and reduce the risk of complications. Remember, taking care of your health is crucial in preventing grave conditions and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
