The concept of atomic mass unit (AMU) and grams per mole (g/mol) are used in chemistry to measure the mass of atoms and molecules. While both units are used to measure mass, they are not interchangeable. In this blog post, we will explore the relationship betwen g/mol and AMU and how to convert between the two units.
Atomic Mass Unit (AMU)
Atomic mass unit (AMU) is a unit of mass used to express the mass of atoms and molecules. It is defined as one-twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. The mass of a single proton or neutron is approximately 1 AMU. The mass of an electron is negligible and is not included in the calculation of atomic mass.
Grams per Mole (g/mol)
Grams per mole (g/mol) is another unit of mass used to express the mass of atoms and molecules. It is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance. One mole of a substance is defined as the amount of the substance that contains the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. The value of Avogadro’s number, which is the number of particles in one mole, is 6.022 x 10^23.
The relationship between g/mol and AMU is straightforward. One AMU is equivalent to 1.66 x 10^-24 grams. Conversely, one gram is equivalent to 6.022 x 10^23 AMU. The characteristic molar mass of an element is simply the atomic mass in g/mol. However, molar mass can also be calculated by multiplying the atomic mass in AMU by the molar mass constant (1 g/mol). To calculate the molar mass of a compound with multiple atoms, sum all the atomic mass of the constituent atoms.
To convert between g/mol and AMU, we can use the relationship mentioned above. Here are some examples:
Example 1: Convert 2 g/mol to AMU
2 g/mol x (1 AMU/1.66 x 10^-24 g) = 1.20 x 10^23 AMU
Example 2: Convert 5 AMU to g/mol
5 AMU x (1.66 x 10^-24 g/1 AMU) = 8.3 x 10^-24 g/mol
Atomic mass unit (AMU) and grams per mole (g/mol) are two different units used to measure mass in chemistry. While they are not interchangeable, the relationship between them is straightforward, and conversion between the two units is simple. Understanding the relationship between g/mol and AMU is essential for various chemical calculations, including molar mass and stoichiometry.
Is the G Mol Unit the Same as the AMU Unit?
The terms g mol and AMU are often used in the field of chemistry to describe the mass of atoms and molecules. While they both refer to mass, they are not interchangeable and have different meanings.
AMU, or atomic mass unit, is a unit of mass that is defined as one-twelfth of the mass of a carbon-12 atom. It is commonly used to express the mass of individual atoms and subatomic particles. For example, the mass of a proton is approximately 1 AMU.
On the other hand, g mol, or grams per mole, is a unit of mass that is used to express the mass of a collection of atoms or molecules. It represents the mass of one mole of a substance. One mole of a substance contains Avogadro’s number of particles, which is approximately 6.02 x 10^23 particles. For example, the molar mass of water is approximately 18 g mol^-1, meaning that one mole of water has a mass of 18 grams.
Therefore, whle both g mol and AMU are units of mass, they have different applications and cannot be used interchangeably. G mol is used to describe the mass of a collection of atoms or molecules, while AMU is used to describe the mass of individual atoms and subatomic particles.
Is the Mass of 1 Gram Equal to the Mass of 1 Atomic Mass Unit?
1g is not equal to 1 amu. AMU stands for Atomic Mass Unit and is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express the mass of atoms and molecules. One AMU is equivalent to 1.66 x 10-24 grams, which is a very small amount of mass.
On the other hand, 1 gram is equivalent to 6.022 x 1023 AMU. This means that one gram is a much larger quantity of mass than one AMU. In fact, one gram is equal to 6.022 x 1023 atomic mass units, which is also kown as Avogadro’s number.
To put it simply, one AMU is a very small amount of mass that is used to describe the mass of individual atoms and molecules. One gram, on the other hand, is a much larger quantity of mass that is used to describe the mass of larger objects, such as chemicals, food, or even people.
1g is not equal to 1 AMU. One AMU is equivalent to 1.66 x 10-24 grams, while one gram is equivalent to 6.022 x 1023 AMU.
Converting Molar Mass to Atomic Mass Units (AMU)
Converting molar mass to AMU (atomic mass units) involves a simple mathematical formula that uses the molar mass constant. The molar mass constant is defined as 1 g/mol. The atomic mass unit (AMU) is defined as 1/12th of the mass of a carbon-12 atom, which is approximately 1.66 x 10^-24 g.
To convert molar mass to AMU, you first need to know the atomic mass of the element or compound. This can be found on the periodic table of elements, where atomic masses are listed in atomic mass units (AMU).
Once you have the atomic mass in AMU, you can use the folowing formula to convert it to molar mass:
Molar mass (g/mol) = Atomic mass (AMU) x Molar mass constant (1 g/mol)
For example, the atomic mass of carbon is 12.011 AMU. To convert this to molar mass, we can use the formula:
Molar mass (g/mol) = 12.011 AMU x 1 g/mol
Molar mass (g/mol) = 12.011 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of carbon is 12.011 g/mol.
If you want to calculate the molar mass of a compound with multiple atoms, you need to sum the atomic masses of all the atoms in the compound. For example, the molar mass of water (H2O) can be calculated as follows:
Molar mass of water (g/mol) = (2 x Atomic mass of hydrogen) + Atomic mass of oxygen
The atomic mass of hydrogen is 1.008 AMU, and the atomic mass of oxygen is 15.999 AMU. Therefore, the molar mass of water is:
Molar mass of water (g/mol) = (2 x 1.008 AMU) + 15.999 AMU
Molar mass of water (g/mol) = 18.015 g/mol
In summary, to convert molar mass to AMU, you can use the formula Molar mass (g/mol) = Atomic mass (AMU) x Molar mass constant (1 g/mol). To calculate the molar mass of a compound with multiple atoms, sum the atomic masses of all the constituent atoms.
Difference Between G Mole and Atomic Mass
Molar mass and atomic mass are two important concepts in chemistry. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, expressed in grams per mole. Atomic mass, on the other hand, is the mass of one atom of an element, expressed in atomic mass units.
To understand the difference between the two, we need to first look at what a mole is. A mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to represent a certain amount of a substance. One mole of a substance contains Avogadro’s number of particles, which is approximately 6.02 x 10^23 particles. This means that one mole of oxygen atoms contains 6.02 x 10^23 oxygen atoms.
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. For example, the molar mass of oxygen is 15.9994 grams per mole. This means that one mole of oxygen atoms has a mass of 15.9994 grams.
Atomic mass, on the other hand, is the mass of one atom of an element. It is expressed in atomic mass units (amu). For example, the atomic mass of oxygen is 15.9994 amu. This means that one oxygen atom has a mass of 15.9994 atomic mass units.
The key difference between molar mass and atomic mass is that molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, while atomic mass is the mass of one atom of an element. Molar mass is expressed in grams per mole, while atomic mass is expressed in atomic mass units.
Molar mass and atomic mass are both important concepts in chemistry, but they represent diferent things. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance, while atomic mass is the mass of one atom of an element. It is important to understand the difference between the two when performing calculations in chemistry.
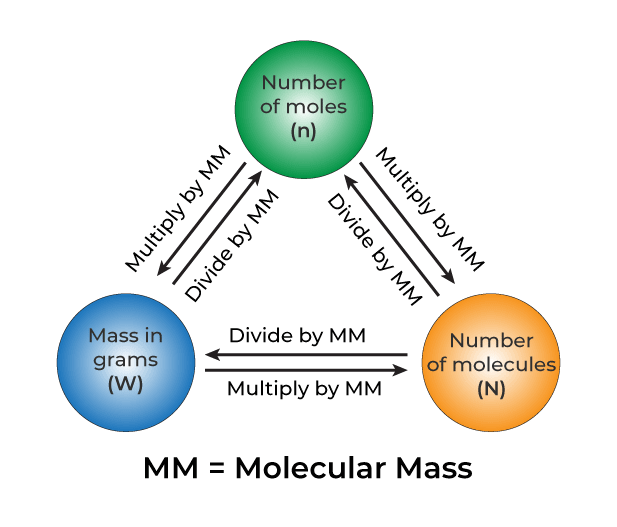
Is G Mol a Unit of Measurement for Mass?
G/mol is a unit of mass that is used to express the molar mass of a substance. Molar mass is an important concept in chemistry, as it is used to convert between the mass of a substance and the number of moles of that substance. One mole of a substance is defined as the amount of that substance that contains Avogadro’s number of particles (approximately 6.02 x 10^23 particles). The molar mass of a substance is simply the mass in grams of one mole of that substance. So, for example, the molar mass of water (H2O) is approximately 18.015 g/mol, which means that one mole of water has a mass of 18.015 grams. It is important to note that molar mass is not the same as molecular weight or atomic weight, although these terms are oftn used interchangeably. Molecular weight refers to the sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in a molecule, while atomic weight refers to the average weight of an atom of a particular element, taking into account the different isotopes of that element.
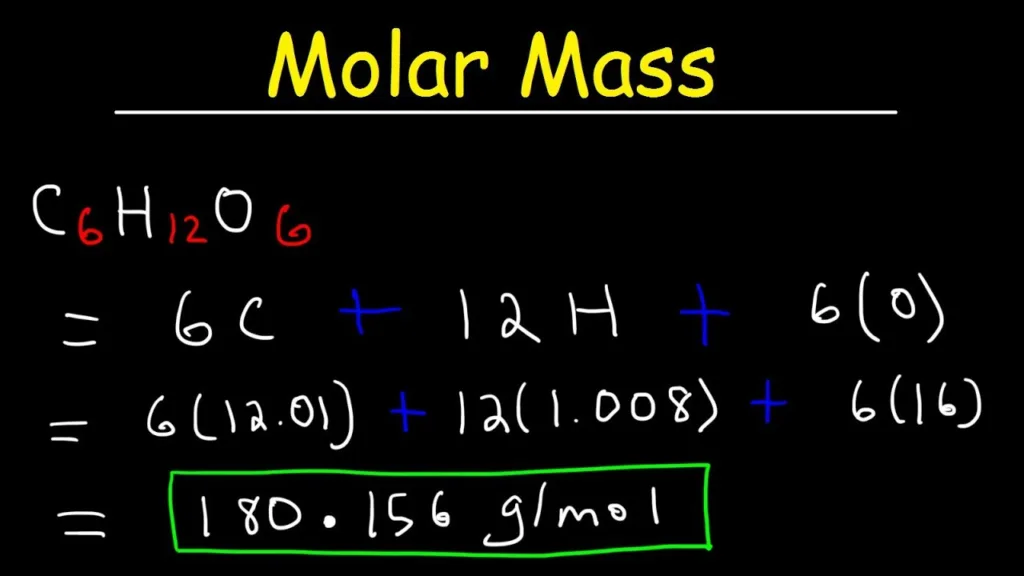
What Is the Unit of Measurement for Formula Mass?
Formula mass is given in atomic mass units (amu). It is a unit that is commonly used in chemistry to express the mass of a molecule. The formula mass of a molecule is calculated by adding the atomic weights of all the atoms present in the empirical formula of the compound. The empirical formula is the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound.
It is important to note that formula mass is not the same as molar mass. Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance and is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). The relationship between formula mass and molar mass is that the molar mass of a compound is equal to its formula mass in grams per mole.
To calculate the formula mass of a compound, one can use the periodic table to determine the atomic weights of all the atoms in the empirical formula, and then add them up. It is important to use the correct atomic weights, wich are typically given in amu.
Formula mass is expressed in atomic mass units (amu), while molar mass is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). The formula mass of a compound is calculated by adding up the atomic weights of all the atoms in the empirical formula of the compound.
Does the Mass of One Gram Equal the Amount of One Mole?
1 gram does not equal 1 mole. The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to represent a specific number of particles, such as atoms or molecules. The number of particles in 1 mole is defined as Avogadro’s number, which is approximately 6.022 x 10^23.
The mass of 1 mole of a substance depends on the substance’s atomic or molecular weight. For example, 1 mole of hydrogen atoms has a mass of approximately 1 gram, while 1 mole of oxygen atoms has a mass of approximately 16 grams.
Therefore, the relationship between grams and moles depends on the substance being measured. To convert between the two units, you need to know the molar mass of the substance, which is the mass of 1 mole of that substance. The molar mass is expressed in grams per mole (g/mol).
Here is an example of how to convert grams to moles using the molar mass:
– Suppose you have 10 grams of water (H2O)
– The molar mass of water is approximately 18 g/mol (2 hydrogen atoms x 1 g/mol + 1 oxygen atom x 16 g/mol)
– To convert grams to moles, divide the gien mass by the molar mass: 10 g / 18 g/mol = 0.556 moles of water
1 gram does not equal 1 mole, but the mass of 1 mole of a substance is equal to its molar mass, which is expressed in grams per mole.
Conversion of Grams to Moles
The molar mass constant, which is also known as the molar mass of atoms of an element, is defined as 1 × 10−3 kg/mol = 1 g/mol. This means that 1 gram of any substance is equal to its molar mass in grams per mole.
For example, the molar mass of oxygen is 16.00 g/mol. This means that 1 mole of oxygen atoms weighs 16.00 grams. Similarly, the molar mass of carbon is 12.01 g/mol, so 1 mole of carbon atoms weighs 12.01 grams.
To calculate the number of moles in a givn mass of a substance, we can use the formula:
Moles = mass (in grams) / molar mass (in grams per mole)
For instance, if we have 5 grams of oxygen, we can calculate the number of moles as follows:
Moles = 5 g / 16.00 g/mol = 0.3125 mol
1 gram of any substance is equal to its molar mass in grams per mole, which is defined as 1 g/mol. This value is used to calculate the number of moles in a given mass of a substance.
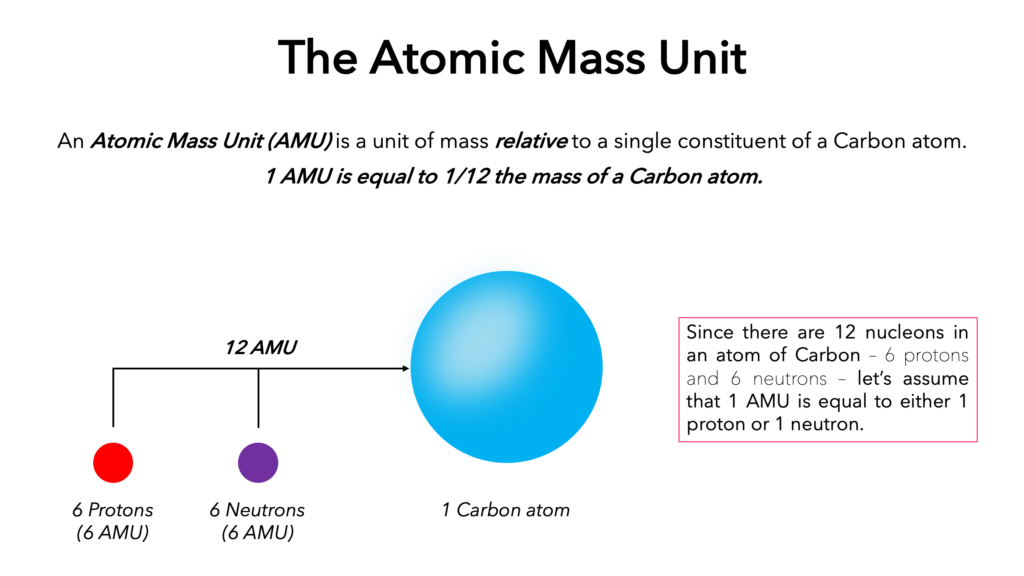
What is an Atomic Mass Unit (AMU)?
One atomic mass unit (AMU) is defined as the mass equal to one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12, which is approximately 1.66 x 10^-27 kg or 1.66 x 10^-24 g. It is a unit of mass commonly used in atomic and nuclear physics to express the mass of atoms, molecules, and other particles.
To put this into perspective, the mass of a proton is approximately 1 AMU, while the mass of a neutron is slightly larger at 1.008 AMU. The mass of an electron, on the other hand, is much smaller at 0.00055 AMU.
It is also important to note that the mass of an atom is not simply the sum of the masses of its constituent particles (protons, neutrons, and electrons), as there is a small loss of mass due to the binding energy that holds the nucleus together. This is known as the mass defect, and it accounts for the difference beteen the atomic mass of an atom and the sum of its constituent masses.
1 AMU is a unit of mass used to describe the mass of atomic and subatomic particles, with a value of approximately 1.66 x 10^-27 kg or 1.66 x 10^-24 g.
What Is the AMU Formula?
The average atomic mass (amu) formula is a mathematical formula that is used to calculate the average mass of an element’s isotopes. This formula takes into account the natural abundance of each isotope and the mass of each isotope. The formula is expressed as follows:
Average atomic mass = f1M1 + f2M2 +… + fnMn
Where f represents the fraction representing the natural abundance of the isotope and M represents the mass number (weight) of the isotope. The subscripts 1, 2, … n represent the different isotopes of the element.
To calculate the average atomic mass of an element usig this formula, you need to know the natural abundance of each isotope and its mass number. The natural abundance of an isotope is the percentage of that isotope that exists in nature. The mass number of an isotope is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom.
Once you have the natural abundance and mass number of each isotope, you can plug them into the formula and solve for the average atomic mass of the element. The result of this calculation is expressed in atomic mass units (amu), which is a unit of measurement for the mass of atoms and molecules.
The amu formula is a mathematical formula used to calculate the average mass of an element’s isotopes, which takes into account the natural abundance and mass of each isotope.
Calculating Atomic Mass Units (AMU)
The atomic mass unit (amu) is a unit of measurement used to express the mass of atoms and molecules. It is defined as one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12. The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of all the isotopes of that element, taking into account teir relative abundance.
To calculate the atomic mass of a single atom of an element, you need to know the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom. The number of protons is equal to the atomic number of the element, which is listed in the periodic table. The number of neutrons can be calculated by subtracting the number of protons from the atomic mass of the atom, which is also listed in the periodic table.
For example, let’s calculate the atomic mass of a single atom of carbon. Carbon has an atomic number of 6, which means it has 6 protons in its nucleus. The atomic mass of carbon is 12.01 amu. To calculate the number of neutrons in a single atom of carbon, we subtract the number of protons from the atomic mass: 12.01 – 6 = 6.01. Therefore, a single atom of carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, and its atomic mass is 12.01 amu.
It’s important to note that the atomic mass listed in the periodic table is not always a whole number. This is because many elements have multiple isotopes, which are atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. The atomic mass listed is the weighted average of all the isotopes, taking into account their relative abundance.
To summarize, the atomic mass of a single atom of an element can be calculated by adding up the number of protons and neutrons in the atom’s nucleus. The atomic mass listed in the periodic table is the weighted average of all the isotopes of the element.
What Has a Mass of One Atomic Mass Unit (amu)?
An atomic mass unit (AMU) is a unit of mass used to express the mass of atomic and subatomic particles. In the context of atomic particles, a proton and a neutron have an approximate mass of 1 AMU each. Therefore, a single proton or neutron has a mass of 1 AMU.
It is important to note that the nucleus of an atom contins almost the entire mass of the atom, which means that the total mass of an atom is mainly determined by the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Electrons, which orbit the nucleus, have a negligible mass compared to protons and neutrons.
The mass of 1 AMU is attributed to a single proton or neutron in the nucleus of an atom.
Conclusion
The relationship between grams per mole and atomic mass units is crucial in the field of chemistry. We have seen that one atomic mass unit is equivalent to 1.66 x 10^-24 grams, whie one gram is equivalent to 6.022 x 10^23 AMU. The molar mass of an element is simply the atomic mass in grams per mole, and this can be calculated by multiplying the atomic mass in AMU by the molar mass constant (1 g/mol). For compounds with multiple atoms, the molar mass can be calculated by summing up the atomic masses of all constituent atoms. Understanding the relationship between grams per mole and atomic mass units is essential for performing accurate calculations in chemistry and for understanding the properties of elements and compounds.
