Frostbite is a serious condition that can lead to permanent tissue damage and scarring. When skin and other tissues freeze, ice crystals form and can cause damage to cells and blood vessels. The severity of frostbite depends on how long the skin is exposed to cold temperatures and how quickly it is treated. If left untreated, it can lead to tissue death and the need for amputation.
One of the long-term effects of frostbite is scarring. The likelihood of scarring depends on the severity of the frostbite and how many layers of tissue are affected. Frostbite can affect the epidermis, or outer layer of skin, as well as the dermis, or lower layer of skin. If the frostbite only affects the epidermis, the risk of scarring is lower than if it affects the dermis.
There are different types of frostbite, and each type can lead to different levels of scarring. Superficial frostbite, also known as second-degree frostbite, is a milder form of frostbite that only affects the outer layer of skin. During this stage, the skin will turn from a reddish color to a paler color, and ice crystals may begin to form in the skin. The affected area may have a hard or frozen feeling when touched. Most frostbitten tissues will blister, except for the most severely damaged ones. If left untreated, the hard, white tissue of mildly frostbitten tissues will becoe red, then mottled purple; within 24-36 hours, blisters will fill with fluid. Blackening of the affected tissues may take up to 10 days to appear.
Deep frostbite, also known as third or fourth-degree frostbite, is a more severe form of frostbite that affects deeper layers of tissue. During this stage, the skin may turn black or blue and may become hard or rubbery. Blisters may also form, and tissue death may occur. Deep frostbite is more likely to result in scarring, as it affects deeper layers of tissue and can cause more damage.
If you have suffered from frostbite and are concerned about scarring, there are steps you can take to minimize scarring. It is important to seek medical treatment as soon as possible to prevent further tissue damage. Your doctor may recommend wound care, including keeping the affected area clean and dry, and applying topical ointments. If the frostbite is severe, you may need surgery to remove dead tissue and promote healing.
In addition to medical treatment, there are also things you can do at home to promote healing and minimize scarring. Staying hydrated and avoiding smoking can help improve circulation and promote healing. Eating a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals can also help promote healing and prevent scarring.
Frostbite can lead to scarring, especially if it affects deep layers of tissue. If you have suffered from frostbite, it is important to seek medical treatment as soon as possible to prevent further tissue damage and scarring. With proper medical care and self-care, you can minimize scarring and promote healing.
The Possibility of Frostbite Leaving Scars
Frostbite is a condition that occurs when the skin and underlying tissues freeze due to prolonged exposure to cold temperatures. The severity of frostbite can range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of tissue damage. In severe cases, frostbite can cause permanent damage to the affected area, including scarring.
The likelihood of scarring from frostbite depends on various factors, including the severity of the frostbite, the area of the body affected, and the depth of tissue damage. In mild cases of frostbite, where only the outer layer of the skin is affected, scarring is unlikely to occur. However, in severe cases of frostbite, where the deeper layers of the skin and underlying tissues are affected, scarring is more likely to occur.
Frostbite scars can vary in appearance, ranging from raised and discolored to indented and white. The severity and appearance of the scar depend on the extent of tissue damage and the body’s healing process. In some cases, frostbite scars can be improved with treatments such as laser therapy, dermabrasion, or skin grafting.
Frostbite can leave scars, prticularly in severe cases where deeper layers of tissue are affected. It is important to seek medical attention immediately if you experience symptoms of frostbite to prevent permanent tissue damage and scarring.
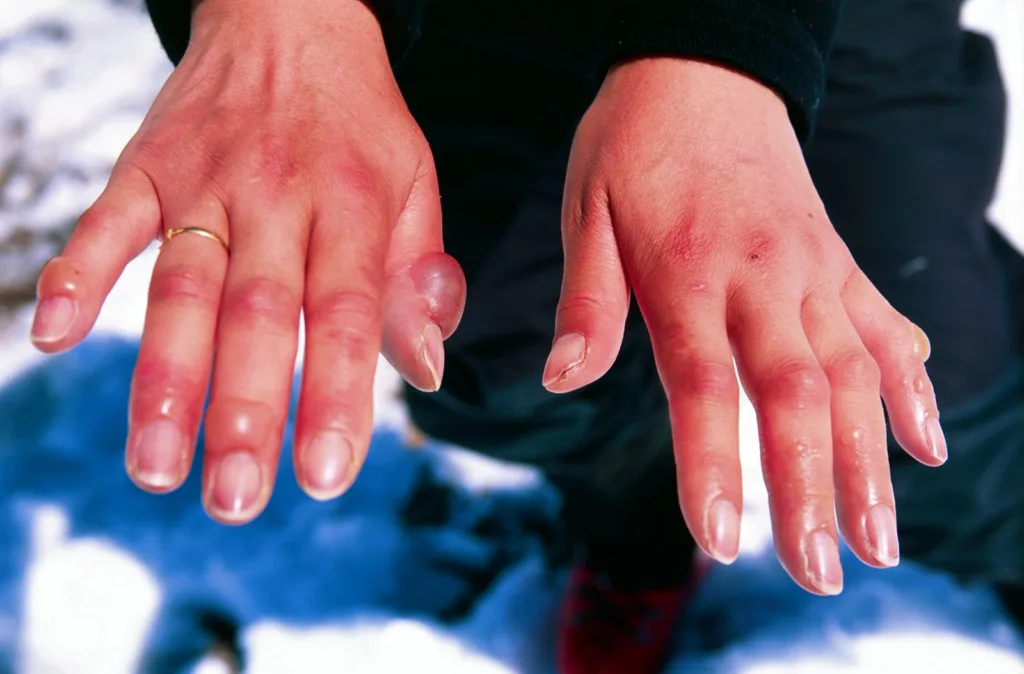
Signs and Symptoms of Frostbite Burns
Frostbite is a severe condition that occurs when the skin and underlying tissues freeze due to exposure to extreme cold. The symptoms of frostbite vary depending on the severity of the condition. In the initial stages, frostbite causes the skin to turn red and feel cold, numb and tingling. As the condition progresses, the skin may turn white or blue-gray, and you may lose all sensation of cold, pain or discomfort in the affected area.
In severe cases, frostbite can case the joints or muscles to stop working. Large blisters may form 24 to 48 hours after rewarming, and the tissue may turn black and hard as it dies. This is a sign of severe frostbite and requires immediate medical attention.
It’s important to note that frostbite can affect any part of the body, but it’s most common in the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks, and chin. Therefore, it’s essential to protect these areas from extreme cold temperatures by wearing warm and protective clothing, limiting exposure to cold weather, and seeking shelter when necessary.
Frostbite burn looks like a skin that turns white or blue-gray, and you may lose all sensation of cold, pain, or discomfort in the affected area. Severe frostbite can cause the tissue to turn black and hard as it dies and requires immediate medical attention.
Appearance of Superficial Frostbite
Superficial frostbite is a condition that occurs when your skin and underlying tissues freeze due to exposure to cold temperatures. During the second-degree frostbite stage, your skin will appear paler than normal, and in some cases, it may turn a bluish color. This discoloration is due to the constriction of blood vessels in the affected area.
Ice crystals may also begin to form in your skin, resulting in a hard or frozen feeling when you touch the affected area. In addition to discoloration and a frozen feeling, you may experience a tingling or burning sensation in the affected area.
Other symptoms of superficial frostbite include swelling and blistering, which can occur as the frozen tissues begin to thaw. In severe cases, the affected area may develop blackened or dead skin tissue, which is a sign of tissue death.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect that you have superficial frostbite. Treatment may include rewarming the affected area, pain management, and wound care. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove dead tissue or repair damaged blood vessels.
To prevent superficial frostbite, it’s important to dress appropriately for the weather, avoid prolonged exposure to cold temperatures, and take breaks to warm up if you’re working or playing otside in the cold.
The Timeframe for Skin to Turn Black After Frostbite
Frostbite is a serious medical condition that occurs when skin and underlying tissues freeze due to exposure to cold temperatures. The extent of damage caused by frostbite is typically categorized into four degrees, ranging from mild to severe. In the case of mild frostbite, the affected skin and tissues may frst become hard and white. Within 24-36 hours, blisters may develop, and the affected area may turn mottled purple before eventually returning to its normal color.
However, in more severe cases of frostbite, the affected tissues may turn black due to tissue death. This process, known as necrosis, occurs when the body’s tissues do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients to survive. The time it takes for skin to turn black after frostbite varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment.
In general, blackening of the affected tissues may take up to 10 days to appear. During this time, it is important to seek medical attention and follow proper treatment protocols to prevent further damage and complications. Treatment for frostbite typically involves rewarming the affected area, administering pain medication, and preventing infection.
The time it takes for skin to turn black after frostbite can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s response to treatment. Seeking prompt medical attention and following proper treatment protocols is essential in preventing further damage and complications associated with frostbite.
Treating Deep Frostbite
Frostbite is a medical condition that occurs when skin and other tissues freeze due to exposure to cold temperatures. Unfortunately, deep frostbite can case severe tissue damage and may lead to the need for surgery or amputation.
If you have experienced severe frostbite, a doctor may recommend surgery or amputation to remove dead or decaying tissue. This is because the tissue cannot be salvaged and may continue to cause damage to surrounding tissues if left untreated.
Another treatment option for severe frostbite is hyperbaric oxygen therapy. This involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room. The increased oxygen levels can help improve blood flow and promote tissue healing, potentially reducing the need for surgery or amputation.
It is essential to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you suspect you have frostbite. Delaying treatment can lead to more severe tissue damage and increase the risk of complications.
While there are treatment options for severe frostbite, prevention is the best approach. To avoid frostbite, be sure to dress warmly in cold weather, avoid prolonged exposure to the cold, and seek shelter if you feel numbness or tingling in your extremities.

Signs and Symptoms of Stage 1 Frostbite
Frostbite is a medical condition that occurs when the skin and underlying tissues freeze due to exposure to cold temperatures. There are four different stages of frostbite, and each stage has its own set of symptoms and treatment options. In this article, we will focus on stage 1 frostbite, whch is also known as frostnip.
During the early stage of frostbite, you may notice some changes in the affected area. The skin will become cold, numb, and white, and you may experience a tingling sensation. This is because the blood vessels in the affected area constrict, reducing blood flow and oxygen to the tissues. You may also experience pins and needles, throbbing, or aching in the affected area.
It is important to note that stage 1 frostbite only affects the surface layers of the skin, and it is usually reversible with proper treatment. If left untreated, however, it can progress to more severe stages of frostbite, which can cause permanent damage to the affected area.
To prevent stage 1 frostbite, it is important to dress appropriately for the weather, avoiding exposure to cold temperatures for extended periods of time. Wearing warm, layered clothing and protecting your hands, feet, and face with hats, gloves, and scarves can help prevent frostnip.
Stage 1 frostbite, also known as frostnip, is characterized by cold, numb, and white skin in the affected area, along with a tingling sensation and possible pins and needles, throbbing, or aching. Proper treatment and prevention can help prevent more severe stages of frostbite and permanent damage to the affected area.
The Recovery Process of Frost Burn
Frostbite is a condition that occurs when the skin and underlying tissues freeze due to exposure to cold temperatures. The amount of time required for frostbite to heal depends on the severity of the injury. Mild frostbite usualy takes a few days to heal, while more severe frostbite can take weeks or even months to heal. The affected area may also develop a scar after the injury has healed.
In mild cases of frostbite, the affected area may appear red and swollen, and the skin may feel cold and numb. In more severe cases, the skin may appear white or blue and feel hard and waxy. Blisters may also develop, and the affected area may feel painful or itchy.
To treat frostbite, it’s important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. The doctor may prescribe pain medication, antibiotics to prevent infection, and dressings to protect the affected area. In severe cases, the doctor may need to surgically remove damaged tissue.
Frostbite can go away over time, but the amount of time required for healing depends on the severity of the injury. Seeking medical attention as soon as possible and following the doctor’s instructions can help speed up the healing process and prevent complications.
Can Frostbite Skin Be Healed?
Frostbite is a condition that occurs when skin and other tissues freeze due to exposure to extremely cold temperatures. The severity of frostbite can vary, and in some cases, it can cause permanent damage to the affected area. However, with proper treatment, most cases of frostbite can heal over time.
The healing process for frostbite skin can take several weeks or even months, depending on the severity of the condition. During the initial stages of treatment, the affected area is usually warmed slowly to prevent further tissue damage. Once the area has been warmed, it may appear discoloured and blistered, and eventually scab over.
In cases where the frostbite is superficial, new pink skin will form beneath the discoloured skin and scabs. The area will usually recover withn six months. However, in more severe cases, the skin may not fully heal, and long-term complications such as nerve damage or chronic pain may occur.
To promote healing, it is essential to keep the affected area clean and dry and avoid exposing it to extreme temperatures until it has fully healed. In some cases, topical creams or ointments may be used to help speed up the healing process.
Frostbite skin can heal, but the healing process can take time and may vary depending on the severity of the condition. With proper treatment and care, most cases of frostbite can fully recover, but it is essential to take steps to prevent long-term complications.
The Long-Term Effects of Frostbite
Frostbite is a serious cold-related illness that can result in permanent damage. When exposed to cold temperatures, the body’s tissues can freeze and become damaged, leading to tissue destruction and nerve injury. The severity of frostbite can range from mild to severe, and the extent of the damage can depend on how long the tissue was exposed to the cold and how cold the temperature was.
In severe cases of frostbite, permanent nerve injury can occur, resulting in numbness or pain that can last a lifetime. The tissue damage can also be severe enough to require amputation of affected fingers or toes. This is because the tissue may become so damaged that it dies and cannot be saved.
On the other hand, frostnip is a milder, reversible form of cold-related illness. In this condition, the numbness and pain are only temporary, and the tissue does not sustain permanent damage. This condition can be treated by rewarming the affected area and protecting it from further exposure to the cold.
Frostbite can cause permanent damage, particularly in severe cases. It is important to take precautions to protect onesef from the cold and to seek medical attention if symptoms of frostbite develop.
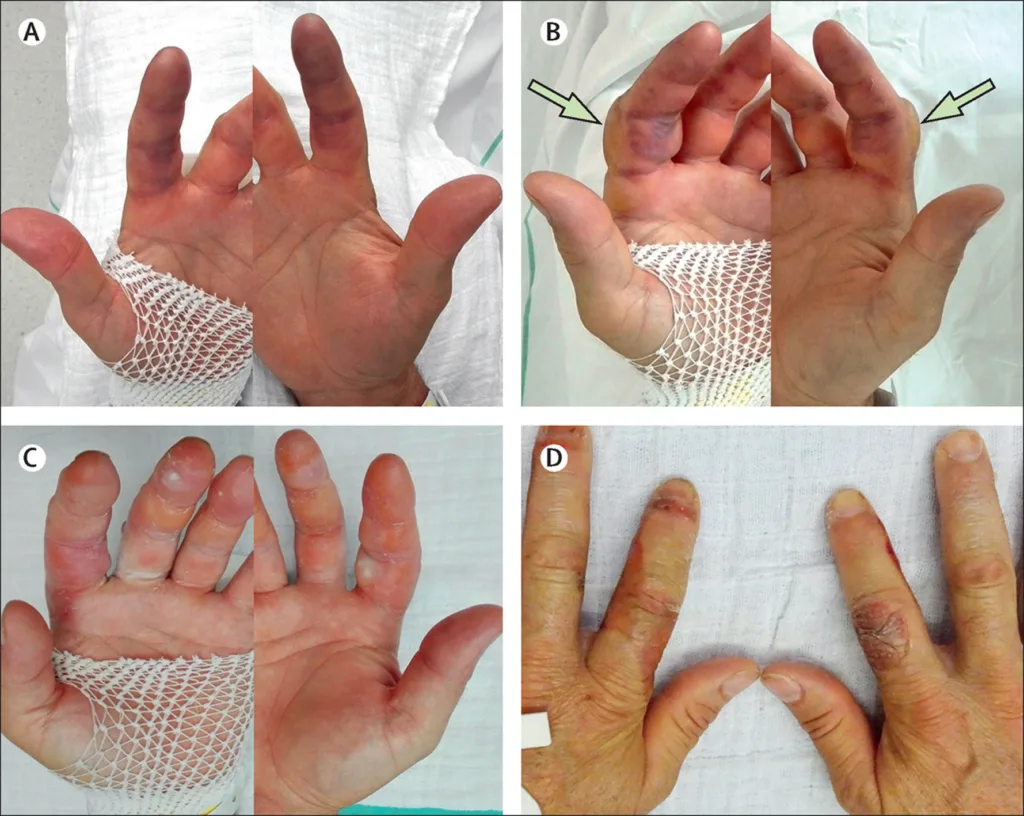
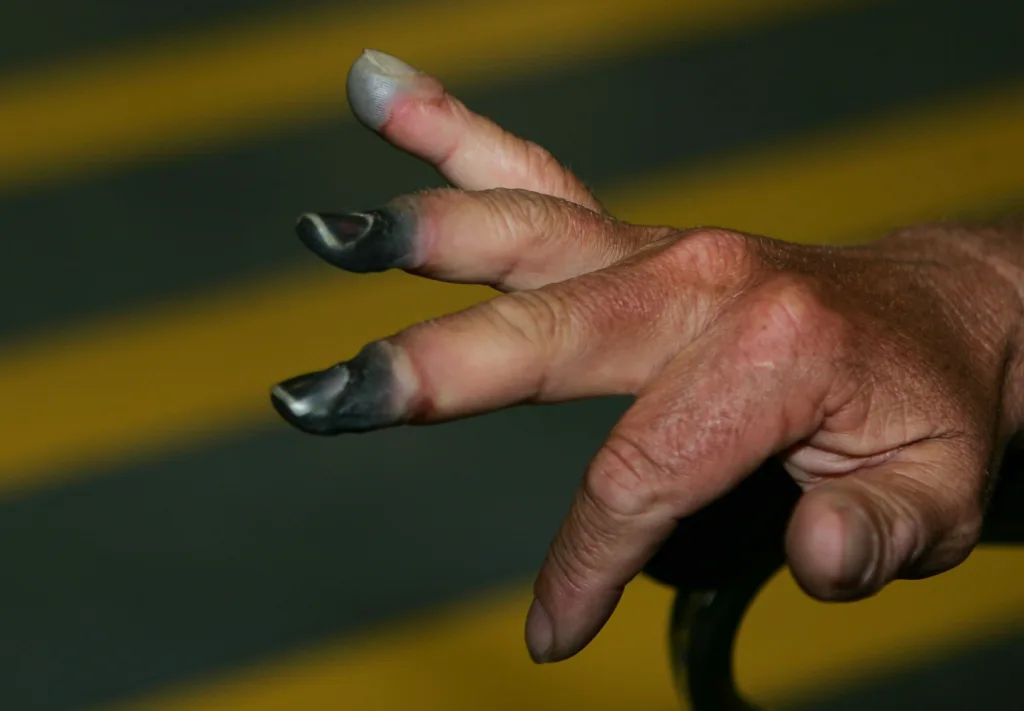
The Duration of First-Degree Frostbite
First-degree frostbite is the mildest form of frostbite, which affects only the outer layer of skin. The recovery period for first-degree frostbite varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overal health. Typically, the affected area will thaw and become tender, red, and swollen.
The pain associated with first-degree frostbite can last for several weeks, and the affected area may remain sensitive to cold temperatures for several months. The healing process can be accelerated by keeping the affected area dry and warm, avoiding exposure to cold temperatures, and avoiding any activity that could cause further damage to the skin.
In addition to these self-care measures, medical intervention may be necessary in severe cases of first-degree frostbite. Doctors may prescribe pain medication or antibiotics to reduce discomfort and prevent infection.
The recovery period for first-degree frostbite can range from several weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. It is essential to seek medical attention if you suspect you have frostbite to receive proper treatment and avoid any further complications.
The Effects of Superficial Frostbite on Skin
When it comes to frostbite, the severity of the injury plays a significant role in whether or not scarring will occur. If the frostbite is superficial or first-degree, it typically won’t result in permanent scarring if it is promptly treated. However, more severe cases of frostbite, including second and third-degree frostbite, can lead to scarring even with proper treatment.
Superficial frostbite affects only the top layer of skin and typically results in numbness, tingling, and discoloration of the affected area. If treated promptly, the affected area may return to normal within a few days to a couple of weeks. However, if left untreated, the damage can progress to deeper layers of skin, leading to more severe frostbite and a higher risk of scarring.
In general, the severity of the frostbite is determined by the depth of the injury. Superficial frostbite affects only the outer layer of skin, whie deep frostbite can extend to the muscle, bone, and even internal organs. The deeper the injury, the more likely it is to result in scarring.
It’s important to note that scarring from frostbite can be both physical and psychological. Physical scarring may be visible on the skin, while psychological scarring can result from the trauma of the injury and its aftermath.
Superficial frostbite typically doesn’t result in permanent scarring if promptly treated. However, more severe cases of frostbite can lead to scarring, both physically and psychologically. It’s essential to seek prompt medical attention for frostbite to minimize the risk of scarring and other complications.
The Long-Term Effects of Deep Frostbite
Deep frostbite is a severe form of frostbite that can result in permanent damage to the affected tissues. When exposed to extreme cold temperatures, the body tries to protect itself by narrowing blood vessels and reducing blood flow to the extremities. If the exposure persists, the tissues in the affected areas can freeze, which can cause them to die.
Deep frostbite can affect the muscles, tendons, nerves, and bones. Symptoms of deep frostbite may include numbness, skin discoloration, blisters, and tissue death. In severe cases, gangrene may develop, which can lead to amputation or even death.
Once the tissue is damaged, it cannot be reversed, and the affected area may have permanent changes in sensation, movement, and appearance. The extent of the damage will depend on the severity of the frostbite, the length of exposure, and the effectiveness of treatment.
If you suspect you have deep frostbite, seek medical attention immediately to prevent furter damage. Treatment may include rewarming the affected area, pain management, and antibiotics to prevent infection. In some cases, surgery may be required to remove dead tissue or to amputate the affected area.
Prevention is the best way to avoid deep frostbite. Dressing appropriately for the weather, staying dry, and avoiding prolonged exposure to cold temperatures can help prevent frostbite. If you must be outside in extreme weather, take frequent breaks to warm up and check your extremities for signs of frostbite.
The Point of Irreversibility of Frostbite
Frostbite is a severe injury caused by exposure of the skin and underlying tissues to extreme cold temperatures. It is a medical emergency that requires prompt attention to prevent complications, including tissue damage, amputation, and even death.
When it comes to frostbite, it is essential to understand that the injury is classified into three zones. These zones are determined by the extent of tissue damage and the chances of recovery. The three zones of frostbite are:
1. Zone of coagulation: This is the most distal and often the most severely injured area. In this zone, the injury is irreversible. The tissue damage is so severe that the cells cannot recover, and the tissue dies. The affected area is usually black and has no sensation.
2. Zone of stasis: This is the area surrounding the zone of coagulation. The tissue damage in this zone is less severe, and there is a chance of recovery. However, if left untreated, the tissue damage can progress, and the injury can become irreversible.
3. Zone of hyperemia: This is the least severe zone of frostbite. In this zone, the tissue damage is minimal, and there is a good chance of recovery with proper treatment.
It is important to note that the extent of tissue damage and the chances of recovery depend on seveal factors, including the severity and duration of the exposure to cold temperatures, the age and overall health of the individual, and the promptness of medical attention.
Frostbite is irreversible in the zone of coagulation, which is the most severely injured area. Therefore, it is essential to seek prompt medical attention to prevent the progression of the injury and increase the chances of recovery.

Consequences of Not Removing Frostbite
Frostbite is a serious condition that occurs when body tissues freeze due to exposure to extremely cold temperatures. If left untreated, frostbite can lead to permanent damage to the affected body part. In severe cases, amputation of the affected body part may be necessary.
When frostbite occurs, ice crystals form in the cells, causing damage to the tissues. The extent of the damage depends on the severity of the frostbite. In mild cases, the affected area may only experience numbness or tingling, and the skin may apear red or white. However, in severe cases, the skin and underlying tissues may turn black and die, leading to permanent damage and loss of the affected body part.
If you do not remove frostbite, the condition can worsen and spread to nearby tissues, leading to further damage and complications. In addition, the risk of infection increases as the skin and tissues become damaged, which can lead to serious health consequences.
Prompt treatment is essential to prevent further damage and complications. Treatment for frostbite typically involves rewarming the affected area, protecting it from further exposure, and seeking medical attention. In some cases, surgery or amputation may be necessary to remove damaged tissue and prevent the spread of infection.
To avoid frostbite, it is important to dress appropriately for cold weather, limit your exposure to extreme temperatures, and seek shelter or warmth if you begin to experience symptoms of frostbite.
The Duration of Redness After Frostbite
Frostbite is a condition that occurs when the skin and underlying tissues freeze due to exposure to cold temperatures. One of the common symptoms of frostbite is redness of the affected area. The duration for which frostbite stays red depends on the severity of the frostbite.
In mild cases of frostbite, whee only the outer layer of the skin is affected, the redness may last for a few hours to a few days. The affected area may also feel tingly or numb during this time. However, with proper care, the skin usually heals completely within a few weeks.
In more severe cases of frostbite, where the deeper tissues are affected, the redness may persist for a longer duration, up to several weeks or even months. The affected area may also develop blisters or blackened skin, which may take longer to heal.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have frostbite, especially if the symptoms persist for more than a few hours or if you develop blisters or blackened skin. In severe cases, frostbite can lead to permanent damage or even amputation of the affected limb.
Conclusion
Frostbite scars can be a seious and long-lasting consequence of severe frostbite. The likelihood of scarring depends on the extent and depth of the initial injury, as well as the effectiveness of treatment and the individual’s healing process. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you suspect you have frostbite, in order to minimize the risk of scarring and maximize the chances of a full recovery. If you do develop frostbite scars, there are a variety of treatments available, including topical creams, laser therapy, and surgical procedures such as skin grafts. With proper care and treatment, many individuals are able to minimize the appearance of frostbite scars and regain a high level of function and appearance in the affected areas.
