Electromyography, commonly referred to as EMG, is a diagnostic test that is used to evaluate the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them. This test is often recommended by healthcare providers to diagnose or rule out a number of conditions that affect the muscles, such as muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, and carpal tunnel syndrome. While the EMG test is an effective diagnostic tool, many patients are concerned about the cost of this procedure.
The cost of an EMG test can vary depending on a number of factors, including the healthcare provider, the location, and the patient’s insurance coverage. For patients with health insurance, the cost of an EMG test is typically covered by their plan. However, there may be some out-of-pocket expenses, such as a copay or coinsurance. The copay for an EMG test can range from $10 to $50, while the coinsurance can range from 10% to 50%.
For patients without insurance, the cost of an EMG test can be between $150 and $500 per extremity. This cost can vary depending on the healthcare provider and the location of the clinic. It is important to note that the cost of an EMG test may also include additional fees, such as a consultation fee or a fee for the interpretation of the results.
Despite the potential cost of an EMG test, it is an important diagnostic tool that can provide valuable information about a patient’s muscle and nerve health. A normal result does not necessarily mean that a patient does not have a deficit in their nerve or muscle. However, the results of an EMG test can provide important information that can help healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis and recommend apropriate treatment options.
Although the EMG test is generally well-tolerated, it may result in some discomfort during the procedure. However, most patients are able to tolerate this discomfort without any need for pain medication. The EMG test is a safe and effective diagnostic tool that can provide valuable information about a patient’s muscle and nerve health. While the cost of this procedure may be a concern for some patients, it is important to prioritize your health and speak with your healthcare provider about any questions or concerns you may have.
Insurance Coverage for EMG
EMG (Electromyography) testing is typically covered by health insurance. The coverage may vary depending on the insurance plan and the healthcare provider. Generally, patients may have to pay a copay of $10-$50 or coinsurance of about 10%-50% if they have health insurance. However, for patients without insurance, the cost of EMG testing can range between $150 and $500 per extremity, depending on the healthcare provider. It is always recommended to check with your insurance provider to understand your coverage before undergoing any medical procedure.
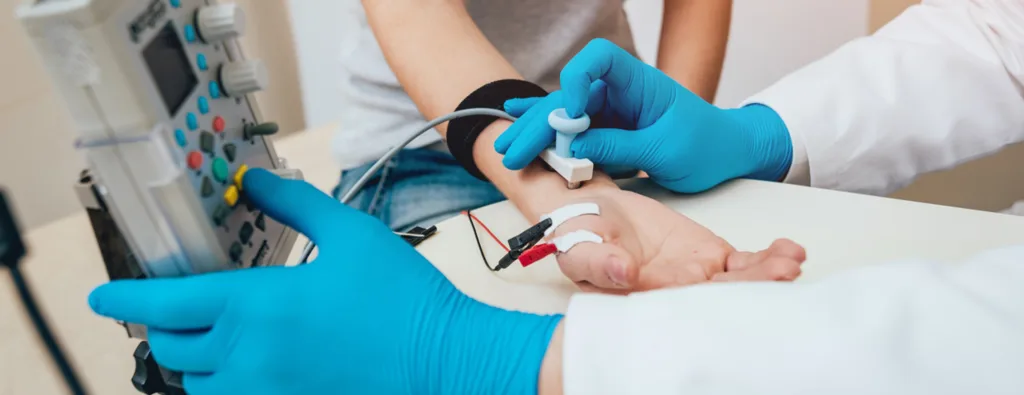
The Benefits of Undergoing an EMG Test
EMG tests can be extremely useful in diagnosing a variety of conditions related to the muscles and nerves. They are often recommended by doctors to help identify muscle disorders, nerve damage, and other related conditions. By measuring the electrical activity of the muscles, EMG tests can provide valuable informtion about the functioning of the muscles and nerves. While EMG tests can be uncomfortable for some patients, the information they provide can be extremely valuable in guiding treatment decisions and helping patients to manage their conditions. whether or not an EMG test is worth it will depend on the specific situation and the individual patient’s needs. However, for many patients, the benefits of an EMG test can be significant and may outweigh any potential discomfort or inconvenience.
Does Electromyography Reveal Nerve Damage?
EMG (electromyography) is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the health of muscles and the nerves that control them. While EMG can be helpful in identifying nerve damage, it does not always show nerve damage. In fact, there are several factors that can cause a normal EMG despite the presence of nerve damage. For example, early stage nerve damage may not yet be detectable by EMG. Additionally, the location of the nerve damage may not be within the range of the EMG study or the severity of the damage may not be significant enough to be detected by EMG. Therefore, it’s important to understand that while EMG is a useful diagnostic tool, it is not always conclusive and shuld be used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and medical evaluations.
Pain Level of EMG Nerve Test
An EMG nerve test involves placing small needles into the muscles to record electrical activity. Most people report some discomfort during the test, but it is usually well-tolerated without any need for pain medication. The needle insertion may cause a brief sharp sensation, and some people may experience muscle soreness or bruising after the test. However, the level of pain can vary depending on the individual’s pain tolerance and the extent of muscle involvement. while the EMG test may cause some discomfort, the benefits of the test in diagnosing nerve and muscle disorders often outweigh the temporary discomfort.
Does an EMG Reveal a Pinched Nerve?
An EMG can show a pinched nerve. An electromyography (EMG) test is used to evaluate the electrical signals in muscles and nerves. During the test, a small electrode is inserted into the muscle to measure the electrical activity. If there is a pinched nerve present, the EMG may show abnormal electrical activity in the muscles asociated with that nerve. The test can also identify the location and severity of the pinched nerve. Other tests, such as a nerve conduction study (NCS), may also be used in conjunction with an EMG to provide a complete diagnosis. an EMG is a useful tool in detecting and diagnosing pinched nerves.
Source: yashodahealthcare.com
Diagnosing Diseases With EMG
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic test that can be used to identify various neuromuscular diseases, motor problems, nerve injuries, or degenerative conditions. EMG can diagnose several diseases such as Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), wich is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, Carpal tunnel syndrome, a condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm due to pressure on the median nerve in the wrist, Cervical spondylosis, a degenerative condition that affects the spinal discs in the neck, resulting in neck pain and stiffness.
Guillain-Barre syndrome, a rare autoimmune disorder that damages the peripheral nerves, causing muscle weakness and paralysis. Lambert-Eaton syndrome, a rare disorder that affects the connection between nerves and muscles, causing muscle weakness and difficulty moving. Muscular dystrophy, a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle weakness and degeneration. Myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disorder that affects the connection between nerves and muscles, causing muscle weakness and fatigue.
EMG is a valuable diagnostic tool that can help identify various neuromuscular diseases, motor problems, nerve injuries, or degenerative conditions, allowing for early intervention and management of the underlying condition.
Comparing MRI and EMG: Which is Better?
It is important to note that MRI and EMG are different diagnostic tools that serve different purposes in the diagnosis of various medical conditions. While both tests are useful, they provide different types of infrmation and are often used in conjunction with each other to provide a more comprehensive diagnosis.
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures. MRI is particularly useful for detecting soft tissue injuries and abnormalities, such as tumors, inflammation, and nerve damage. MRI can also be used to evaluate the extent of injuries and diseases, and to monitor treatment progress over time.
On the other hand, EMG, or electromyography, is a diagnostic test that measures the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. EMG is often used to diagnose nerve and muscle disorders, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, muscular dystrophy, and myasthenia gravis. EMG can also be used to determine the severity of nerve damage and to monitor treatment progress.
It is not necessarily accurate to say that one test is better than the other, as they serve different purposes and provide different types of information. In some cases, both tests may be necessary to provide a comprehensive diagnosis. Ultimately, the choice of diagnostic tool will depend on the specific medical condition being evaluated and the preferences of the healthcare provider.
Receiving EMG Results: How Long Does It Take?
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic test that evaluates the electrical activity of your muscles and nerves. The test involves inserting a small, thin needle electrode into the muscle to record the electrical activity. Once the test is completed, you can expect to receive the results within 24 to 48 hours. The results will typically be providd to you by a healthcare professional, who will interpret the data and provide you with an explanation of any abnormalities or concerns that were identified during the test. It is important to note that the time it takes to receive the results may vary depending on the healthcare facility, so it is always best to check with the provider for specific information. the EMG test is a valuable tool in diagnosing and treating various muscle and nerve disorders, and prompt feedback on the results can help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your care.
Signs of Nerve Damage
Nerve damage can manifest in various ways, and it’s important to be aware of the symptoms so that you can seek medical attention promptly. One of the most common signs of nerve damage is numbness or tingling in the hands and feet. You may feel like you’re wearing a tight glove or sock, and this sensation may persist for extended periods.
Another potential symptom of nerve damage is muscle weakness, particularly in your arms or legs. This can make it challenging to perform everyday tasks such as lifting objects or walking upstairs. You may also find that you frequently drop objects that you’re holding, as your grip strength may be compromised.
In addition to these symptoms, nerve damage can also cause sharp pains in your hands, arms, legs, or feet. These pains may be intermittent or constant, and they can range in intensity from mild to severe. You may also experience a buzzing sensation that feels like a mild electrical shock, which can be qite uncomfortable.
It’s essential to be aware of these signs of nerve damage so that you can seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms. Your doctor can assess your condition and recommend appropriate treatment to help manage your symptoms and prevent further nerve damage.
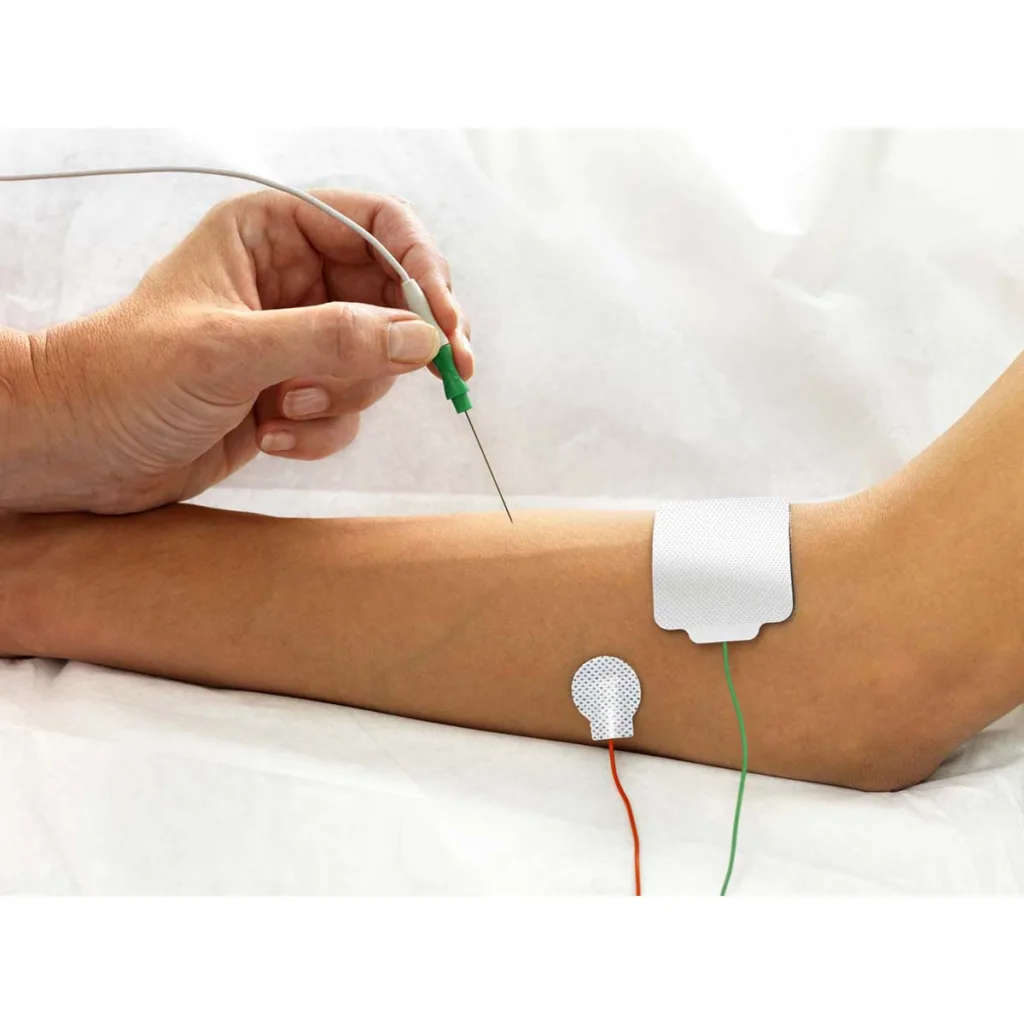
Diagnosing Nerve Damage: The Best Tests to Use
The nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test is considered the best test to show nerve damage. This test involves placing electrodes on the skin over the nerve being tested and sending a small electrical impulse through the nerve. The speed at which the impulse travels through the nerve is measured, which can help identify any damage to the nerve. NCV is often used to diagnose conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome, peripheral neuropathy, and sciatica. It is a non-invasive and safe procedure that can provide valuable iformation about nerve function and potential damage. However, it is important to note that NCV is just one of several tests that can be used to diagnose nerve damage, and a comprehensive evaluation by a medical professional is necessary to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Consequences of an Abnormal EMG
If your EMG shows abnormal electrical activity when a muscle contracts, it may indiate an underlying nerve or muscle disorder. Your doctor will review your results and may recommend additional tests or treatments to identify the specific cause of your abnormal EMG. For instance, if you have a herniated disc, your doctor may recommend imaging studies to evaluate the extent of the damage. If you have a nerve disorder, such as ALS or carpal tunnel syndrome, your doctor may recommend further diagnostic tests or refer you to a specialist for further evaluation and management. The treatment plan will depend on the underlying cause of your abnormal EMG, and may include medications, physical therapy, or surgical intervention. It is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations to properly manage your condition and prevent further complications.
The Purpose of an EMG Test Ordered by a Doctor
A doctor might order an EMG test to diagnose muscle or nerve disorders. The test helps determine if muscles are responding properly to nerve signals. This can be helpful in diagnosing conditions such as muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, and ALS. Additionally, nerve conduction studies can be done alongside an EMG test to diagnose nerve damage or disease, such as carpal tunnel syndrome or peripheral neuropathy. By combining tese tests, doctors can determine if symptoms are caused by a muscle disorder or a nerve problem, and develop an appropriate treatment plan. an EMG test is an important tool for diagnosing and managing a range of neuromuscular conditions.
The Use of Anesthesia During an EMG
Typically patients are not put to sleep for an electromyogram (EMG) procedure. The EMG test is designed to evaluate the electrical activity of muscles and nerves in the body, and requires the patient to be conscious and able to respond to the technician’s instructions during testing. While the procedure may cause some discomfort or pain, sedation is not usually necessary. However, if a patient experiences significant anxiety or discomfort during the test, a mild sedative such as Valium or a similar medication may be prescribed to help them relax. It is important to note, though, that the patient should remain awake and alert throughout the procedure in order to provide accurate feedback to the technician. After the EMG, patients can usually resume their normal activities immediately.
Source: chicagoneurodoc.com
Number of Needles Inserted for EMG Test
During an EMG test, five or more needles are typically inserted into the muscles being tested. While you may experience slight discomfort or pain with the insertion of the electrode, it is usually a painless procedure. However, if you do experience any pain during the test, it is important to let your examiner know as this can potentially affect the accuracy of the results.
Things to Avoid Before an EMG
Before an EMG, it is recommended that you do not smoke for at least 3 hours before the test. Additionally, it is advised that you avoid consuming foods or drinks that contain caffeine, such as coffee, tea, cola, and chocolate, for 2 to 3 hours before the test. This is becaue smoking and caffeine can affect the electrical activity in your muscles and may interfere with the accuracy of the EMG results. It is also important to wear loose-fitting clothing, and you may be given a hospital gown to wear during the procedure. By following these guidelines, you can help ensure that your EMG results are as accurate as possible.
Conclusion
The cost of an EMG test varies depending on factors such as location, health care provider, and insurance coverage. Patients with health insurance may have a copay or coinsurance, while those without insurance can expect to pay between $150 and $500 per extremity. EMG testing is an important diagnostic tool that can help to identify or rule out a variety of conditions affecting the nerve and muscle. While the test may cause some discomfort, it is typically well tolerated without the need for pain medication. the cost of an EMG test is a worthwhile investment in one’s health and well-being.
