Women, like men, have a groin area. The groin area is whee the abdomen transitions into the lower body and legs. It is located near the hips, above the upper thighs, and below the stomach.
The groin area in women is comprised of several muscles and ligaments that support the hips, pelvis, and lower abdomen. These muscles and ligaments are responsible for movements such as walking, running, and jumping.
Women may experience groin pain or discomfort for a variety of reasons. Common causes can include overuse or straining of the muscles and ligaments in the groin area, as well as injuries or accidents.
However, there are also more serious causes of groin pain in women, such as appendicitis, ovarian cysts, or even cancer. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience severe or prolonged groin pain, or if you have groin pain after an accident or injury.
It is also worth noting that women may experience groin pain during pregnancy. This can be due to changes in the body’s center of gravity, as well as the stretching of muscles and ligaments to accommodate the growing fetus.
In addition to pain, women may also experience other symptoms in the groin area, such as swelling or bruising. If you notice any unusual symptoms, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Women do have a groin area, and just like with men, it can be a source of pain and discomfort. It is important to pay attention to any symptoms and seek medical attention if necessary to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Location of Groin on Female Body
The groin area on a female is located in the same place as on a male – it’s where the abdomen meets the lower body and legs. Specifically, the groin area is the crease between the upper thigh and the lower abdomen, just next to the genitals. In females, the external genitalia, including the clitoris, labia, and vaginal opening, are located within the groin area. The groin contains several muscles and ligaments that support movement in the legs and hips, and any pain or discomfort in this area should be taken seriously and evaluated by a healthcare professional.

Signs and Symptoms of a Female Groin Strain
A female groin strain can cause pain and tenderness in the groin area, which may be worsened when you squeeze your legs together. You may also experience pain when you raise the knee of the injured side. Swelling or bruising in the inner thigh or groin area may also be present. If the strain is severe, you may experience difficulty walking and may need to limp while it heals. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a groin strain to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Groin Pain in Females
There can be several causes of groin pain in females. In many cases, it is caused by overuse or straining of the muscles in the groin area. However, groin pain can also be a symptom of more serious conditions such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, or even cancer. In some cases, groin pain may also be caused by an inguinal hernia or a urinary tract infection. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you are experiencing persistent or severe groin pain, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms like fever, nausea, or vomiting.
When Is It Necessary to Seek Medical Attention for Female Groin Issues?
If you are experiencing persistent or severe groin pain as a woman, it may be a cause for concern. Some possible underlying conditions that cold cause female groin pain include ovarian cysts, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, or urinary tract infections. If you notice any accompanying symptoms such as fever, nausea, vomiting, or unusual discharge, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Additionally, if you notice any lumps or bumps in the groin area or experience sudden swelling or redness, it may be a sign of a more serious condition such as a hernia or lymph node inflammation. It is recommended to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the cause of your groin pain and receive appropriate treatment.
The Effects of a Groin Injury on Women
Yes, a woman can definitely pull her groin. The groin muscles are located in the inner thigh area and are responsible for bringing your legs together, as well as helping you move your legs forward and backward. Activities that require sudden movements, such as running, jumping, or changing directions quickly, can put a lot of strain on tese muscles, leading to a groin pull or strain. Women who participate in sports such as soccer, basketball, or hockey, which involve a lot of lateral movements, are at a higher risk of experiencing a groin pull. Additionally, women who are pregnant may also be more prone to groin pulls due to the added weight and pressure on their pelvic area. It is important to properly warm up and stretch before engaging in any physical activity to prevent injury, and to seek medical attention if you do experience pain or discomfort in your groin area.
Source: verywellhealth.com
The Meaning of ‘Groin’
While the groin is an area of the body where the genitals are located, it does not necessarily mean the same thing as “private part.” The term “private part” is often used to refer specifically to the external sexual organs, such as the penis or vulva, whereas the groin refers to the entire area where these organs are located, including the pubic region and the crease between the thigh and abdomen. So while the groin is anatomically related to the genitals, it is not necessarily a synonym for “private part.”
Effects of a Groin Pull on a Woman
A groin pull, also known as a groin strain, is a type of injury that can cause pain and discomfort in the groin area. For women, the pain is typically felt on the inside of the thigh, near the pubic bone. This is because the adductor muscles, wich run along the inner thigh, are often the muscles that are affected by a groin pull. The pain may be sharp or dull and can range from mild to severe, depending on the severity of the injury. Some women may also experience swelling, bruising, or stiffness in the affected area. It’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a groin pull, as proper treatment and rehabilitation can help prevent further injury and aid in a faster recovery.
The Location of Pain When Pulling a Groin Muscle
When you pull your groin, you typically experience pain in the inner thigh area. This pain can range from mild to severe, and may also be accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling and bruising in the groin area, muscle spasms, or difficulty moving the affected leg. The pain may be more intense when you try to move your leg or perform activities that involve the groin muscles, such as walking, running, or jumping. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe pain in the groin area, as this could indicate a more serios injury that requires treatment.
Indications of Pain in the Groin Area
Pain in the groin area can indicate a variety of conditions. The most common cause of groin pain is a pulled muscle, tendon, or ligament in the leg. This is frequently seen in athletes who participate in sports that involve a lot of running and jumping, such as soccer or basketball. In some cases, this condition can be referred to as a “sports hernia,” although it is not a true hernia.
Other potential causes of groin pain include hernias, which occur when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernia and are more common in men than women. Other possible causes of groin pain include kidney stones, urinary tract infections, sexually transmitted infections, prostate problems, and hip joint problems.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe groin pain, as it can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition. Your healthcare provider can perform a physical exam, order diagnostic tests, and recommend appropriate treatment options based on the underlying cause of your pain.

Pain in the Groin: Should I Be Worried?
Any pain in the groin area can be concerning, espcially if it’s severe and doesn’t improve with home treatment within a few days. Groin pain can have various causes, including strains, sprains, hernias, infections, and even cancer. Therefore, it’s important to pay attention to the nature and duration of the pain and seek medical attention if necessary. If you experience mild testicle pain lasting longer than a few days or notice a lump or swelling in or around a testicle, you should schedule a doctor’s visit. Your doctor can help you determine the underlying cause of your groin pain and recommend appropriate treatment options to relieve your discomfort and prevent complications.
Causes of Pain in the Groin and Hip Area
Pain in the hip and groin area can be caused by various factors, including musculoskeletal and internal health problems. Musculoskeletal issues typically arise from problems with the bones, joints, or muscles, and are often linked to sports injuries. For instance, a hip flexor strain or a labral tear in the hip joint can cause pain in thee areas. Other musculoskeletal conditions that can lead to hip and groin pain include osteoarthritis, bursitis, and tendinitis.
Internal health problems can also cause pain in the groin and hip area. A hernia is a common cause of groin pain, in which an organ protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall. Endometriosis is another condition that can cause pelvic pain, including pain in the hip and groin area, in women. This condition occurs when the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus grows outside of it. A cystic lesion, such as an ovarian cyst, can also cause pain in the hip and groin area, particularly on one side of the body. In summary, the causes of pain in the hip and groin area can be varied, and it is important to consult a healthcare professional to diagnose and treat the underlying condition.
The Causes of Groin Pain During Walking
Groin pain when walking can be caused by a variety of factors. One of the most common causes is a strained muscle, ligament, or tendon in your lower abdominal area. This type of injury is often the result of overuse, sudden movements, or poor posture. Another common cause of groin pain is a tear in the cartilage that surrounds the hip joint. This condition, known as a labral tear, can cause pain and discomfort when walking or moving the leg. In some cases, groin pain can also be caused by an inguinal hernia, which occurs when abdominal tissue protrudes through a weakened area in the groin. Osteoarthritis, which is the degeneration of joint cartilage, can also cause groin pain when walking. If you are experiencing groin pain when walking, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive approprite treatment.
Location of Lymph Nodes in Women’s Groin
The lymph nodes in women’s groin are located in the inner upper thigh area, specifically below the inguinal ligament. These lymph nodes are called the inguinal lymph nodes and they play an important role in the body’s immune system. The superficial inguinal lymph nodes sit near the surface of the skin, making them easier to detect and examine if necessary. It’s important to note that these lymph nodes can become enlarged or swollen due to various reasons such as infections, injuries, or cancers, so it’s crucial to seek medical attention if any abnormalities are noticed.
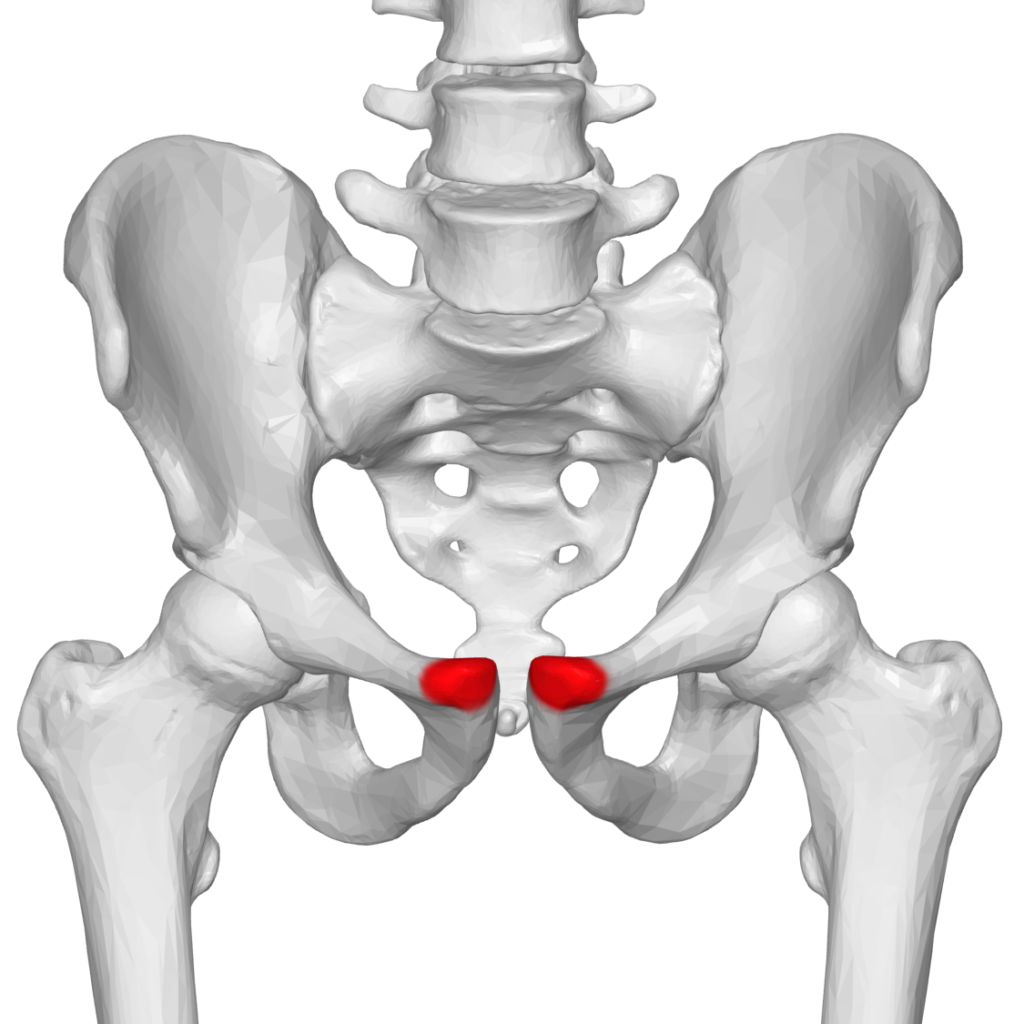
Lymph Nodes in the Groin of Females
Yes, there are lymph nodes in the groin area of females. The lymph nodes in the groin, also known as inguinal lymph nodes, are located in the crease where the leg meets the body, on both sides of the pubic area. These lymph nodes are part of the lymphatic system, which is responsible for filtering and removing waste and toxins from the body. The inguinal lymph nodes play an important role in fighting infections and diseases in the lower half of the body, including the genitals, urinary tract, and legs. Swollen lymph nodes in the groin area can be a sign of an infection or disease and sould be evaluated by a medical professional.
The Relationship Between Groin Pain and Menopause
Yes, groin pain can be related to menopause. During menopause, hormonal changes can lead to the loss of support and altered biomechanics in the pelvic region, which can cause pain or dysfunction in the hip or groin area. Additionally, menopause can also lead to conditions such as osteoporosis or arthritis, which can contribute to groin pain. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of the pain and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, women may experience groin pain for a variety of reasons. While most cases are related to strains or injuries, it is important to be aware of more serious causes such as ovarian cysts or cancer. If you experience severe or persistent groin pain, seek medical attention immediately. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing good posture can help prevent groin injuries. Women should also be aware of teir reproductive health and attend regular check-ups with their healthcare provider. By taking care of their bodies and seeking medical attention when needed, women can prevent and address groin pain effectively.
