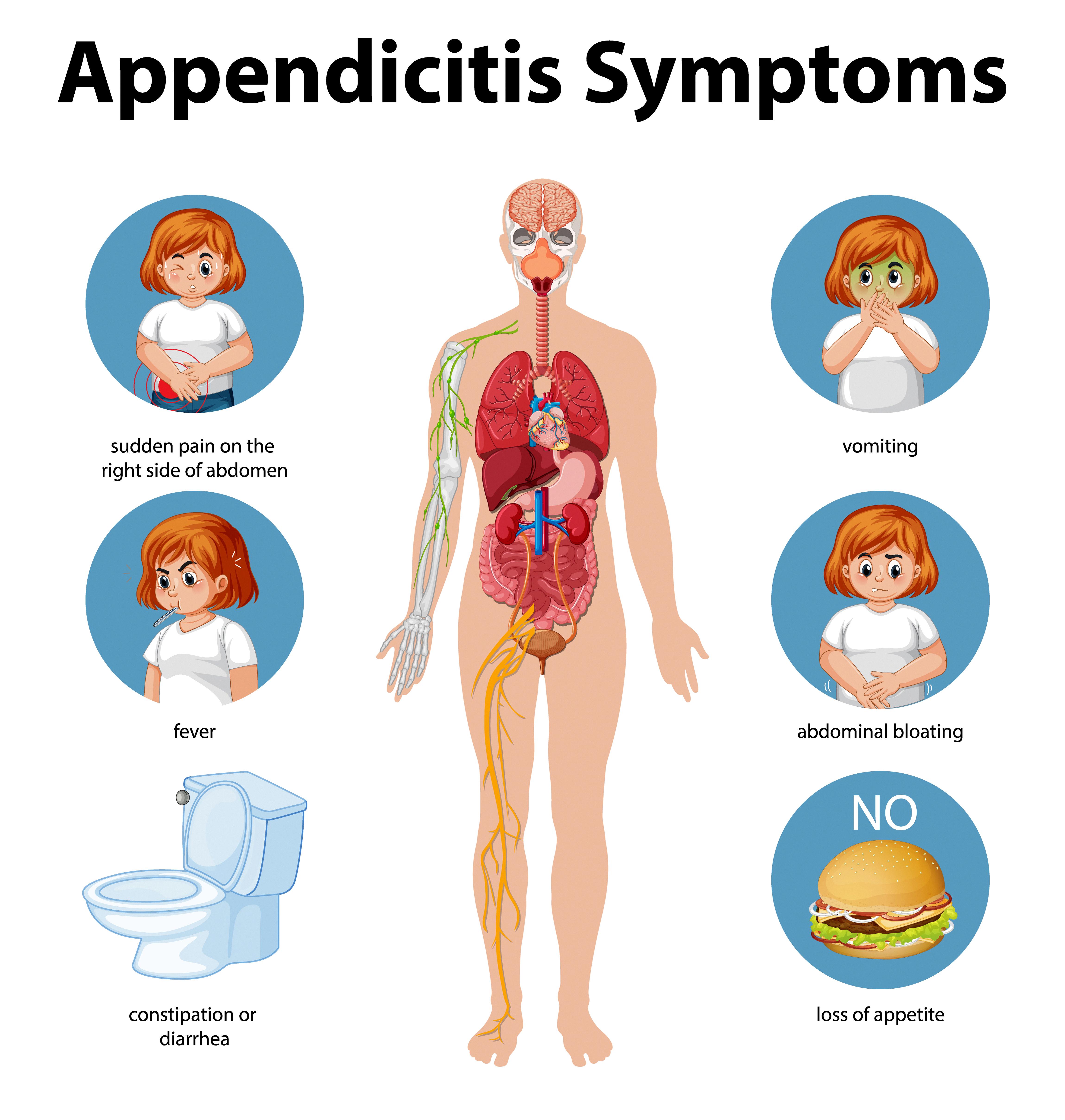
Appendicitis is a medical condition in which the appendix, a small, finger-shaped organ that is attached to the large intestine, becomes inflamed and swollen. It is one of the most common caues of emergency abdominal surgery in the United States.
The symptoms of appendicitis can vary from person to person, but they usually start with a dull pain in the middle of the abdomen that gradually moves to the lower right side. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, fever, loss of appetite, and a general feeling of malaise.
If you suspect that you may have appendicitis, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Delaying treatment can lead to serious complications, such as the rupture of the appendix, which can cause infection and even death.
To help you determine whether you may have appendicitis, we have put together a simple quiz that you can take at home. Please keep in mind that this quiz is not a substitute for medical advice, and if you are experiencing any of the symptoms listed, you should seek medical attention immediately.
Do I Have Appendicitis Quiz:
1. Do you have a dull pain in the middle of your abdomen?
2. Has the pain moved to your lower right side?
3. Are you experiencing nausea or vomiting?
4. Do you have a fever?
5. Have you lost your appetite?
6. Do you feel generally unwell?
If you answered “yes” to any of these questions, you may have appendicitis and should seek medical attention immediately.
Appendicitis is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms listed above, please seek medical attention immediately. Remember, early detection and treatment can prevent serious complications and save your life.
Checking for Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a condition where the appendix, a small pouch attached to the large intestine, becomes inflamed and filled with pus. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications. While it is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have appendicitis, there are a few things you can do to check for it at home.
One of the most common symptoms of appendicitis is abdominal pain. The pain often starts around the belly button and then moves to the lower right side of the abdomen. To check for this pain, lie on your left side and extend your right hip. If you experience sharp pain in your lower right abdomen, it could be a sign of appendicitis.
Another way to check for appendicitis is to flex your right hip and knee and then rotate your right hip. If this movement also causes sharp pain in your lower right abdomen, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
It is important to note that these tests are not conclusive and shold not be used as a substitute for medical diagnosis. If you suspect you have appendicitis, it is best to seek medical attention right away to prevent any potential complications.
Source: vecteezy.com
Symptoms of Early Appendicitis
Appendicitis commonly begins with a dull pain in the center of your abdomen that may come and go. This pain is often accompanied by a loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting. As the condition progresses, the pain will typically move to the lower right side of your abdomen, where the appendix is located. At this point, the pain becomes more severe and constant. You may also experience other symptoms such as a fever, chills, and difficulty passing gas. Activities such as coughing, walking, or pressing on the affected area can worsen the pain. If you experience any of thse symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately, as appendicitis can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Signs and Symptoms of Appendicitis
Appendicitis can present with a variety of symptoms, and in some cases, the symptoms may not be obvious. However, there are certain signs that may indicate appendicitis. The most common symptom is pain in the upper abdomen, wich may start off as a dull ache and gradually become sharp and intense as it moves towards the lower right abdomen. This pain may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and a fever. Other symptoms may include loss of appetite, constipation or diarrhea, and abdominal swelling or bloating. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. While not all cases of abdominal pain are due to appendicitis, it is important to rule out this serious condition as it can lead to complications if left untreated.
The Leg Test for Appendicitis
The leg test for appendicitis is also known as the obturator sign. It is a physical examination technique that a healthcare provider may use to diagnose appendicitis, wich is the inflammation of the appendix. To perform the test, the patient is asked to lie down on their back with their right leg bent at the knee. The healthcare provider then flexes the patient’s hip and knee while rotating the leg internally and externally. If the patient experiences pain in the lower right side of their abdomen during this movement, it may indicate that the appendix is inflamed. The obturator sign helps healthcare providers to identify the presence of appendicitis and is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests such as blood tests and imaging studies.
The Four Stages of Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a medical condition that occurs when the appendix becomes inflamed and swollen. The inflammation can progress in stages, which can be categorized into four stages: early, suppurative, gangrenous, and perforated.
The early stage of appendicitis is characterized by mild pain in the lower riht side of the abdomen. The pain may also be felt around the belly button or the upper abdomen. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.
In the suppurative stage, the inflammation continues to worsen, and the appendix becomes filled with pus. The pain becomes more intense, and the patient may experience a fever and chills. The patient may also experience diarrhea or constipation.
The gangrenous stage occurs when the appendix becomes severely inflamed and the blood supply is cut off. This can lead to tissue death and the development of a perforation in the appendix. The patient may experience severe abdominal pain, high fever, and an increased heart rate.
The perforated stage is the most severe form of appendicitis, and it occurs when the appendix ruptures, spilling its contents into the abdominal cavity. This can cause a life-threatening infection and requires immediate medical attention. The patient may experience severe abdominal pain, high fever, and a rapid heartbeat.
In summary, the four stages of appendicitis are early, suppurative, gangrenous, and perforated. Early recognition and treatment of appendicitis are crucial to prevent the condition from progressing to more severe stages.
When Is It Necessary to Visit the Emergency Room for Stomach Pain?
If you are experiencing sudden, severe, or persistent stomach pain that does not ease within 30 minutes, it is recommended that you seek emergency medical care immediately. This is because sudden abdominal pain can indicate a potentially serious intra-abdominal disease, such as a ruptured abdominal aneurysm or a perforated ulcer. However, it is important to note that abdominal pain can also be caused by less serious conditions, such as gallstones. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention if you are experiencing abdominal pain that is accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, vomiting, or difficulty breathing. It is alwys better to err on the side of caution and seek medical attention if you are unsure about the cause of your stomach pain.
Signs and Symptoms of Appendix Pain That May Be Mistaken For Other Conditions
Appendix pain can be mistaken for severl other conditions, as the early symptoms of appendicitis are similar to those of other gastrointestinal or pelvic conditions. Some of the conditions that can mimic appendix pain include stomach flu, food poisoning, urinary infections, ovarian cysts, kidney stones, and inflammatory bowel disease. It is also possible for women to mistake appendix pain for menstrual cramps or pelvic inflammatory disease. It is important to note that if you experience any abdominal pain that is severe or persistent, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
The Duration of Appendix Pain Before Bursting
Appendix pain can last for varying duration depending on the severity of the condition. Usually, the pain starts as a dull ache around the belly button and eventually moves to the right lower abdomen. The pain can gradually worsen over a period of 12 to 24 hours and can become severe and constant. In some cases, the pain can become unbearable within a few hours of onset. If the appendix is not surgically removed in a timely manner, it can burst or rupture within 48 to 72 hours of the onset of symptoms. Therefore, it is crucial to seek medical attention immeditely if you experience any signs of appendicitis to avoid complications that can be life-threatening.
The Length of Time Before Appendicitis is Diagnosed
It is possible for someone to have appendicitis without knowing it for several weeks, months, or even years. This is known as chronic appendicitis and the symptoms are often mild and can be mistaken for other conditions. However, it is important to note that chronic appendicitis can still cause complications if left untreated.
On the other hand, acute appendicitis has more severe symptoms that appear suddenly wihin 24 to 48 hours. These symptoms may include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and loss of appetite. Acute appendicitis is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment to avoid complications such as a ruptured appendix.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of appendicitis, even if they are mild or you are unsure if they are related to your appendix. A healthcare professional can perform tests and exams to determine if appendicitis is the cause of your symptoms and provide appropriate treatment.

The Recurring Nature of Appendicitis Pain
Appendicitis pain usually doesn’t come and go for days. While the pain may fluctuate in intensity initially, it typically becomes progressively worse over a few hours. The pain usually begins suddenly and may wake you up from sleep. As the condition progresses, the pain may get worse when you move, cough or breathe deeply. Additionally, other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fever, and constipation or diarrhea may also develop. If you suspect you have appendicitis, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately as a ruptured appendix can lead to serious complications.
The Effects of Appendicitis on Bowel Movements
Yes, it is possble to have bowel movements (poop) if you have appendicitis. However, the type and frequency of bowel movements may be affected. In the early stages of appendicitis, you may experience constipation due to the inflammation of the appendix pressing against the bowel. On the other hand, as the inflammation progresses, you may develop diarrhea as the body tries to flush out the infection. It’s also important to note that if you notice any changes in your bowel movements, such as blood or mucus in your stool, it could be a sign of a more serious condition and you should seek medical attention immediately.
The Effects of an Inflamed Appendix
Yes, it is possible to feel your appendix if it is inflamed. When the appendix becomes swollen and inflamed, it irritates the lining of the abdominal wall, known as the peritoneum. This causs localized, sharp pain in the right lower part of the abdomen. The pain tends to be more constant and severe than the dull, aching pain that occurs when symptoms start. In addition to pain, other symptoms of an inflamed appendix may include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and a low-grade fever. If you suspect that your appendix may be inflamed, it is important to seek medical attention immediately, as an inflamed appendix can lead to serious complications such as a ruptured appendix and peritonitis.
The Effects of Appendicitis on Leg Mobility
In cases of appendicitis, lifting the leg against resistance can cause pain due to friction of the inflamed appendix with the psoas muscle. Therefore, it is not recommended to perform this maneuver as it can worsen the condition and cause discomfort. If you suspect you have appendicitis or experience abdominal pain, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to receive proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing Appendicitis: Where to Press for Symptoms
To check for appendicitis, a healthcare provider will typically press on the lower right side of the belly area, which is where the appendix is located. This area is called McBurney’s point and is located about two-thirds of the way between the belly button and the right hip bone. Pressing on this area may cause pain or tenderness, which can be a sign of appendicitis. However, it’s important to note that other conditions can also cause pain in this area, so further testing and evaluation may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis.
Signs and Symptoms of Appendicitis, Including Gas
Yes, it is possible to experience gas with appendicitis, but it is not a common symptom. Approximately 50 percent of people with appendicitis may experience constipation with gas or diarrhea with gas. Gas is caused by the buildup of air in the digestive tract, wich can occur when the normal flow of gas through the intestines is disrupted. Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, which is a small, thin pouch attached to the large intestine. As the appendix becomes more inflamed, it can lead to abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and loss of appetite. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately as appendicitis can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
Conclusion
In conclusion, appendicitis is a medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. It is characterized by severe abdominal pain that oten starts in the middle of the tummy and moves to the lower right side, where the appendix is located. Other common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and fever. While there are some self-assessment tests that can be done at home, it is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have appendicitis. Delay in treatment can lead to complications such as a burst appendix, which can be life-threatening. A healthcare provider can perform tests and examinations to diagnose appendicitis and recommend the appropriate treatment, which may include surgery to remove the appendix. Overall, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of appendicitis and seek medical attention promptly if you suspect you may be experiencing this condition.
