Bacteria are one of the most ancient and diverse forms of life on Earth. These tiny single-celled organisms are ubiquitous in our environment and play a crucial role in many biological processes. One of the most fundamental structures in bacterial cells are ribosomes.
Ribosomes are microscopic “factories” that are found in all cells, including bacteria. These structures are essential for the synthesis of proteins, which are required for metabolic activities and growth. Proteins are the building blocks of life and perform a wide range of functions in cells, including catalyzing chemical reactions, providing structural support, and acting as receptors and transporters.
In most bacteria, the most numerous intracellular structure is the ribosome. These structures are the site of protein synthesis in all living organisms. The ribosomes found in bacteria are different from those found in eukaryotic cells, which are more complex and larger in size.
Bacterial ribosomes are small, measuring only 70S (where S=Svedberg units) in size. They are made up of two subunits, the 50S and 30S subunits. The 50S subunit contains two ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and 34 proteins, wile the 30S subunit contains one rRNA molecule and 21 proteins.
Ribosomes are synthesized in the cytoplasm of bacterial cells through the transcription of multiple ribosome gene operons. These operons contain the genes that encode the RNA and proteins that make up the ribosomes. The process of ribosome synthesis is highly regulated and involves the coordinated expression of multiple genes.
In eukaryotic cells, the process of ribosome synthesis takes place both in the cell cytoplasm and in the nucleolus, which is a region within the cell nucleus. Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger and more complex than bacterial ribosomes, with a size of 80S. They are made up of four subunits, the 60S, 40S, 5.8S, and 28S subunits.
Ribosomes are essential structures for the synthesis of proteins in all living organisms, including bacteria. Bacterial ribosomes are small and simple, while eukaryotic ribosomes are larger and more complex. The study of ribosomes has played a crucial role in our understanding of the molecular basis of life and has led to many breakthroughs in medicine and biotechnology.
Do Bacteria Cells Contain Ribosomes?
Yes, bacteria cells do have ribosomes. Ribosomes are essential organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis, which is a critical function carried out by all living cells. Bacterial ribosomes are smaller in size compared to the ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells, but they perform the same function. Ribosomes are composed of two subunits, and they work togethr to translate the genetic code into proteins. In bacteria, ribosomes are suspended in the cytoplasm and can be found in large numbers, often forming clusters known as polysomes. Ribosomes play a vital role in the growth, replication, and survival of bacteria, and they are a target for many antibiotics that are used to treat bacterial infections.
The Role of Ribosomes in Bacterial Cells
Bacteria cells have ribosomes because they need them for the synthesis of proteins. Ribosomes are the cellular structures responsible for the translation of genetic informaion encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins. Proteins are essential molecules for the survival and growth of bacterial cells, playing crucial roles in metabolic activities, cell division, and adaptation to environmental changes. Therefore, ribosomes are essential components of bacterial cells, ensuring the production of the proteins needed for their biological functions. In summary, ribosomes are vital for the survival and growth of bacterial cells, as they enable the synthesis of proteins that are essential for their metabolic activities and adaptation to their environment.
Do All Bacteria Possess 70S Ribosomes?
Yes, all bacteria have 70S ribosomes. The 70S ribosome is the most common type of ribosome found in prokaryotes, wich include bacteria and archaea. The 70S ribosome is composed of two subunits, the 50S and 30S subunits, which come together to form the functional ribosome. The 50S subunit is responsible for the catalytic activity of protein synthesis, while the 30S subunit is responsible for binding to mRNA and decoding the genetic information. In contrast, eukaryotic cells, such as those found in animals and plants, contain larger 80S ribosomes in their cytosol. These ribosomes are composed of a 60S and a 40S subunit and are responsible for protein synthesis in the eukaryotic cell.
Location of Ribosomes in Bacteria
In bacterial cells, ribosomes are located in the cytoplasm, whih is the gel-like substance that fills the cell. The ribosomes are synthesized in the cytoplasm through the transcription of multiple ribosome gene operons. These ribosomes are responsible for the synthesis of proteins, which are essential for the survival and growth of the bacterial cell. The ribosomes in bacteria are smaller than those found in eukaryotic cells and consist of two subunits, the 30S and 50S subunits, which come together to form the functional 70S ribosome. The location of ribosomes in bacterial cells is critical for the efficient synthesis of proteins, which is essential for the survival and growth of the cell.
Are Bacteria Lacking Ribosomes?
No, ribosomes are not absent in bacteria. In fact, ribosomes are essential components of bacterial cells and are considered the protein factories of the cell. Ribosomes are present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and bacterial ribosomes are slightly smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes. Bacterial ribosomes are composed of two subunits, the small subunit and the large subunit, which work together to synthesize proteins. These ribosomes are freely present in the bacterial cytoplasm and are responsible for translating the genetic information stored in the bacterial DNA into functional proteins. Therefore, it is safe to say that ribosomes are an integral part of bacterial cells and play a vital role in ther survival and growth.
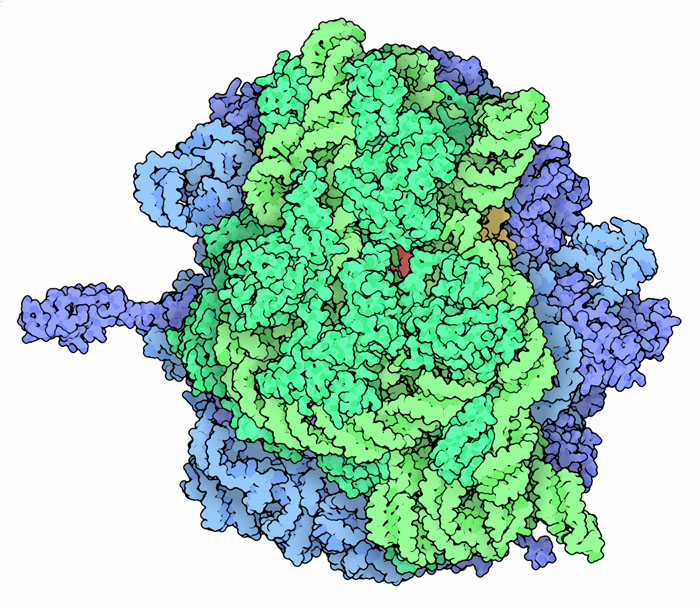
Do Bacteria Have Ribosomes?
No, bacteria do not lack ribosomes. In fact, ribosomes are essential structures for bacteria as they are responsible for synthesizing proteins, which are necessary for their growth and survival. Bacterial ribosomes are composed of two subunits – the small subunit and the large subunit – and are generally smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes. Unlike eukaryotic cells, bacteria do not have membrane-bound organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum, where ribosomes are usually found. Instead, bacterial ribosomes are free-floating in the cytoplasm. Therefore, ribosomes are ubiquitous in all living organisms, including bacteria.
Absence of Ribosomes in Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes do have ribosomes. In fact, prokaryotes were the firt organisms to be discovered to have ribosomes. Ribosomes are essential structures involved in protein synthesis, and they are present in all living cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic ribosomes are smaller than eukaryotic ribosomes and consist of two subunits, the 30S and 50S subunits. These subunits combine to form a functional ribosome, which then initiates the translation of messenger RNA (mRNA) into protein. The ribosomes in prokaryotic cells are not enclosed in a membrane-bound organelle as they are in eukaryotic cells. Instead, they are free-floating in the cytoplasm. In summary, prokaryotes do have ribosomes, and these structures are essential for protein synthesis, which is a fundamental process required for the survival of all living cells.
Do Bacteria and Viruses Contain Ribosomes?
Yes, both bacteria and viruses have ribosomes, but they differ in their structure and function. In bacteria, ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis and are composed of two subunits, one larger and one smaller. These subunits are made up of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and protein molecules, and they work together to translate messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins.
On the oher hand, viruses do have ribosomes, but they are much smaller and simpler than bacterial ribosomes. Viral ribosomes are made up of fewer protein and rRNA molecules and are used to synthesize viral proteins within the host cell. However, some viruses do not have their own ribosomes and instead rely on the host cell’s ribosomes for protein synthesis.
It is also important to note that viruses do not have other organelles, such as mitochondria, and are completely dependent on their host cells for energy production and protein synthesis.
Do Bacteria Have 70S or 80S Ribosomes?
Bacteria have 70S ribosomes. These ribosomes are smaller than the ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells, which are referred to as 80S ribosomes. 70S ribosomes are composed of a small 30S subunit and a large 50S subunit, and they play a critical role in protein synthesis in bacteria. Despite the smaller size of 70S ribosomes, they are highly efficient at synthesizing proteins, allowing bacteria to carry out essential cellular functions and survive in a variety of environments.
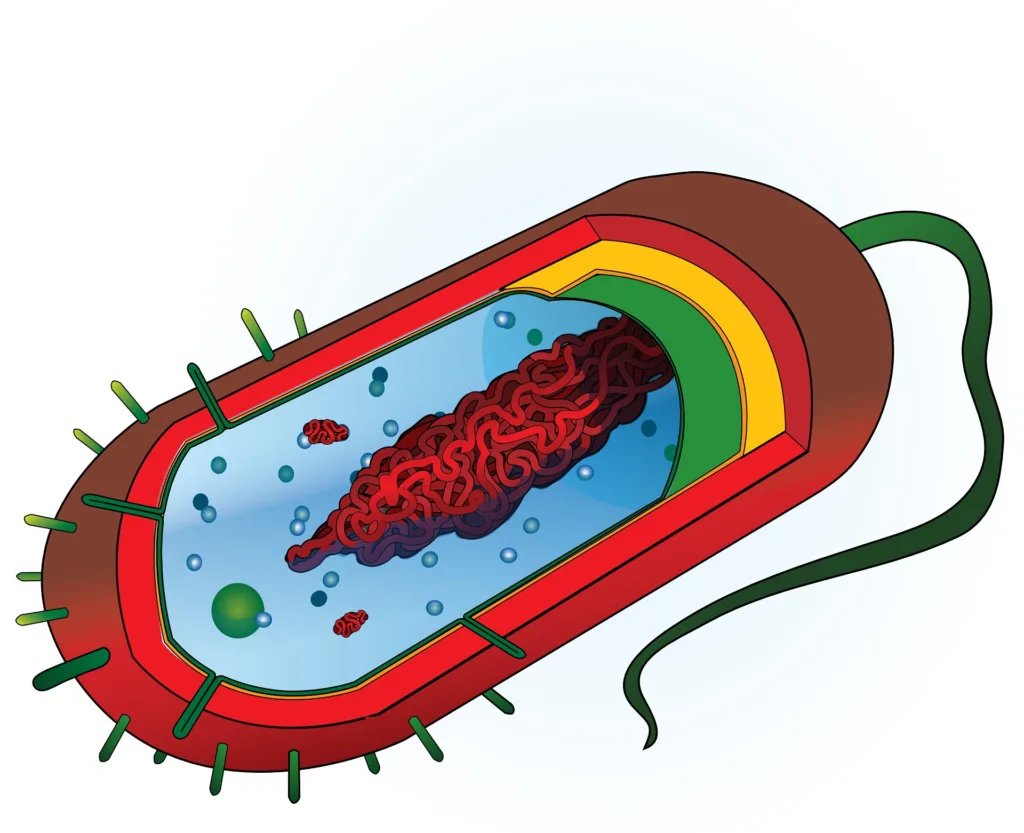
Types of Bacterial Ribosomes
Bacteria have a distinct type of ribosome called 70S ribosomes. These ribosomes are smaller in size compared to eukaryotic ribosomes, whih are referred to as 80S ribosomes. The 70S ribosome in bacteria consists of two subunits, a smaller 30S subunit, and a larger 50S subunit. The smaller subunit contains the decoding center that recognizes the messenger RNA (mRNA), while the larger subunit contains the active site for catalyzing peptide bond formation during protein synthesis. In contrast, eukaryotic ribosomes consist of a 40S subunit and a 60S subunit, which combine to form an 80S ribosome. These differences in ribosome structure and composition are significant and reflect the distinct evolutionary paths taken by prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms.
Cell Containing 70S and 80S Ribosomes
The ribosomes are the cellular organelles responsible for synthesizing proteins. Ribosomes can be found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, but they differ in size and composition. Prokaryotic cells, which include bacteria and archaea, conain ribosomes that are smaller and have a sedimentation coefficient of 70S. The 70S ribosome is composed of a 30S small subunit and a 50S large subunit. In contrast, eukaryotic cells, which include animals, plants, fungi, and protists, contain ribosomes that are larger and have a sedimentation coefficient of 80S. The 80S ribosome is made up of a 40S small subunit and a 60S large subunit. Therefore, prokaryotic cells have 70S ribosomes, while eukaryotic cells have 80S ribosomes.
Are Ribosomes Found in Bacteria and Humans Identical or Different?
Ribosomes found in bacteria and humans are not identical, they are noticeably different. While both bacterial and human ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, the structure and composition of thir respective ribosomes differ greatly. Bacterial ribosomes are composed of a small 16S subunit and a large 23S subunit, while human mitochondrial ribosomes consist of a small 28S subunit and a large 39S subunit. Additionally, the small subunit of human mitochondrial ribosomes contains a 12S rRNA and 29 proteins, while the large subunit contains a 16S rRNA and 48 proteins. These differences in structure and composition reflect the evolutionary divergence of bacterial and human cells, and are important for understanding the mechanisms of protein synthesis in each organism.
Do Prokaryotes Possess Ribosomes?
Yes, prokaryotes have ribosomes. Ribosomes are essential molecular machines that function as protein factories in living cells. They are responsible for translating genetic information from DNA into proteins, which are the building blocks of life. In prokaryotic cells, ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm and are not attached to any membrane. They are smaller than the ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells, which are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Prokaryotic ribosomes are composed of two subunits, designated as 30S and 50S, which come together to form a 70S ribosome. The ribosomes in prokaryotes are vital for ther survival, and they are an excellent target for antibiotics, which can interfere with bacterial protein synthesis and lead to bacterial death.
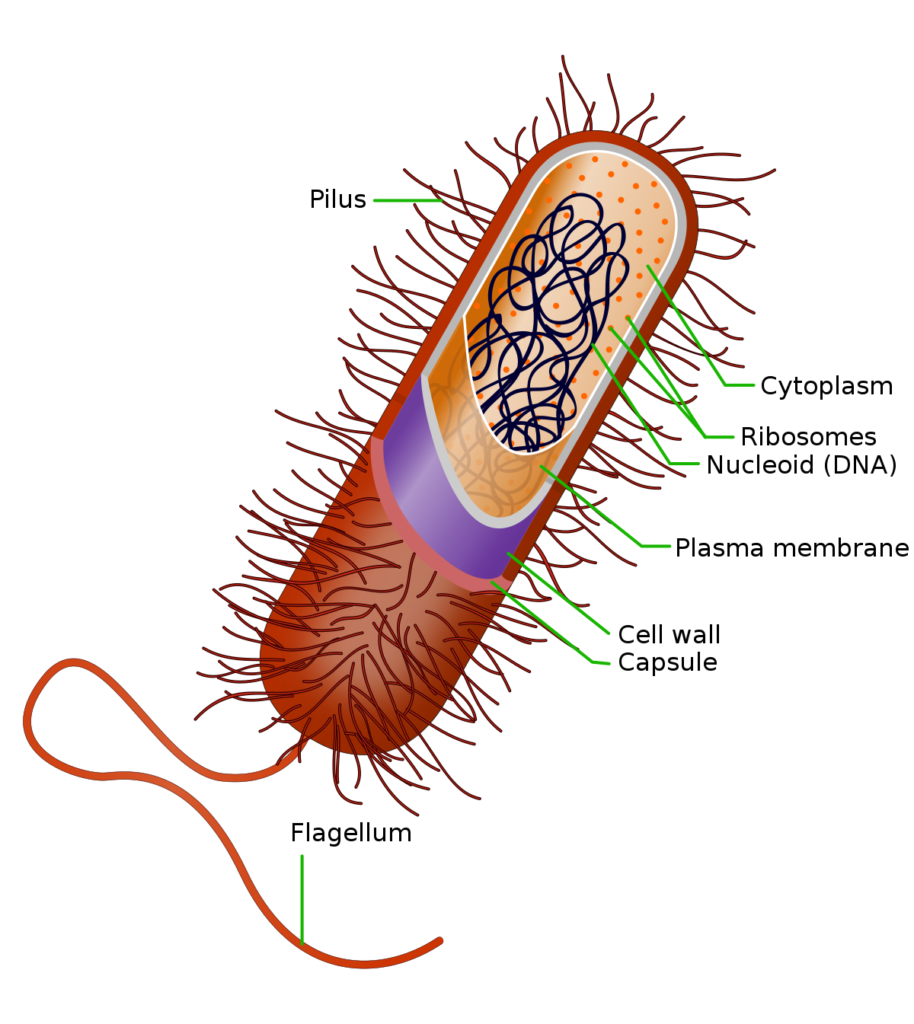
Do Fungi Contain Ribosomes?
Yes, fungi do have ribosomes. Ribosomes are essential structures found in all living cells, including fungi. They are responsible for the synthesis of proteins, which is a fundamental process for the survival and growth of the organism. Fungal cells contain 80S ribosomes, which are made up of two subunits: the large subunit and the small subunit. These ribosomes work in conjunction with messenger RNA (mRNA) and transfer RNA (tRNA) to read the genetic code and synthesize specific proteins. Therefore, the presence of ribosomes in fungi is essential for their function and survival.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ribosomes are essential structures found in all living cells, including bacteria. These microscopic factories are responsible for the synthesis of proteins needed for metabolic activities and growth. Bacteria have 70S ribosomes, which are composed of a 50S and 30S subunit. The ribosomes are synthesized in the cytoplasm through the transcription of multiple ribosome gene operons. It is worth noting that eukaryotes contain larger 80S ribosomes in their cytosol. Therefore, it can be concluded that ribosomes are vital organelles in bacterial cells, and their absence can lead to a significant decrease in protein synthesis and ultimately affect the overall growth and survival of the bacteria.
